Abstract
Huntington's disease (HD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive motor dysfunction, including chorea and dystonia, emotional disturbances, memory, and weight loss. The medium spiny neurons of striatum and cortex are mainly effected in HD. Various hypotheses, including molecular genetics, oxidative stress, excitotoxicity, metabolic dysfunction, and mitochondrial impairment have been proposed to explain the pathogenesis of neuronal dysfunction and cell death. Despite no treatment is available to fully stop the progression of the disease, there are treatments available to help control the chorea. The present review deals with brief pathophysiology of the disease, plants and phytochemicals that have shown beneficial effects against HD like symptoms. The literature for the current review was collected using various databases such as Science direct, Pubmed, Scopus, Sci-finder, Google Scholar, and Cochrane database with a defined search strategy.
Keywords: Brahmi, Celastrol, Ginkgo biloba, Sesamol, Withania somnifera
INTRODUCTION
George Huntington, an Ohio physician, first described Huntington's chorea or Huntington's disease (HD). It is an autosomal dominant inherited neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive motor dysfunction, including chorea and dystonia, emotional disturbances, memory, and weight loss.[1,2,3] The pathological alterations mainly affect the medium spiny neurons (MSNs) of striatum, and to lesser extent of cortex. There is also loss of γ-amino butyric acid (GABA) and enkephalin neurons of basal ganglia in HD[2,4] along with modifications in the number of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors.[5] HD is also caused by expansion of the Cytosine-Adenine-Guanine (CAG) repeats which leads to the formation of polyglutamine stretch. The CAG repeat length and the onset age for HD are inversely correlated to each other.[1] Death normally occurs 15–20 years after the first appearance of symptoms.[6] Various biochemical alterations [Figure 1] found in the caudate of patients with HD include decreased GABA and acetylcholine (ACh) levels, and their synthesizing enzymes glutamate decarboxylase (GAD), and choline-acetyl transferase (CAT), respectively. There is also a decrease in the concentration of certain peptides that are present specifically in middle-sized spiny neurons.[7,8]
Figure 1.
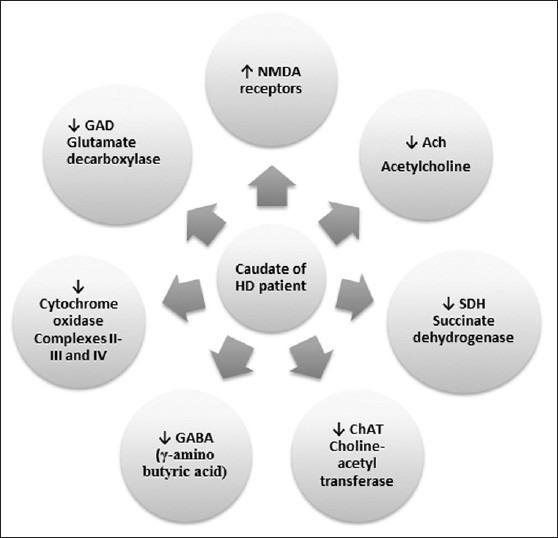
Various biochemical changes during Huntington's disease
HD currently occurs in many different countries and ethnic groups across the globe.[9] It has a worldwide prevalence of five to eight per 100,000 people with no gender predominance. Europe and countries of European origin have utmost frequencies of HD. In the USA, estimates of the prevalence of HD range from 4.1 to 8.4 per 100,000 people.[10,11] In India, pervasiveness of HD is higher and is closer to that occurs in Western Europe.[12] In the present review, an attempt has been made to highlight various plants and phytochemicals that have shown beneficial effects against this neurodegenerative disorder. Evidences used are mostly details from researches on animal models or on bioactive principles.
CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS
The whole course of HD progression has been divided into three major stages based on the severity of the disease: Early, middle, and late. HD is usually associated with the triad of motor, cognitive, and emotional disturbances.
Motor symptoms
The movement difficulties are associated with involuntary movements and abnormal voluntary movements.[2,6] The involuntary movements usually follow a biphasic pattern, initially hyperkinetic that increase with time, followed by bradykinesia leading to severe hypokinesia and rigid-akinetic state.[13] Characteristic abnormal involuntary movements involve Chorea, or choreoathetosis, which consist of continuous and irregular jerky or writhing motions.[6,14]
Non-motor symptoms
Patients suffering from HD have particular and distinctive cognitive impairments.[2,6] The nature of the progressive cognitive disorder is “frontal-subcortical”, and is also called as subcortical dementia. Common cognitive features include bradyphrenia, defective recall, deterioration of complex intellectual functions, difficulty in executing functions, and personality changes.[6,13] Apart from various cognitive abnormalities, various other psychiatric disturbances such as depression, anxiety, irritability, aggression, impulsivity, and tendency to suicide are also the key features of HD.[6,10,13,14,15]
PATHOLOGICAL FEATURES OF HD
Oxidative stress in HD
Oxidative stress (OS) is a mainstay of the pathology of neurodegenerative disorders. In neurodegenerative diseases, high levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and decreased activity of anti-oxidant mechanisms leads to neuronal cell death.[16,17] Oxidative stress leads to lipid peroxidation, protein oxidation, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) mutation, and oxidation causing damage to nerve cells. Various studies have shown a significant increase in levels of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (an oxidized DNA marker) in the caudate, mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) of the parietal cortex of HD patients, and in forebrain tissue and striatum of rodents.[18,19,20,21] Elevated levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), a marker of lipid peroxidation, 3-nitrotyrosine, and heme-oxygenase have also been observed in the brain of HD patients and rodents.[22,23] OS also promotes mutant Huntingtin aggregation and mutant Huntingtin-dependent cell death by mimicking proteasomal malfunction.[24] Increased levels of free radicals impair mitochondrial functions, energy production, and metabolic inhibition predisposes to excitotoxic damage.[3,25] The studies mentioned above clearly indicate the OS plays an important role in pathogenesis of HD but a direct association between OS and HD has not been reported.
