Abstract
Background
Although Pisa syndrome and scoliosis are sometimes used interchangeably to describe a laterally flexed postural deviation in Parkinson's disease (PD), the imaging findings of Pisa syndrome in PD have not been previously studied in detail.
Methods
Patients with PD and Pisa syndrome (lateral flexion >10° in the standing position) were examined clinically and underwent radiological assessment using standing radiograph and supine CT scan of the whole spine.
Results
Fifteen patients were included in this observational study. All patients had scoliosis on standing radiographs, and 12 had scoliosis persisting in the supine position. Scoliotic curves improved by a mean of 44% when patients moved from standing to supine. Only a quarter of patients with structural scoliosis had evidence of bony fusion on the side of their lateral deviation rendering their deformity fixed.
Conclusions
Pisa syndrome describes a patient who lists to the side whereas scoliosis is defined by spinal curvature and rotation and may not be associated with lateral flexion. The finding of ‘structural scoliosis’ in Pisa syndrome should not preclude intervening to improve posture as most patients had little or no evidence of structural bony changes even when the deformity had been present for a number of years.
Keywords: PARKINSON'S DISEASE
Introduction
Pisa syndrome is defined as >10° lateral flexion in the standing position,1 and it has been suggested that in the context of Parkinson's disease (PD) it is an axial dystonia analogous to that seen as a rare consequence of neuroleptic therapy.2 Scoliosis is defined as a curvature of the spine with a Cobb angle of 10° or more in the coronal plane (as measured on a radiograph), combined with rotation of the vertebrae.3 A scoliosis in the standing position reflects bone, muscle and soft tissue alterations (fixed and reducible changes) leading to spinal curvature and the impact from ‘collapse of posture’ or failure of postural tone against gravity. In the supine position the latter is eliminated and the factors resulting in spinal curvature include the fixed bony deformity and the ‘elastic’ connective tissue elements (eg, muscle spasm or shortening, contractures), in short a curve persisting in the supine position may be due to ‘fixed’ spinal changes, muscle changes or both. The flexibility of scoliosis can be considered to be due to a combination of collapse and reducibility (the elasticity element of the deformity that can be eliminated with corrective forces).4
Methods
Subjects
We prospectively recruited patients with PD presenting to a specialist movement disorder clinic with lateral flexion deformity more than 10° which had developed after their diagnosis of PD. Patients with a history of childhood or adolescent scoliosis, surgical spinal correction, unable to stand unsupported or those with an atypical parkinsonian condition were excluded. None of the patients had a known history of osteoporosis, had received neuroleptic or cholinesterase inhibitor medication.
Clinical evaluation
There were 12 males and 3 females with a mean age of 72 years, disease duration of 15 years and duration of Pisa syndrome 6 years. Patients completed quality of life, fatigue and pain questionnaires and were examined for evidence of active dystonia, muscle wasting or hypertrophy, limb or joint deformity. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA, V.7.1),5 the Frontal Assessment Battery6 and motor evaluation using the Movement Disorder Society revised Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale II and III7 were also performed. Lateral flexion was measured using an iPhone application goniometer (Yong Li, Angle protractor V.1.0, 2010, retrieved from http://itunes.apple.com/) which measured the angle of deviation from the vertical.
