Abstract
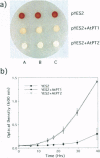
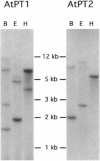
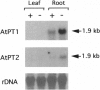
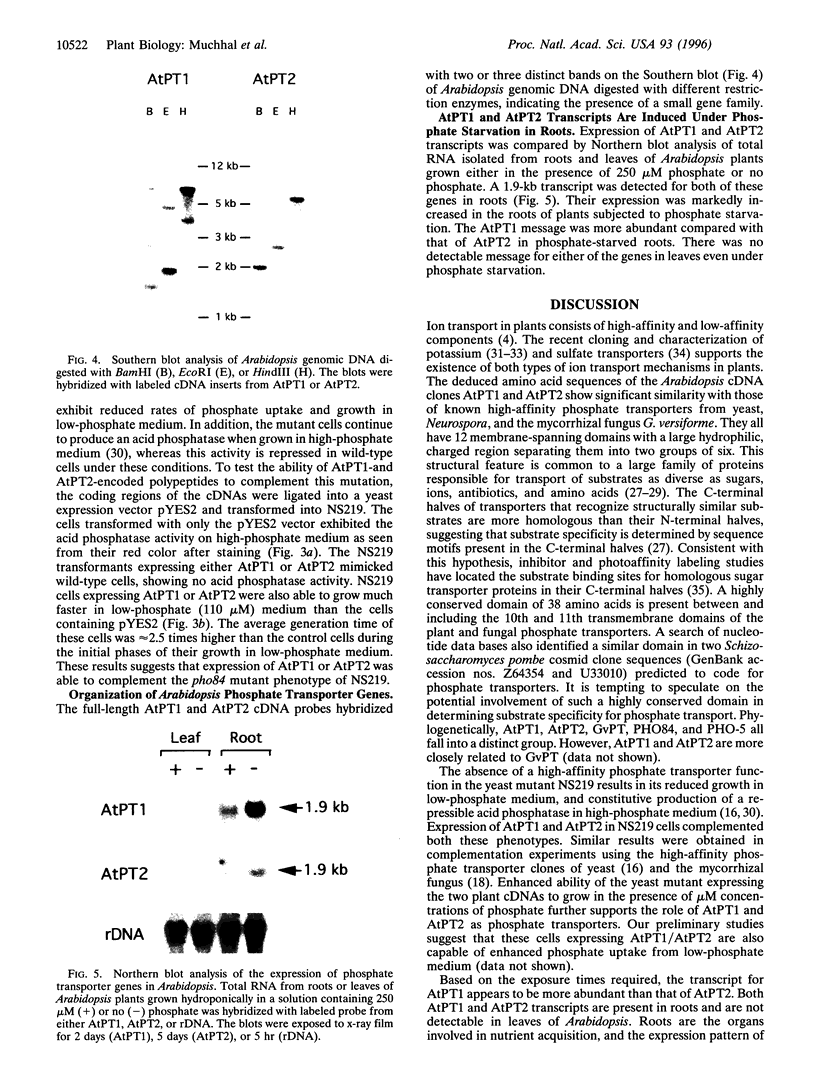
Two cDNAs (AtPT1 and AtPT2) encoding plant phosphate transporters have been isolated from a library prepared with mRNA extracted from phosphate-starved Arabidopsis thaliana roots, The encoded polypeptides are 78% identical to each other and show high degree of amino acid sequence similarity with high-affinity phosphate transporters of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Neurospora crassa, and the mycorrhizal fungus Glomus versiforme. The AtPT1 and AtPT2 polypeptides are integral membrane proteins predicted to contain 12 membrane-spanning domains separated into two groups of six by a large charged hydrophilic region. Upon expression, both AtPT1 and AtPT2 were able to complement the pho84 mutant phenotype of yeast strain NS219 lacking the high-affinity phosphate transport activity. AtPT1 and AtPT2 are representatives of two distinct, small gene families in A. thaliana. The transcripts of both genes are expressed in roots and are not detectable in leaves. The steady-state level of their mRNAs increases in response to phosphate starvation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. A., Huprikar S. S., Kochian L. V., Lucas W. J., Gaber R. F. Functional expression of a probable Arabidopsis thaliana potassium channel in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3736–3740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bun-Ya M., Nishimura M., Harashima S., Oshima Y. The PHO84 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes an inorganic phosphate transporter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3229–3238. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. J., Beever R. E. Kinetic characterization of the two phosphate uptake systems in the fungus Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):511–519. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.511-519.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers A. Facilitated diffusion of glucose. Physiol Rev. 1990 Oct;70(4):1135–1176. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.4.1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claros M. G., von Heijne G. TopPred II: an improved software for membrane protein structure predictions. Comput Appl Biosci. 1994 Dec;10(6):685–686. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/10.6.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delhaize E., Randall P. J. Characterization of a Phosphate-Accumulator Mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 1995 Jan;107(1):207–213. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Rains D. W., Elzam O. E. RESOLUTION OF DUAL MECHANISMS OF POTASSIUM ABSORPTION BY BARLEY ROOTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 May;49(5):684–692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.5.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. K., Baker M. E., Rouch D. A., Page M. G., Skurray R. A., Paulsen I. T., Chater K. F., Baldwin S. A., Henderson P. J. Membrane transport proteins: implications of sequence comparisons. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;4(4):684–695. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90090-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison M. J., van Buuren M. L. A phosphate transporter from the mycorrhizal fungus Glomus versiforme. Nature. 