Excitotoxicity
It is one of the suppositions that have been set forth to explain the degeneration of spiny projection neurons of the striatum in HD. According to this hypothesis, there is excessive activation of glutamate receptors and decreased uptake of glutamate by glia or hypersensitivity of post-synaptic glutamate receptors on striatal projection neurons. These biochemical changes, along with pathological signaling downstream of glutamate receptor activation (due to altered intracellular calcium homeostasis) and mitochondrial dysfunction, results in neuronal dysfunction and death of striatal MSNs.[26,27]
Metabolic dysfunction and mitochondrial impairment in HD
Mitochondria, the power source of the cell, are the sites of oxidative phosphorylation and cellular respiration leading to generation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). They also play a significant role in the maintenance of a low concentration of calcium within the cytosol. Mitochondrial dysfunction, leading to decreased mitochondrial oxygen consumption, glucose metabolism, and levels of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), has been reported in individuals affected from HD[28,29,30] and in HD post-mortem brain.[31] Further, there is an augmentation in the lactate levels in the CSF as well as in cerebral cortical tissue.[32,33] Deregulation of mitochondrial function by a mitochondrial toxin, 3-nitropropionic acid (3-NP), causes metabolic impairment due to energy impairment, oxidative stress, and excitotoxicity[34,35,36,37] leading to cytotoxicity mainly in the striatum despite the fact that metabolic impairment actually occurs throughout the entire body and brain.[37,38] All these changes due to mitochondrial dysfunction also make striatal neurons sensitive to excitotoxicity in HD.
Protective effects of herbs and secondary metabolites in HD
Nature is the best combinatorial chemist and possibly has answers to all diseases of mankind. Many of the thousands of plant species growing throughout the world have a direct pharmacological action on the body. Natural compounds with the effects of anti-oxidant, anti-inflammation, calcium antagonization, anti-apoptosis, and neurofunctional regulation exhibit preventive or therapeutic effects on various neurodegerative diseases.[39,40] Some of the plants and phytochemicals that have shown efficacy against 3-NP-induced neuronal impairment, a widely used animal model for HD, are discussed below:
Bacopa monnieri
Bacopa monnieri (BM) or Herpestis monniera, commonly known as Brahmi (Fam: Scrophulariaceae), is found throughout the Indian subcontinent and is classified as a medhyarasayana in Ayurveda.[41,42] It is used for the treatment of epilepsy, insomnia, anxiety, and as memory enhancer for centuries.[43,44]
The major chemical constituents present in the plant are dammarane type of tri-terpenoid saponins, Bacosides A and B [Figure 2].[41,45] Apart from these major constituents, it also contain various types of saponin including bacopasaponin A-G[46,47,48,49] along with pseudojujubogenin, jujubogenin,[50] bacopaside I-V, X, and N1 and N2.[51,52,53] The plant has also been reported to contain brahmine, herpestine, and monnierin.[54,55] Ample reports have shown memory enhancing effects of the plant.[44,56,57,58] Among various constituents, Bacoside A has shown to improve memory.[42,59] Various clinical trials have also shown beneficial effects of Brahmi in improving memory.[60] The neuroprotective and memory enhancing effects of BM extracts have been reported due to several mechanisms such as chelation of metal ions,[61] scavenging of free radicals,[62] and enhanced antioxidative defense enzymes.[62,63] Besides this, it also displays antioxidant,[63] anti-stress,[64] antidepressant,[65] anxiolytic,[66] free radical scavenging capacity,[62] hepatoprotective,[67] and antiulcerogenic activity.[68]
Figure 2.
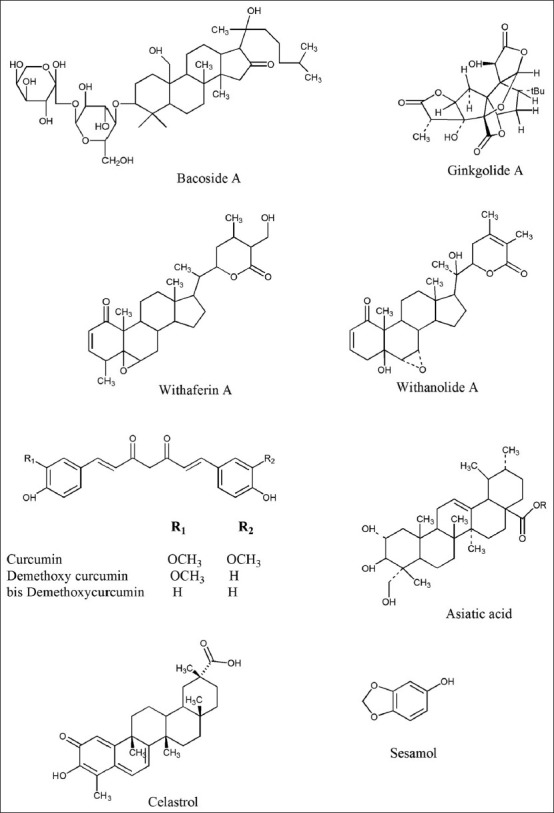
Various chemical constituents
3-NP inactivates the mitochondrial enzyme succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) and complex II-III of the electron transport chain.[2,69,70] It also increases the levels of ROS, MDA, and free fatty acids, suggesting the vital role of oxidative stress in the manifestation of neurotoxicity.[71] The dietary intake of BM leaf powder significantly decreased the basal levels of several oxidative markers, enhanced thiol-related antioxidant molecules and activities of antioxidant enzymes suggesting its antioxidant potential. One of the study has showed that dietary BM supplements leads to a significant protection against neurotoxicant-induced oxidative damage in brain.[43] The study further suggests that due to strong antioxidant effect and protective effect against stress-mediated neuronal dysfunctions BM can be useful in HD treatment.