Radiography methods and analysis
Plain x-ray and CT of the spine was carried out in all patients. The true anterior-posterior radiographic projections reconstructed from the CT acquired data (figure 1A-3,B-3) provided a dataset for like comparison with the standing radiographs (figure 1A-2,B-2). Measurements of the spinal parameters were undertaken by two of the researchers on the radiographs and CT projections, measurements were taken based on the guidelines set out by the Spinal Deformity Study Group consensus.8
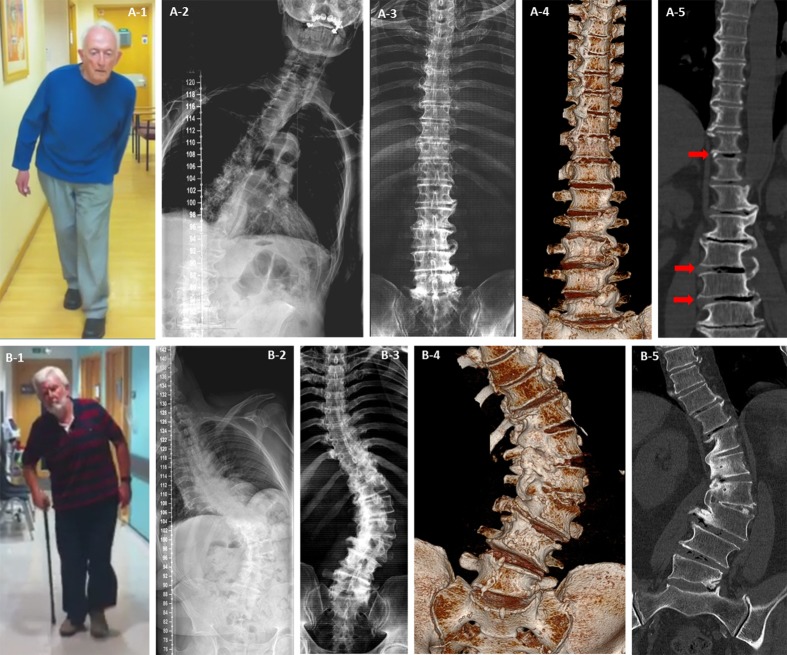
Figure 1.
Mobile and fixed scoliosis in Pisa syndrome. Patient A had scoliosis on standing radiograph (A-2) but not when he was scanned supine (A-3, A-4 and A-5). There was evidence of osteophytic overgrowth below the apex of the scoliosis in the lumbar spine and above on the opposite side in the thoracic spine (A-4 and A-5), this pattern suggests the degenerative changes were working to stabilise his spine but stopped short at the apex of his curve leaving him mobile but tilted at that level when standing (A-1 and A-2). The reduction in curve with position, presence of interdiscal gas (red arrows A-5) and gaps between the osteophytes are evidence that despite attempts the deformity is not fixed. Patient B had only minor improvement of his scoliosis on supine positioning (9% reducibility) (B-2 and B-3). Fusion of vertebral segments due to complete osteophytic bridging at the apex of the curve was clearly seen (B-4 and B-5) resulting in a fixed and possibly stable spinal deformity. Key: 1=patient photographs of Pisa syndrome while walking; 2=standing full spine anterior–posterior radiograph; 3=supine CT scan two-dimensional composite image; 4=supine CT scan three-dimensional surface rendered image; 5=supine CT scan two-dimensional fine cut in coronal plane.
(Please refer to online supplementary material for full details of radiography methods and analyses).
Results
All patients with clinically defined Pisa syndrome had a radiologically defined scoliosis, of these 12 had a curve that persisted in the supine position (what we will term ‘structural scoliosis’) (table 1).
Table 1.
Results and comparisons between those with mobile and those with ‘structural scoliosis’
| Patients with Pisa syndrome | Mobile scoliosis | Structural scoliosis | p Value** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | 15 | 3 | 12 | |
| Age (years) | 72.1 (5.7, 63.3–82.3) | 70.5 | 72.5 | 0.6 |
| Male: female | 12:3 | 2:1 | 10:2 | 0.5 |
| PD duration (years) | 15 (6.1, 7.3–27.3) | 15 | 15 | 0.99 |
| Deformity duration (years) | 5.8 (3, 0.6–13.2) | 5.2 | 5.9 | 0.7 |
| Daily levodopa LED (mg) | 647 (242, 300–1197) | 666 | 642 | 0.9 |
| Daily dopamine agonist LED (mg) | 250 (161, 0–480) | 275 | 244 | 0.8 |
| Daily PD medication LED (mg) | 1010 (330, 498–1697) | 1041 | 1003 | 0.9 |
| Lateral flexion angle (°) | 17.2 (5, 10–25) | 18 | 17 | 0.6 |
| Standing radiograph Cobb angle (°) | 35 (16.4, 8.6–67) | 20.8 | 38.8 | 0.08 |
| Supine CT Cobb angle (°) | 20.4 (12.4, 3.2–45) | 6 | 24.8 | <0.01* |
| Relative collapse scoliosis (%) | 44.4 (21.4, 7.8–87.6) | 68.7 | 37.7 | 0.02* |
| PDQ-39 total score (0–156) | 67 (26, 20–116) | 61 | 68 | 0.7 |
| WHO well-being index (0–25) | 13 (6, 3–25) | 15 | 13 | 0.6 |
| Fatigue severity scale (0–63) | 40 (15, 21–63) | 42 | 40 | 0.9 |
| Pain visual analogue scale (0–10) | 4 (2, 0–8) | 3.7 | 4.1 | 0.8 |
| MoCA (0–30) | 22.6 (4.6, 10–27) | 21 | 25 | 0.4 |
| FAB (0–18) | 12.5 (3.8, 6–18) | 11 | 13 | 0.4 |
| MDS-UPDRS II | 26 (5.6, 20–38) | 29 | 25 | 0.3 |
| MDS-UPDRS III | 43.5 (11.2, 27–61) | 50 | 41 | 0.2 |
*Significant difference between groups.
