Abstract
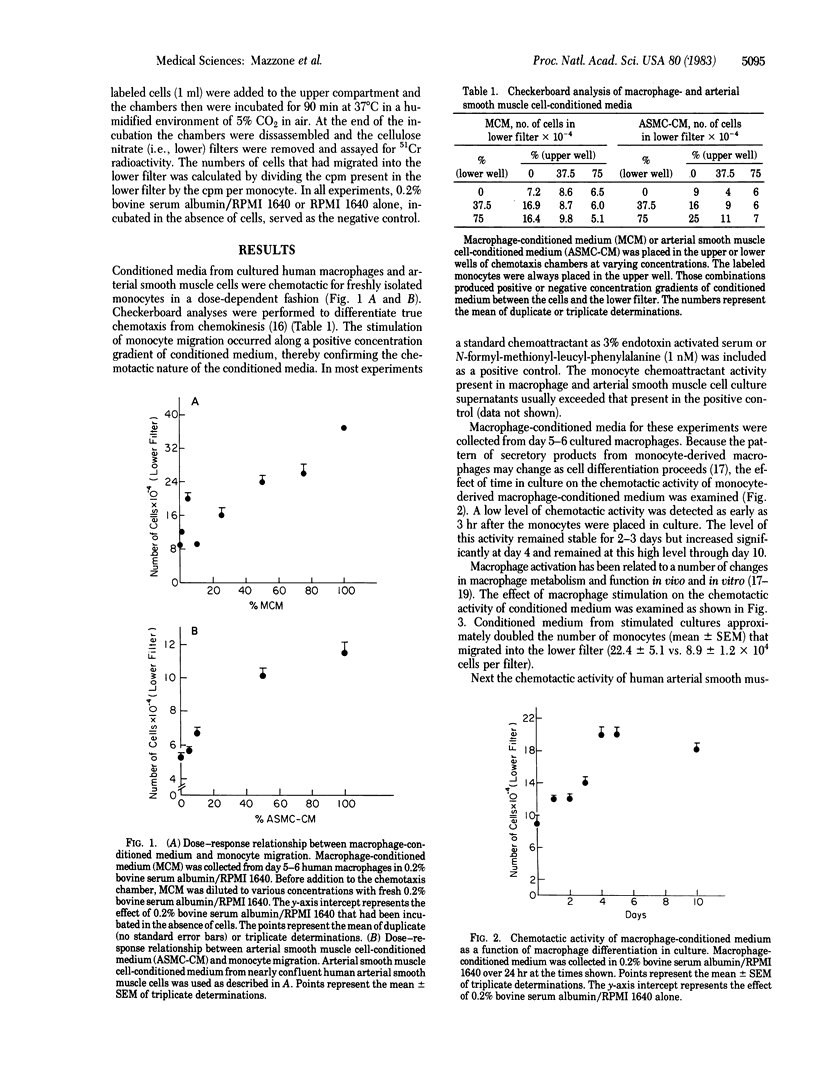
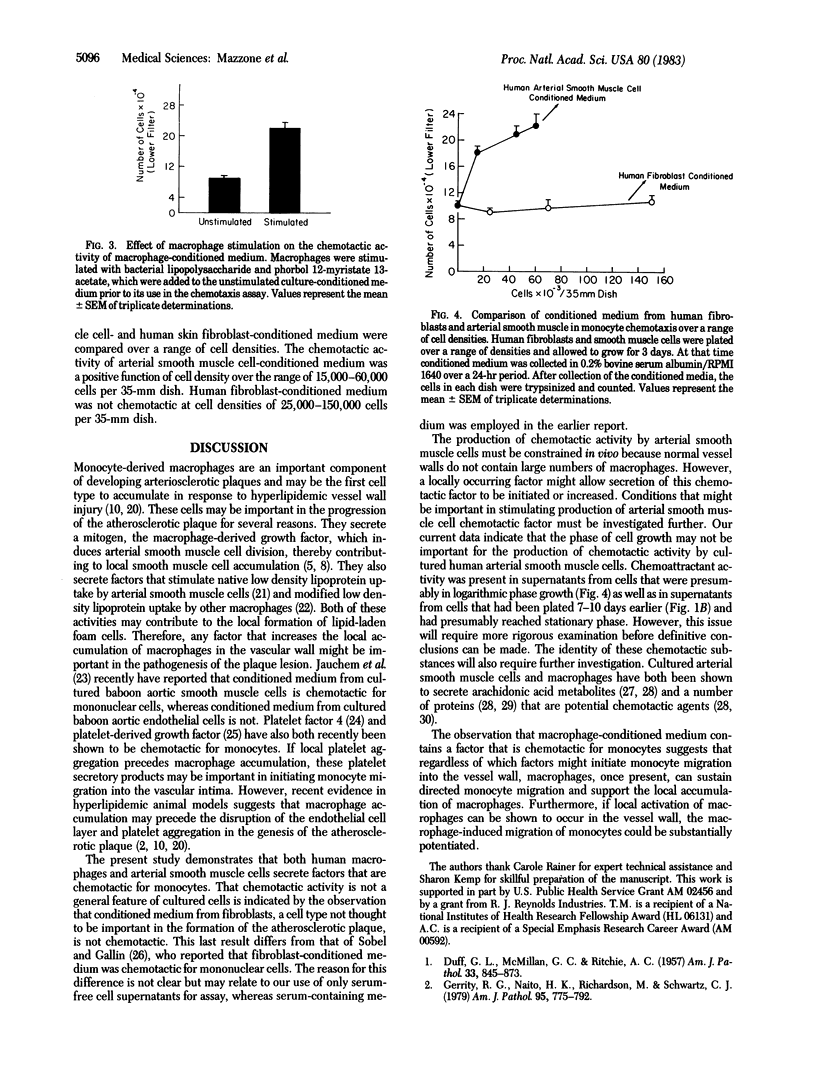
Macrophages and arterial smooth muscle cells comprise the cellular components of the atherosclerotic plaque. The vessel wall accumulation of macrophages occurs by a process of increased circulating monocyte migration into the vessel wall. In these studies it is demonstrated that human macrophages and arterial smooth muscle cells in culture secrete potent chemotactic factors for freshly isolated human monocytes. In contrast, human fibroblast-conditioned medium has no chemotactic activity. The effect of macrophage-conditioned medium is a function of macrophage differentiation and can be potentiated by macrophage activation. These results suggest that secretory products of human macrophages and arterial smooth muscle cells may be important stimuli for increased monocyte migration into the vessel wall in vivo.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baenziger N. L., Becherer P. R., Majerus P. W. Characterization of prostacyclin synthesis in cultured human arterial smooth muscle cells, venous endothelial cells and skin fibroblasts. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):967–974. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell G. R., Chamley-Campbell J. H. Invited review: the cellular pathobiology of atherosclerosis. Pathology. 1981 Jul;13(3):423–440. doi: 10.3109/00313028109059061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chait A., Bierman E. L., Albers J. J. Low-density lipoprotein receptor activity in cultured human skin fibroblasts. Mechanism of insulin-induced stimulation. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1309–1319. doi: 10.1172/JCI109587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chait A., Henze K., Mazzone T., Jensen M., Hammond W. Low density lipoprotein receptor activity in freshly isolated human blood monocytes and lymphocytes. Metabolism. 1982 Jul;31(7):721–727. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90204-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chait A., Mazzone T. A secretory product of human monocyte-derived macrophages stimulates low density lipoprotein receptor activity in arterial smooth muscle cells and skin fibroblasts. Arteriosclerosis. 1982 Mar-Apr;2(2):134–141. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.2.2.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUFF G. L., McMILLAN G. C., RITCHIE A. C. The morphology of early atherosclerotic lesions of the aorta demonstrated by the surface technique in rabbits fed cholesterol; together with a description of the anatomy of the intima of the rabbit's aorta and the spontaneous lesions which occur in it. Am J Pathol. 1957 Sep-Oct;33(5):845–873. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Bonney R. J. Secretory products of mononuclear phagocytes: a brief review. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Jul;26(1):37–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Senior R. M., Chang D., Griffin G. L., Heinrikson R. L., Kaiser E. T. Platelet factor 4 is chemotactic for neutrophils and monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4584–4587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Senior R. M., Huang J. S., Griffin G. L. Chemotaxis of monocytes and neutrophils to platelet-derived growth factor. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):1046–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI110509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek C., DiCorleto P., Ross R., Schwartz S. M. An endothelial cell-derived growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1980 May;85(2):467–472. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.2.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Clark R. A., Kimball H. R. Granulocyte chemotaxis: an improved in vitro assay employing 51 Cr-labeled granulocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):233–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrity R. G., Naito H. K., Richardson M., Schwartz C. J. Dietary induced atherogenesis in swine. Morphology of the intima in prelesion stages. Am J Pathol. 