Ginkgo biloba (maidenhair tree, family: Ginkgoaceae)
Ginkgo biloba L. was mentioned in Chinese Materia Medica 5,000 years ago.[72] Since ginkgo tree is known to be among the oldest living species on this planet, it is called a “living fossil”.[73] The chemical constituents present in the leaf are the trilactonic diterpenes: Ginkgolide A-C, Ginkgolide J-M; a trilactonic sesquiterpene: Bilobalide; flavonoids including quercetin, kaempferol, isorhamnetins, and biflavonoids (amentoflavone, bilobetin, 5-methoxybilobetol, ginkgetin, isoginkgetin, and sciadopitysin); and proanthocyanidins [Figure 2].[73,74,75] Ginkgo leaf extract has exhibited protective effects against neurodegenerative diseases like dementia (Alzheimer's disease), cardiovascular diseases, cancer, stress, tinnitus, geriatric complaints like vertigo, age-related macular degeneration, and psychiatric disorders like schizophrenia.[76] These versatile activities of the Ginkgo leaf extract are due its antioxidant effect,[77] anti-platelet activating factor (Anti-PAF) activity (cardio and cerebral vascular diseases),[75] inhibition of beta amyloid peptide (Aβ) aggregation (prevent Alzheimer's progression),[78] decreased expression of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor (stress alleviation),[79] and stimulation of endothelium derived relaxing factor (improve blood circulation).[74] The G. biloba extract (100 mg/kg, i.p. for 15 days) improved the 3-NP induced neurobehavioral deficits[80] and also decreased the level of striatal MDA. Standardized G. biloba extract (EGb 761) also caused down- and up-regulation of striatal glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and Bcl-xl expression levels, respectively. These biochemical results, supported by the histopathological studies suggested neuroprotective role of EGb 761 in HD.[80]
Withania somnifera
Withania somnifera (WS), commonly known Ashwagandha (Fam: Solanaceae), has been used since ages in Ayurvedic medicine to increase longevity and vitality.[81] The plant has reported for its antioxidant,[82,83] anti-inflammatory,[84] immune-modulating,[85] anti-stress,[86] memory enhancing,[87] and anti-convulsant properties.[88] As an antioxidant, WS and its active constituents (sitoindosides VII-X and withaferin A) increase the levels of endogenous superoxide dismutase, catalase, and ascorbic acid, and decrease lipid peroxidation.[83,89,90,91] It acts as an anti-inflammatory agent through inhibition of complement, lymphocyte proliferation, and delayed-type hypersensitivity.[84] Various studies have shown that WS increase circulating cortisol, decrease fatigue, increase physical performance, and decrease refractory depression in stress.[92,93] It also modulates various neurotransmitter receptor systems in the CNS. Recently, WS has been found beneficial in 18 clinically diagnosed Parkinson's patients.[87,94]
Chemical analysis of Ashwagandha shows that it mainly contains steroidal lactones (collectively known as withanolides) and alkaloids. The important withanolides isolated from plant are withaferin A, withanolide A, withanolide D-P, withanone, sitoindoside VII-X [Figure 2]. Various alkaloids that have been reported from WP are withanine (major alkaloid), somniferine, somnine, somniferinine, withananine, pseudo-withanine, tropine, pseudo-tropine, 3-a-gloyloxytropane, choline, cuscohygrine, isopelletierine, anaferine, anahygrine, and anahydrine.[95,96,97,98]
Role of GABAergic in the pathogensis of HD has been well documented and WS has been well reported to act by GABAergic system. WS root extract pretreatment significantly improved cognitive function, restored acetyl cholinesterase enzyme activity and glutathione enzyme level system in 3-NP treated animals.[99,100] The root extract of WS exhibited possible neuroprotective effect against a 3-NP-induced neurotoxicity in rats due to its GABAergic and antioxidant action and make it a suitable lead in the treatment of HD.[99,100]
Curcuma longa
Curcuma longa (CL), commonly known as Haldi or turmeric, is a perennial herb of family Zingiberaceae. Its rhizomes have been used since ages in the traditional medicinal system of India, China, Japan, and other South Asian countries.[101] It has a long history of use as a spice and a household remedy for the treatment of inflammation, skin diseases, wounds, and as an antibacterial and antiseptic.[102]
CL contains yellow coloring matter, various curcuminiods, sesquiterpenes, essential oil, and starch. Most of the curcuminiods are diarylheptanoid, a derivative of which curcumin is the major bioactive component. The other two curcuminoids are desmethoxycurcumin, and bis-desmethoxycurcumin [Figure 2].[102,103] Curcumin has antioxidant,[104] anti-inflammatory,[105] antifungal, antibacterial, antiparasitic, choleretic, analgesic, hepatoprotective, free radical scavenging, iron chelating, antiviral,[102,106] and anti-mutagenic activity.[107] Various mechanisms like direct scavenging activity of superoxide, hydroxyl radicals, metal chelating property[104,108,109] and ability to induce antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione-S-transferase, and hemeoxygenase) have been responsible for the antioxidant potential of CL.[110] Its anti-inflammatory property may be related to its ability to inhibit upregulation of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2. Furthermore, it showed neuroprotective action in various neurological disorders. Curcumin and manganese complex of curcumin offer protective action against vascular dementia by virtue of its antioxidant activity,[111,112] and is useful in the treatment of aging and memory dysfunctions.[113] Chronic administration of curcumin consistently improved body weight, reversed motor deficits, and increase SDH activity in 3-NP treated rats. The improved 3-NP-induced motor and cognitive impairment along with a strong antioxidant property indicates that curcumin could be useful and can act as a lead molecule in the treatment of HD.[114]
Ginsenosides