1995 Dec 7;378(6557):626–629. doi: 10.1038/378626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson P. J. The 12-transmembrane helix transporters. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;5(4):708–721. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90144-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowendorf H. S., Bazinet G. F., Jr, Slayman C. W. Phosphate transport in Neurospora. Derepression of a high-affinity transport system during phosphorus starvation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 21;389(3):541–549. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marger M. D., Saier M. H., Jr A major superfamily of transmembrane facilitators that catalyse uniport, symport and antiport. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jan;18(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90081-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier Y., Thoma S., Somerville C., Schiefelbein J. Mutant of Arabidopsis deficient in xylem loading of phosphate. Plant Physiol. 1991 Nov;97(3):1087–1093. doi: 10.1104/pp.97.3.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano K. Proton/Phosphate Stoichiometry in Uptake of Inorganic Phosphate by Cultured Cells of Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jun;93(2):479–483. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.2.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtman D. P., Schroeder J. I. Structure and transport mechanism of a high-affinity potassium uptake transporter from higher plants. Nature. 1994 Aug 25;370(6491):655–658. doi: 10.1038/370655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentenac H., Bonneaud N., Minet M., Lacroute F., Salmon J. M., Gaymard F., Grignon C. Cloning and expression in yeast of a plant potassium ion transport system. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):663–665. doi: 10.1126/science.1585180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. W., Ealing P. M., Hawkesford M. J., Clarkson D. T. Plant members of a family of sulfate transporters reveal functional subtypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 26;92(20):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamai Y., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Regulation of inorganic phosphate transport systems in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):964–968. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.964-968.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda Y., Oshima Y. A constitutive mutation, phoT, of the repressible acid phosphatase synthesis with inability to transport inorganic phosphate in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1975;136(3):255–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00334020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich-Eberius C. I., Novacky A., Fischer E., Lüttge U. Relationship between Energy-dependent Phosphate Uptake and the Electrical Membrane Potential in Lemna gibba G1. Plant Physiol. 1981 Apr;67(4):797–801. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.4.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Versaw W. K. A phosphate-repressible, high-affinity phosphate permease is encoded by the pho-5+ gene of Neurospora crassa. Gene. 1995 Feb 3;153(1):135–139. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)00814-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]