Abstract
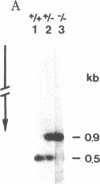
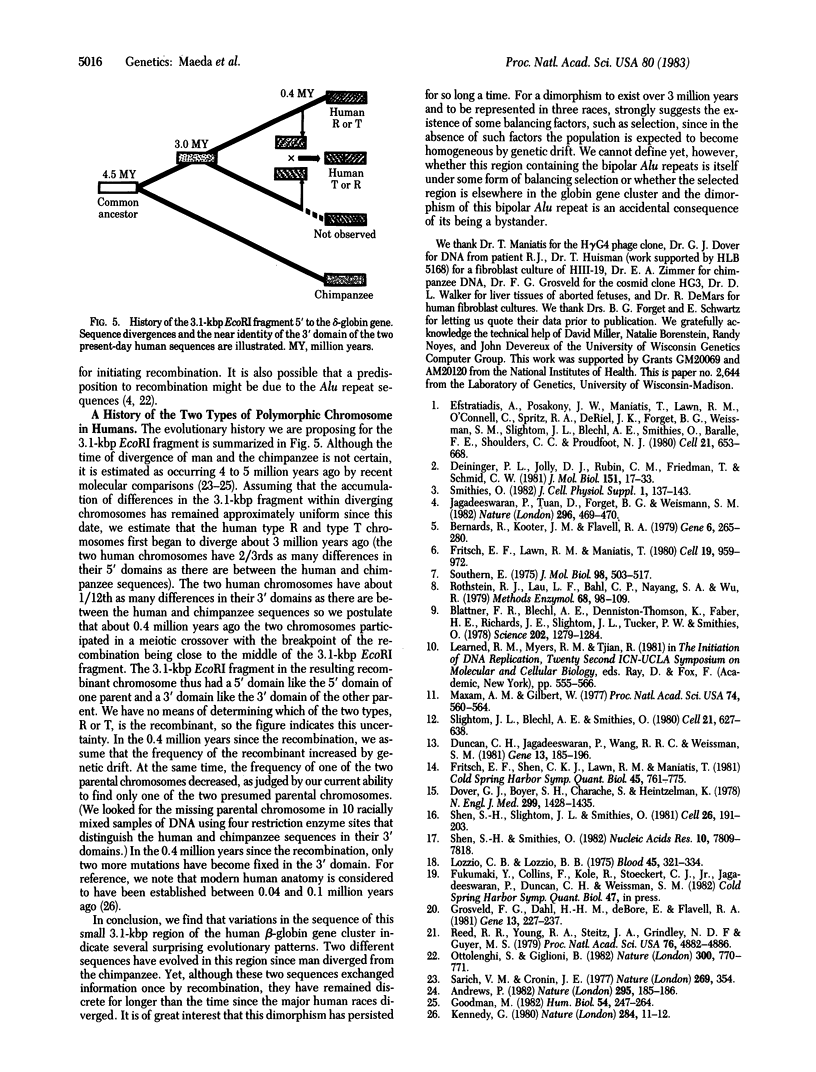
Two types of chromosome (R and T) were found by cloning from six human individuals the 3.1-kilobase-pair EcoRI fragment that contains the bipolar Alu family repeat 5' to the delta-globin gene. Two type T fragments were identical in nucleotide sequence. Two type R fragments were identical except for one base. Both types are found in whites, blacks, and orientals. The differences between R and T sequences (16 base substitutions and two deletions) were mostly in the 5' domain of the fragment (0.91% difference in 1.7 kilobases), which contains the bipolar Alu repeat, whereas the 3' domain of the fragment was more conserved (0.14% difference in 1.4 kilobases). To help understand the history of this human polymorphism, the equivalent fragment from a chimpanzee was cloned and its sequence was determined. The chimpanzee sequence differed from both human sequences at 39 positions distributed almost uniformly along the whole 3.1-kilobase-pair fragment. Assuming that humans and chimpanzees diverged 4 to 5 million years ago, the data indicate that the divergence of the two types of human chromosome started about 3 million years ago but about 0.4 million years ago an interchromosomal recombination rendered the two types of human chromosome alike in their 3' domains. The two chromosomes have since remained discrete and have persisted in several populations. These observations suggest that factors are operating to maintain a balanced chromosomal polymorphism in this region 5' to the human delta-globin gene.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Hominoid evolution. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):185–186. doi: 10.1038/295185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards R., Kooter J. M., Flavell R. A. Physical mapping of the globin gene deletion in (delta beta (0)) -thalassaemia. Gene. 1979 Jul;6(3):265–280. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Richards J. E., Slightom J. L., Tucker P. W., Smithies O. Cloning human fetal gamma globin and mouse alpha-type globin DNA: preparation and screening of shotgun collections. Science. 1978 Dec 22;202(4374):1279–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.725603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Jolly D. J., Rubin C. M., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Base sequence studies of 300 nucleotide renatured repeated human DNA clones. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. J., Boyer S. H., Charache S., Heintzelman K. Individual variation in the production and survival of F cells in sickle-cell disease. N Engl J Med. 1978 Dec 28;299(26):1428–1435. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197812282992603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. H., Jagadeeswaran P., Wang R. R., Weissman S. M. Structural analysis of templates and RNA polymerase III transcripts of Alu family sequences interspersed among the human beta-like globin genes. Gene. 1981 Mar;13(2):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch E. F., Lawn R. M., Maniatis T. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human beta-like globin gene cluster. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):959–972. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch E. F., Shen C. K., Lawn R. M., Maniatis T. The organization of repetitive sequences in mammalian globin gene clusters. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):761–765. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. Biomolecular evidence on human origins from the standpoint of Darwinian theory. Hum Biol. 1982 May;54(2):247–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F. G., Dahl H. H., de Boer E., Flavell R. A. Isolation of beta-globin-related genes from a human cosmid library. Gene. 1981 Apr;13(3):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeeswaran P., Tuan D., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. A gene deletion ending at the midpoint of a repetitive DNA sequence in one form of hereditary persistence of fetal haemoglobin. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):469–470. doi: 10.1038/296469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy G. E. The emergence of modern man. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):11–12. doi: 10.1038/284011a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottolenghi S., Giglioni B. The deletion in a type of delta 0-beta 0-thalassaemia begins in an inverted AluI repeat. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):770–771. doi: 10.1038/300770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R., Young R. A., Steitz J. A., Grindley N. D., Guyer M. S. Transposition of the Escherichia coli insertion element gamma generates a five-base-pair repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4882–4886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J., Lau L. F., Bahl C. P., Narang S. A., Wu R. Synthetic adaptors for cloning DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:98–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarich V. M., Cronin J. E. Generation length and rates of hominoid molecular evolution. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):354–355. doi: 10.1038/269354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. H., Slightom J. L., Smithies O. A history of the human fetal globin gene duplication. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):191–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90302-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. H., Smithies O. Human globin psi B2 is not a globin-related sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7809–7818. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Blechl A. E., Smithies O. Human fetal G gamma- and A gamma-globin genes: complete nucleotide sequences suggest that DNA can be exchanged between these duplicated genes. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O. The control of globin and other eukaryotic genes. J Cell Physiol Suppl. 1982;1:137–143. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041130421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]