Ginseng root is a well-known herbal medicine and has been used as a representative tonic for over 2,000 years in the far eastern countries like China, Japan, and Korea.[115] Asian ginseng (Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer) and American ginseng (Panax quinquefolium L.) belonging to family Araliaceae are the most common ginseng species.[116] Ginseng contains a series of tetracyclic dammarane triterpenoid saponin glycosides called, ginsenosides, which are active constituents of the drug.[117] Ginsenosides, depending on their structural differences, are classified into three categories: the panaxadiols (e.g., Rb1-Rb3, Rc, Rd, Rg3, Rh2, and Rs1), panaxatriols (e.g., Re, Rf, Rg1-2, and Rh1) and oleanolic acid derivatives (e.g., Ro).[118] Ginseng has been used primarily as a tonic to revitalize weak bodies and help the restoration of proper metabolism in the body. Various studies (in vitro and in vivo) have exhibited beneficial effects of ginseng in several pathological conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, CNS disorders, cancer, immune deficiency, and hepatotoxicity. It has also been reported that ginseng and some of its active constituents also exert beneficial effects on aging and neurodegenerative diseases.[118,119] It also possesses antioxidant,[120] anti-apoptotic,[120] anti-inflammatory,[121] and immune-stimulatory activities.[119] It also reduces lipid peroxidation, inhibits excitotoxicity, and Ca2+ over-influx into neurons, maintains cellular ATP levels, preserves structural integrity of neurons, and increase cognitive performance.[119] Ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg3 have exhibited protective effects on cortical neurons against glutamate-induced cell death by blocking Ca2+ influx through glutamate receptors.[122] Saponins from ginseng also inhibit both NMDA and glutamate-induced increase Ca2+ levels in rat hippocampal neurons.[123] Ginsenosides Rb1, Rb3, and Rd have exhibited neuroprotective effect against 3-NP-induced striatal neuronal damage.[124,125] Ginsenoside Rb1, Rc, and Rg5 have shown to protect medium spiny neurons from glutamate-induced apoptosis in genetically modified rodents. It has been hypothesized that neuroprotective effect of these ginsenosides could be due to their ability to inhibit glutamate-induced Ca2+ responses in cultured spinal neuronal cultures.[126] Such reports strongly support that potential of ginseng and ginsenosides can be exploited in developing new therapeutics for the treatment of HD and other neurodegenerative disorders.
Centella asiatica (syn. Hydrocotyle asiatica)
Centella asiatica (CA), commonly known as Gotu kola, Indian Pennywort and Jal brahmi, belongs to family Umbelliferae. It has been categorized as Rasayanas in Ayurveda due to its ability to improve memory and age related brain disorders.[127] Studies have shown various neuropharmacological effects of CA which comprises of memory enhancement,[128,129] increased neurite elongation and acceleration of nerve regeneration.[130] It also possesses anti-oxidant property.[131,132] The most important chemical constituents from CA are triterpenoid saponins including asiaticoside, asiatic acid, madecassoside, and madecassic acid [Figure 2].[133,134] Other saponins present in minor quantities are brahmoside and brahminoside.[133,135] Various triterpene acids, betullic acid, brahmic, and isobrahmic acid are reported from the plant.[133,135] The essential oil from the leaves of the plant contains monoterpenes, including bornyl acetate, α-pinene, β-pinene, and γ-pinene.[136] Apart from these constituents flavones, sterols, and lipids have also been reported from CA.
CA attenuated the 3-NP-induced depletion of GSH levels, total thiols, and endogenous antioxidants in striatum and other brain regions.[137] It also exhibited protection against 3-NP-induced mitochondrial dysfunctions viz., reduction in the activity of SDH, electron transport chain enzymes, and decreased mitochondrial viability.[137] The results of this study clearly indicate that the protective effect of CA against neuronal damage induced by OS and mitochondrial dysfunctions along with its memory enhancing activity can be helpful in controlling HD-related impairments.
Flavonoids
Flavonoids are a group of polyphenolic compounds, distributed throughout the plant kingdom. They possess a common phenylbenzopyrone structure (C6-C3-C6).[138,139] Flavonoids exhibit several biological effects such as anti-inflammatory, anti-hepatotoxic, anti-ulcer, anti-allergic, and antiviral actions.[139,140,141] They are potent antioxidants and have free radical scavenging abilities by virtue of their aromatic hydroxyl groups.[142,143]
Recent studies, both pre-clinical and clinical, suggested that flavonoids prevent and delay neurodegeneration (especially in aged-population), cognitive dysfunction, mood decline, and oxidative pathologies.[144] They also exert protective action against peroxynitrite-induced oxidative damage.[145] Flavonoids inhibit nitric oxide synthase (involved in neurodegenerative process including HD),[146,147,148] cyclooxygenase expression,[147] protect against oxidative stress,[148] and modulate calcium homeostasis.[144] These polyphenols act by direct scavenging of various ROS and reactive nitrogen species.[144,149] Antioxidants have shown beneficial effects agains 3-NP induced toxicity possibly by free radical scavenging activity (decreases MDA and nitrite concentration) and increased endogenous antioxidant defense (increased levels of superoxide, catalase, and glutathione).[99,150,151] Various flavonoides such as naringin,[149] hesperidin,[149] kaempferol,[152] and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)[151,153] have been reported to provide beneficial effects against 3-NP-induced neurotoxicity.
Celastrol
Celastrol [Figure 2] is a triterpenoid quinone methide isolated from Tripterygium wilfordi (Thunder of God vine) and Celastrus regelii belonging to the Celastraceae family, exhibits antioxidant (15 times the potency of α-tocopherol),[154] anti-inflammatory,[155] anticancer,[156] and insecticidal[157] activities. It is known to prevent the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, inducible nitric oxide synthase, and lipid peroxidation. Celastrol attenuated the loss of dopaminergic neurons and dopamine depletion in MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine) treated rodents.[158] It also protect from 3-NP-induced striatal damage by regulating heat shock protein (hsp) gene expression in dopaminergic neurons.[158,159] The above reports indicate celastrol to be a promising neuroprotective agent against Parkinson's disease and HD.