**Group means compared using Student's t test except for gender when Fisher's exact test was used.
No significant differences were found between those with and without a structural scoliosis in terms of PD duration, deformity duration, medication usage, quality of life, pain, cognition or Parkinson's severity (UPDRS II and III). Values given=mean (SD, range).
FAB, frontal assessment battery; LED, Levodopa equivalent dose; MDS-UPDRS, Movement Disorder Society revised Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale; MoCA, Montreal Cognitive Assessment; PD, Parkinson's disease; PDQ, Parkinson's Disease Questionnaire.
The mean percentage of scoliosis attributed to collapse of posture on standing was 44%; this was significantly greater in the patients with mobile scoliosis (69%) versus those with a structural scoliosis (38%) (p=0.02, Student's t test). On examination none of the patients with Pisa syndrome had any evidence of dynamic dystonia (posturing with jerks or tremor, active spasms or asymmetrical contractions of paraspinal muscles or paradoxical muscle groups associated with the abnormal posture, or sensory gestes) although paraspinal electromyography did not form part of the study. Seven patients were unable to perform or had impaired trunk extension from the prone position. Severity of posture as scored by the Movement Disorder Society revised Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale III item 13 was scored as moderate in three patients and severe in 12, and the mean angle of lateral flexion was measured at 17° from the vertical.
Similar to adult degenerative scoliosis, all patients had a very low apex to their scoliotic curve (L3 or L4) with evidence of lumbar degenerative changes, but in contrast to typical adult deformity a ‘lumbar take-off’ picture (a significant scoliotic curve located in the lower lumbar spine for which no correction to the midline was present) was often observed. Osteophytosis was present in the majority of patients with structural curves, but fused vertebral segments corresponding to the direction of lateral deviation rendering the deformity fixed was visible in only three (figure 1B). Even in those with mobile scoliosis (figure 1A) there appeared to be an attempt to stabilise the spine with osteophytic bridging between vertebral segments, but there was often also evidence of failed fusion or a cleft through the osteophytes which may explain why the scoliosis resolved in the supine position.
Discussion
This study has provided evidence that scoliosis and Pisa syndrome are not synonymous. Although all patients with Pisa syndrome had radiologically confirmed scoliosis, this was not always structural, involved a large element of collapse and differed from that seen in adult degenerative scoliosis.9
A large element of the deformity in Pisa syndrome reflects the inability to assume an erect posture in the presence of normal physiological loading of the spine. On examination many of our patients had difficulty recruiting paraspinal muscles when asked to stand up straight, instead they would push down on one knee or hyperextend their neck in order to appear taller and when asked to extend their trunk from the prone position they also appeared to have difficulty recruiting trunk muscles without evidence of weakness or atrophy. This may suggest that abnormal posture cannot be entirely explained by active dystonia (although this cannot be excluded from this study), and instead may reflect either intrinsic muscle and soft tissue changes resulting from a dystonia present earlier in the course of the disease or another more complex impairment of proprioceptive motor control in PD.