1979 Jun;95(3):775–792. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrity R. G. The role of the monocyte in atherogenesis: I. Transition of blood-borne monocytes into foam cells in fatty lesions. Am J Pathol. 1981 May;103(2):181–190. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn K. C., Ross R. Human monocyte-derived growth factor(s) for mesenchymal cells: activation of secretion by endotoxin and concanavalin A. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):603–615. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jauchem J. R., Lopez M., Sprague E. A., Schwartz C. J. Mononuclear cell chemoattractant activity from cultured arterial smooth muscle cells. Exp Mol Pathol. 1982 Oct;37(2):166–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(82)90033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris I., Stetz E., Majno G. Lymphocytes and monocytes in the aortic intima--An electron-microscopic study in the rat. Atherosclerosis. 1979 Nov;34(3):221–231. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(79)80003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledet T., Vuust J. Arterial procollagen type I, and type III, and fibronectin: effects of diabetic serum, glucose, insulin, ketone, and growth hormone studied on rabbit aortic myomedial cell cultures. Diabetes. 1980 Dec;29(12):964–970. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.12.964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovich S. J., Ross R. A macrophage-dependent factor that stimulates the proliferation of fibroblasts in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1976 Sep;84(3):501–514. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzone T., Chait A. Autoregulation of the modified low density lipoprotein receptor in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Arteriosclerosis. 1982 Nov-Dec;2(6):487–492. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.2.6.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. The macrophage as an effector cell. N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 11;303(11):622–626. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009113031106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Kang A. H. Collagen-and collagen peptide-induced chemotaxis of human blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1299–1307. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. George Lyman Duff Memorial Lecture. Atherosclerosis: a problem of the biology of arterial wall cells and their interactions with blood components. Arteriosclerosis. 1981 Sep-Oct;1(5):293–311. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.1.5.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J., Kariya B., Harker L. A platelet-dependent serum factor that stimulates the proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1207–1210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The smooth muscle cell. II. Growth of smooth muscle in culture and formation of elastic fibers. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jul;50(1):172–186. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner T., Taylor K., Bartucci E. J., Fischer-Dzoga K., Beeson J. H., Glagov S., Wissler R. W. Arterial foam cells with distinctive immunomorphologic and histochemical features of macrophages. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jul;100(1):57–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel J. D., Gallin J. I. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte and monocyte chemoattractants produced by human fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):609–618. doi: 10.1172/JCI109343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. F., Price T. H., Schwartz S. M., Dale D. C. Neutrophil-endothelial cell interactions on endothelial monolayers grown on micropore filters. J Clin Invest. 1981 Feb;67(2):584–587. doi: 10.1172/JCI110071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