Trehalose
It is a non-reducing disaccharide found in many organisms, including bacteria, yeast, fungi, insects, invertebrates, and plants. It is a natural hemolymph sugar of invertebrates and protects the integrity of cells by preventing protein denaturation due to various environmental stresses.[160,161] Though it is not synthesized in mammals, still it has exhibited various beneficial effects in them.[160] Various reports have shown that it inhibits amyloid formation,[162] aggregation of β-amyloid,[163] polyglutamine (polyQ)3-mediated protein aggregation, and decreased Huntingtin aggregates-induced toxicity. It also alleviated polyQ-induced pathology in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington disease by stabilizing the partially unfolded mutant protein.[164,165] It has also been reported that trehalose increase the autophagic activity against various aggregation proteins such as mutant Huntingtin, thereby, by providing neruoprotective activity against HD.[165] Hence, both properties of trehalose (inducer of autophagy and chemical chaperone) can be utilized in developing a new therapeutic agent for HD.[165]
Lycopene
It is a well-known carotenoids present in considerable amounts in tomatoes and tomato-based products.[166] Several studies have reported their therapeutic potential against oxidative stress and its related pathologies, including HD.[167,168] It has been reported to possess potent neuroprotective,[169] antioxidant,[170] antiproliferative, anticancer,[171] anti-inflammatory,[172] memory enhancing,[173] and hypocholesterolemic activities.[174] Lycopene is more powerful carotenoid quencher of singlet oxygen with respect to vitamin E and glutathione.[174] Lycopene treatment significantly attenuated various behavioral and biochemical changes-induced by 3-NP, suggesting its therapeutic potential against HD-like behavior.[175] The results of the study clearly indicated that lycopene exhibited its protected effect through its antioxidant property and nitric oxide pathway.[151,175]
Sesamol
Sesamum indicum Linn. (Pedaliaceae), commonly known as sesame, has been used as a health food in India and other East Asian countries.[176] Sesamol [Figure 2], one of the main constituents in sesame oil, is responsible for its antioxidant activity.[177] Sesamol has shown to control increased blood pressure, hyperlipidemia and lipid peroxidation (by increasing enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants),[176] and a strong antitumor action.[178] It has been reported that sesamol exhibited its protective effect through nitric oxide mechanism (suppression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression).[179] It also attenuated 3-NP-induced Huntington-like behavioral, biochemical, and cellular alterations in rodents.[180] It also protects against 3-NP-induced memory impairment,[150] oxidative stress, neuroinflammation in hippocampus neurons, and consequently improves synaptic plasticity and neurotransmission.[181] It also inhibits nitrite production and inducible NOS expression in the liver of septic rats.[182] Protective effect of sesamol against 3-NP induced HD like symptoms can make it a lead molecule against HD. Detailed and mechanistic based studies are still warranted.
CONCLUSION
The above data clearly indicates that the oxidative stress plays a significant role in the pathophysiology of HD. Further, the plants having well established antioxidant and neuroprotective effects have shown beneficial effects against the symptoms of HD in both in vivo and in vitro studies. Still ample work is required to fully elucidate the mechanism of these plants and phytochemicals against HD. Furthermore, lot of other plants with significant antioxidant and neuroprotective potential can be explored for their protective effect against HD.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared
REFERENCES
- 1.Krobitsch S, Kazantsev AG. Huntington's disease: From molecular basis to therapeutic advances. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011;43:20–4. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kumar P, Kalonia H, Kumar A. Huntington's disease: Pathogenesis to animal models. Pharmacol Rep. 2010;62:1–14. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(10)70238-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sawa A, Tomoda T, Bae BI. Mechanisms of neuronal cell death in Huntington's disease. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2003;100:287–95. doi: 10.1159/000072864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zadori D, Geisz A, Vamos E, Vecsei L, Klivenyi P. Valproate ameliorates the survival and the motor performance in a transgenic mouse model of Huntington's disease. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009;94:148–53. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2009.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ellerby LM. Hunting for excitement: NMDA receptors in Huntington's disease. Neuron. 2002;33:841–2. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00631-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ross CA, Margolis RL. Huntington disease. American College of Neuropsychopharmacol. 2002 [Google Scholar]
- 7.Perez-De La Cruz V, Santamaria A. Integrative hypothesis for huntington's disease: A brief review of experimental evidence. Physiol Res. 2007;56:513–26. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.931049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shoulson I. Huntington's disease. A decade of progress. Neurol Clin. 1984;2:515–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kent A. Huntington's disease. Nurs Stand. 2004;21:45–51. doi: 10.7748/ns2004.04.18.32.45.c3596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kumar P, Naidu PS, Padi SS, Kumar A. Huntington's disease: A review. Indian J Pharm Edu Res. 2007;41:287–94. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Harper PS. The epidemiology of Huntington's disease. Hum Gen. 1992;89:365–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00194305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jha S, Patel R. Some observations on the spectrum of dementia. Neurol India. 2004;52:213–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sturrock A, Leavitt BR. The clinical and genetic features of Huntington disease. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2010;23:243–59. doi: 10.1177/0891988710383573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Purdon SE, Mohr E, Ilivitsky V, Jones BD. Huntington's disease: Pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1994;19:359–67. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Phillips W, Shannon KW, Barker RA. The current clinical management of Huntington's disease. Mov Disord. 2008;23:1491–504. doi: 10.1002/mds.21971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Farooqui T, Farooqui AA. Aging: An important factor for the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Mech Aging Dev. 2009;130:203–15. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2008.