Few patients had evidence of complete fusion between vertebral segments at the site of their curves, in the majority there must exist non-bony changes holding their spine curved. Non-surgical therapies may have a potential role in managing these ‘mobile’ patients. Techniques such as functional electrical stimulation10 or proprioceptive reinforcement using lumbar supports may have a role in the control of the collapse element, while mobility around the axial skeleton suggests muscle and balance retraining perhaps combined with the use of spinal orthotics11 might be helpful in improving the reducible axial changes. The lack of stabilising rigid struts (osteophytic bridging between vertebrae) however, means that there is a risk that any lateral deviation will progress without aggressive intervention.
Our study concentrated on patients with long standing PD, medium-to-long term deformity and moderate to severe posture. In patients with subacute onset of mild Pisa syndrome, the deformity is likely to be more mobile and the radiological findings less pronounced. It may be that those with and those without structural scoliosis are two points on a spectrum, but advancing age, disease duration, disease severity, medication use and cognition do not seem to influence the propensity to develop a more immobile (and potentially stable) curve. Although the mechanism may differ from other types of scoliosis this study raises an important question: does PD accelerate a degenerative process in those with a propensity to develop a curve, or is PD a risk factor for scoliosis? We favour the latter explanation because degenerative scoliosis is most likely due to asymmetrical loading of the spine and in PD this may be inferred from the asymmetry which is a key feature of PD, and the loss of postural tone or righting reflexes when a patient does begin to list to one side.
In conclusion long-standing moderate-to-severe Pisa syndrome deformity in PD is often associated with underlying axial skeletal deformity. A large proportion of the scoliosis underlying the deformity in Pisa syndrome reflects collapse or impaired postural tone, but the remainder of the deformity is rarely due to bony changes suggesting that non-surgical interventions should always be considered to maximise a patient's potential to achieve balance in the coronal plane.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We would like to graciously thank all the patients who participated in this research study.
Footnotes
Contributors: All authors were involved in the conception and/or design of this study. KMD collected the data, KMD and ID analysed the data. KMD and LSM performed the statistical analyses. KMD wrote the original manuscript, with important contributions from SM and AJL. All authors provided input into the final manuscript.
Funding: This project was supported by an innovation project grant from Parkinson's UK, grant number K-1010. KMD is a beneficiary of a Reta Lila Weston fellowship.
Competing interests: None.
Patient consent: Obtained.
Ethics approval: Ethical approval for this study was granted by the Central London REC 2, REC reference number 10/H0713/41.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1.Doherty KM, van de Warrenburg BP, Peralta MC, et al. Postural deformities in Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol 2011;10:538–49 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ekbom K, Lindholm H, Ljungberg L. New dystonic syndrome associated with butyrophenone therapy. Z Neurol 1972;202:94–103 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schwab FJ, Smith VA, Biserni M, et al. Adult scoliosis: a quantitative radiographic and clinical analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2002;27:387–92 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Duval-Beaupere G, Lespargot A, Grossiord A. Flexibility of scoliosis. What does it mean? Is this terminology appropriate? Spine 1985;10:428–32 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bédirian V, et al. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc 2005;53:695–99 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dubois B, Slachevsky A, Litvan I, et al. The FAB: a Frontal Assessment Battery at bedside. Neurology 2000;55:1621–6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Goetz CG, Tilley BC, Shaftman SR, et al. Movement Disorder Society-sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS): scale presentation and clinimetric testing results. Mov Disord 2008;23:2129–70 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.O'Brien M, Kuklo T, Blanke K, et al. Radiographic measurements manual: spinal deformity study group. USA: Metronic Sofamor Danek, 2004 [Google Scholar]
- 9.Berven SH, Lowe T. The Scoliosis Research Society classification for adult spinal deformity. Neurosurg Clin N Am 2007;18:207–13 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.McQuain MT, Sinaki M, Shibley LD, et al. Effect of electrical stimulation on lumbar paraspinal muscles. Spine 1993;18:1787–92 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.de Seze MP, Creuze A, de Seze M, et al. An orthosis and physiotherapy programme for camptocormia: a prospective case study. J Rehabil Med 2008;40:761–5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.