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dong XX, Wang Y, Qin ZH. Molecular mechanisms of excitotoxicity and their relevance to pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2009;30:379–87. doi: 10.1038/aps.2009.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bogdanov MB, Andreassen OA, Dedeoglu A, Ferrante RJ, Beal MF. Increased oxidative damage to DNA in a transgenic mouse model of Huntington's disease. J Neurochem. 2001;79:1246–9. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tabrizi SJ, Workman J, Hart PE, Mangiarini L, Mahal A, Bates G, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and free radical damage in the Huntington R6/2 transgenic mouse. Ann Neurol. 2000;47:80–6. doi: 10.1002/1531-8249(200001)47:1<80::aid-ana13>3.3.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Polidori MC, Mecocci P, Browne SE, Senin U, Beal MF. Oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA in Huntington's disease parietal cortex. Neurosci Lett. 1999;272:53–6. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(99)00578-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Browne SE, Bowling AC, MacGarvey U, Baik MJ, Berger SC, Muqit MM, et al. Oxidative damage and metabolic dysfunction in Huntington's disease: Selective vulnerability of the basal ganglia. Ann Neurol. 1997;41:646–53. doi: 10.1002/ana.410410514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chen CM. Mitochondrial dysfunction, metabolic deficits, and increased oxidative stress in Huntington's disease. Chang Gung Med J. 2011;34:135–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Browne SE, Ferrante RJ, Beal MF. Oxidative stress in Huntington's disease. Brain Pathol. 1999;9:147–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1999.tb00216.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Goswami A, Dikshit P, Mishra A, Mulherkar S, Nukina N, Jana NR. Oxidative stress promotes mutant huntingtin aggregation and mutant huntingtin-dependent cell death by mimicking proteasomal malfunction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;342:184–90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.01.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Túnez I, Tasset I, Pérez-De La Cruz V, Santamaría A. 3-Nitropropionic acid as a tool to study the mechanisms involved in Huntington's disease: Past, Present and Future. Molecules. 2010;15:878–916. doi: 10.3390/molecules15020878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Raymond LA, Andre VM, Cepeda C, Gladding CM, Milnerwood AJ, Levine MS. Pathophsiology of Huntington's disease: Time-dependent alterations in synaptic and receptor function. Neuroscience. 2011;198:252–73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.08.052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.DiFiglia M. Excitotoxic injury of the neostriatum: A model for Huntington's disease. Trends Neurosci. 1990;13:286–9. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90111-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Leenders KL, Frackowiak RS, Quinn N, Marsden CD. Brain energy metabolism and dopaminergic function in Huntington's disease measured in vivo using positron emission tomography. Mov Disord. 1986;1:69–77. doi: 10.1002/mds.870010110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Stahl WL, Swanson PD. Biochemical abnormalities in Huntington's chorea brains. Neurology. 1974;24:813–9. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.9.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cramer H, Warter JM, Renaud B. Analysis of neurotransmitter metabolites and adenosine 3’,5’-monophosphate in the CSF of patients with extrapyramidal motor disorders. Adv Neurol. 1984;40:431–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gines S, Seong IS, Fossale E, Ivanova E, Trettel F, Gusella JF, et al. Specific progressive cAMP reduction implicates energy deficit in presymptomatic Huntington's disease knock-in mice. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12:497–508. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddg046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Koroshetz WJ, Jenkins BG, Rosen BR, Beal MF. Energy metabolism defects in Huntington's disease and effects of coenzyme Q10. Ann Neurol. 1997;41:160–5. doi: 10.1002/ana.410410206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Jenkins BG, Koroshetz WJ, Beal MF, Rosen BR. Evidence for impairment of energy metabolism in vivo in Huntington's disease using localized 1H NMR spectroscopy. Neurology. 1993;43:2689–95. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.12.2689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Fatokun AA, Smith RA, Stone TW. Resistance to kynurenic acid of the NMDA receptor-dependent toxicity of 3-nitropropionic acid and cyanide in cerebellar granule neurons. Brain Res. 2008;1215:200–7. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Huang QY, Yu L, Ferrante RJ, Chen JF. Mutant SOD1G93A in bone marrow-derived cells exacerbates 3-nitropropionic acid induced striatal damage in mice. Neurosci Lett. 2007;418:175–80. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.03.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Alexi T, Borlongan CV, Faull RL, Williams CE, Clark RG, Gluckman PD, et al. Neuroprotective strategies for basal ganglia degeneration: Parkinson's and Huntington's diseases. Prog Neurobiol. 2000;60:409–70. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(99)00032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Alexi T, Hughes PE, Faull RL, Williams CE. 3-Nitropropionic acid's lethal triplet: Cooperative pathways of neurodegeneration. Neuroreport. 1998;9:R57–64. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199808030-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fontaine MA, Geddes JW, Banks A, Butterfield DA. Effect of exogenous and endogenous antioxidants on 3-nitropropionic acid-induced in vivo oxidative stress and striatal lesions: Insights into Huntington's disease. J Neurochem. 2000;75:1709–15. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0751709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wu PF, Zhang Z, Wang F, Chen JG. Natural compounds from traditional medicinal herbs in the treatment of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010;31:1523–31. doi: 10.1038/aps.2010.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sandhya S, Vinod KR, Kumar S. Herbs used for brain disorders. Hygeia J Drugs Med. 2010;2:38–45. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gohill KJ, Patel JA. A review on Bacopa monnieria: Current research and future prospects. Int J Green Pharm. 2010;4:1–9. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Russo A, Borrelli F. Bacopa monniera, a reputed nootropic plant: An overview. Phytomedicine. 2005;12:305–17. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2003.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Shinomol GK, Muralidhara Bacopa monnieri modulates endogenous cytoplasmic and mitochondrial oxidative markers in prepubertal mice brain. Phytomedicine. 2011;18:317–26. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2010.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Calabrese C, Gregory WL, Leo M, Kraemer D, Bone K, Oken B. Effects of a standardized Bacopa monnieri extract on cognitive performance, anxiety, and depression in the elderly: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Altern Complement Med. 2008;14:707–13. doi: 10.1089/acm.2008.0018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bammidi SR, Volluri SS, Chippada SC, Avanigadda S, Vangalapati M. A review on pharmacological studies of Bacopa monniera. J Chem Biol Phys Sci. 2011;1:250–9. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hou CC, Lin SJ, Cheng JT, Hsu FL. Bacopaside III, bacopasaponin G, and bacopaside A, B and C from Bacopa monniera. J Nat Prod. 2002;65:1759–63. doi: 10.1021/np020238w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mahato BS, Garai S, Chakravarty AK. Bacosaponins E and F: Two jujubogenin bisdesmosides from Bacopa monniera. Phytochemistry. 2000;53:711–4. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(99)00384-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Garai S, Mahato BS, Ohtani K, Yamasaki K. Dammarane-type triterpenoid saponins from Bacopa monniera. Phytochemistry. 1996;42:815–20. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(95)00936-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Garai S, Mahato BS, Ohtani K, Yamasaki K. Bacopasaponin D: A pseudojujubogenin glycoside from Bacopa monniera. Phytochemistry. 1996;43:447–9. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(96)00250-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kawai KI, Shibata S. Pseudojujubogenin: A new sapogenin from Bacopa monniera. Phytochemistry. 1978;17:287–9. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Murthy PB, Raju VR, Ramakrisana T, Charavarthy MS, Kumar KV, Kannababu S, et al. Estimation of twelve Bacopa saponins in Bacopa monniera extracts and formulations high-performance liquid chromatography. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 2006;54:907–11. doi: 10.1248/cpb.54.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Chakarvarty AK, Garai S, Masuda K, Nakane T, Kawahara N. Bacopasides III-V: Three new triterpenoid glycosides from Bacopa monniera. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 2003;51:215–7. doi: 10.1248/cpb.51.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Chakarvarty AK, Sarkar T, Masuda K, Shiojima K, Nakane T, Kawahara N. Bacopaside I and II: Two pseudojujobogenin glycosides from Bacopa monniera. Phytochemistry. 2001;58:553–6. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(01)00275-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kapoor R, Srivastava S, Kakkar P. Bacopa monnieri modulated antioxidant responses in brain and kidney of diabetic rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2009;27:62–9. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2008.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Deepak M, Amit A. The need for establishing the identities of ‘bacoside A and B’, the putative major bioactive saponins of Indian medicinal plant Bacopa monnieri. Phytomedicine. 2004;11:264–8. doi: 10.1078/0944-7113-00351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Vollala VR, Upadhya S, Nayak S. Learning and memory-enhancing effect of Bacopa monniera in neonatal rats. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2011;112:663–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Roodenrys S, Booth D, Bulzomi S, Phipps A, Micallef C, Smoker J. Chronic effects of brahmi (Bacopa monnieri) on human memory. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002;27:279–81. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(01)00419-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Singh HK, Dhawan BD. Neuropsychopharmacological effects of the Ayurvedic nootropic Bacopa monniera Linn. (Brahmi) Indian J Pharmacol. 1997;29:359–65. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Vohora D, Pal SN, Pillai KK. Protection from phenytoin-induced cognitive deficit by Bacopa monniera, a reputed Indian nootropic plant. J Ethnopharmacol. 2000;71:383–90. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(99)00213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Stough C, Lloyd J, Clarke J, Downey LA, Hutchison CW, Rodgers T, et al. The chronic effects of an extract of Bacopa monniera (Brahmi) on cognitive function in healthy human subjects. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2001;156:481–4. doi: 10.1007/s002130100815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Tripathi YB, Chaurasia S, Tripathi E, Upadhyay A, Dubey GP. Bacopa monnieri Linn. as an antioxidant: Mechanism of action. Indian J Exp Biol. 1996;34:523–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Russo A, Izzo AA, Borrelli F, Renis M, Vanella A. Free radical scavenging capacity and protective effect of Bacopa monnieri L. on DNA damage. Phytother Res. 2003;17:870–5. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Bhattacharya SK, Bhattacharya A, Kumar A, Ghosal S. Antioxidant activity of Bacopa monniera in rat frontal cortex, straitum and hippocampus. Phytother Res. 2000;14:174–9. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1099-1573(200005)14:3<174::aid-ptr624>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Chowdhuri DK, Parmar D, Kakkar P, Shukla R, Seth PK, Srimal RC. Antistress effect of bacosides of Bacopa monnieri: Modulation of Hsp70 expression, superoxide dismutase and cytochrome P450 activity in rat brain. Phytother Res. 2002;16:639–45. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Sairam K, Dorababu M, Goel RK, Bhattacharya SK. Antidepressant activity of standardized extract of Bacopa monnieri in experimental models of depression in rats. Phytomedicine. 2002;9:207–11. doi: 10.1078/0944-7113-00116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Shanker G, Singh HK. Anxiolytic profile of standardized Brahmi extract. Indian J Pharmacol. 2000;32:152. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Sumathy T, Subramanian S, Govindaswamy S, Balakrishna K, Veluchany G. Protective role of Bacopa monnieri on morphine induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Phytother Res. 2001;15:643–5. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Sairam K, Rao CV, Babu MD, Goel RK. Prophylactic and curative effects of Bacopa monniera in gastric ulcer models. Phytomedicine. 2001;8:423–30. doi: 10.1078/S0944-7113(04)70060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Andreassen OA, Ferrante RJ, Hughes DB, Klivenyi P, Dedeoglu A, Ona VO, et al. Malonate and 3-nitropropionic acid neurotoxicity are reduced in transgenic mice expressing a caspase-1 dominant-negative mutant. J Neurochem. 2000;75:847–52. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0750847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Coles CJ, Edmondson DE, Singer TP. Inactivation of succinate dehydrogenase by 3-nitropropionate. J Biol Chem. 1979;254:5161–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Kim GW, Copin JC, Kawase M, Chen SF, Sato S, Gobbel GT, et al. Excitotoxicity is required for induction of oxidative stress and apoptosis in mouse striatum by the mitochondrial toxin, 3-Nitropropionic acid. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20:119–29. doi: 10.1097/00004647-200001000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Nakanishi K. Terpene trilactones from Gingko biloba: From ancient times to 21st century. Bioorg Med Chem. 2005;13:4987–5000. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2005.06.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.McKenna DJ, Jones K, Hughes K. Efficacy, safety, and use of Ginkgo biloba in clinical and preclinical applications. (88-90).Altern Ther Health Med. 2001;7:70–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Smith JV, Luo Y. Studies on molecular mechanisms of Ginkgo biloba extract. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004;64:465–72. doi: 10.1007/s00253-003-1527-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.DeFeudis FV, Drieu K. Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) and CNS functions: Basic studies and clinical applications. Curr Drug Targets. 2000;1:25–58. doi: 10.2174/1389450003349380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Ramassamy C, Longpre F, Christen Y. Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) in Alzheimer's disease: Is there any evidence? Curr Alzheimer Res. 2007;4:253–62. doi: 10.2174/156720507781077304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Pietri S, Maurelli E, Drieu K, Culcasi M. Cardioprotective and anti-oxidant effects of the terpenoid constituents of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1997;29:733–42. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.1996.0316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Mahadevan S, Park Y. Multifaceted therapeutic benefits of Ginkgo biloba L.: Chemistry, efficacy, safety, and uses. J Food Sci. 2008;73:R14–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2007.00597.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Amri H, Ogwuegbu SO, Boujrad N, Drieu K, Papadopoulos V. In vivo regulation of peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor and glucocorticoid synthesis by Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 and isolated ginkgolides. Endocrinology. 1996;137:5707–18. doi: 10.1210/endo.137.12.8940403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Mahdy HM, Tadros MG, Mohamed MR, Karim AM, Khalifa AE. The effect of Ginkgo biloba extract on 3-nitropropionic acid-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Neurochem Int. 2011;59:770–8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2011.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Winters M. Ancient medicine, modern use: Withania somnifera and its potential role in integrative oncology. Altern Med Rev. 2006;11:269–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Yadava SA, Hakkim L, Sathishkumar F, Sathishkumar R. Antioxidant activity of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal by different solvent extraction methods. J Pharm Res. 2011;4:1428–30. [Google Scholar]
- 83.Bhattacharya SK, Satyan KS, Ghosal S. Antioxidant activity of glycowithanolides from Withania somnifera. Indian J Exp Biol. 1997;35:236–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Davis L, Kuttan G. Effect of Withania somnifera on cell mediated immune response in mice. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2002;21:585–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Davis L, Kuttan G. Immunomodulatory activity of Withania somnifera. J Ethnopharmacol. 2000;71:193–200. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(99)00206-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Bhattacharya SK, Goel RK, Kaur R, Ghosal S. Anti-stress activity of sitoindosides VII and VIII, new acylsterylglucosides from Withania somnifera. Phytother Res. 1987;1:32–7. [Google Scholar]
- 87.Kulkarni SK, Verma A. Ashwagandha and Bramhi: Nootropic and de-addiction profile of psychotropic indigenous plants. Drugs Today. 1993;29:257–63. [Google Scholar]
- 88.Kulkarni SK, Akula KK, Dhir A. Effect of Withania somnifera Dunal root extract against pentylenetetrazol seizure threshold in mice: Possible involvement of GABAergic system. Indian J Exp Biol. 2008;46:465–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Bhatnagar M, Sisodia SS, Bhatnagar R. Antiulcer and antioxidant activity of Asparagus racemosa Willd and Withania somnifera Dunal in rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1056:261–78. doi: 10.1196/annals.1352.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Gupta SK, Dua A, Vohra BP. Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) attenuates antioxidant defense in aged spinal cord and inhibits copper induced lipid peroxidation and protein oxidative modifications. Drug Metabol Drug Interact. 2003;19:211–22. doi: 10.1515/dmdi.2003.19.3.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Bhattacharya SK, Bhattacharya D, Sairam K, Ghosal S. Effect of Withania somnifera glycowithanolides on a rat model of tardive dyskinesia. Phytomedicine. 2002;9:167–70. doi: 10.1078/0944-7113-00089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Singh B, Chandan BK, Gupta DK. Adaptogenic activity of a novel withanolide-free aqueous fraction from the roots of Withania somnifera Dun. (Part II) Phytother Res. 2003;17:531–6. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Singh B, Saxena AK, Chandan BK, Gupta DK, Bhutani KK, Anand KK. Adaptogenic activity of a novel, withanolide-free aqueous fraction from the roots of Withania somnifera Dun. Phytother Res. 2001;15:311–8. doi: 10.1002/ptr.858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Naidu PS, Singh A, Kulkarni SK. Effect of Withania somnifera root extract on reserpine-induced orofacial dyskinesia and cognitive dysfunction. Phytother Res. 2006;20:140–6. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Singh G, Sharma PK, Dudhe R, Singh S. Biological activities of Withania somnifera. Ann Biol Res. 2010;1:56–63. [Google Scholar]
- 96.Mirjalili MH, Moyano E, Bonfill M, Cusido RM, Palazon J. Steroidal lactones from Withania somnifera, an ancient plant for novel medicine. Molecules. 2009;14:2373–93. doi: 10.3390/molecules14072373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Kapoor LD. London, UK: CRC Press; 2001. Handbook of Ayurvedic Medicinal Plants. [Google Scholar]
- 98.Kirtikar KR, Basu BD. Dehradun, India: Shiva Publishers; 1991. Indian Medicinal Plants. [Google Scholar]
- 99.Kumar P, Kumar A. Possible neuroprotective effect of Withania somnifera root extract against 3-Nitropropionic acid-induced behavioral, biochemical, and mitochondrial dysfunction in an animal model of Huntington's disease. J Med Food. 2009;12:591–600. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2008.0028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Kumar P, Kumar A. Effects of root extract of Withania somnifera in 3-Nitropropionic acid-induced cognitive dysfunction and oxidative damage in rats. Int J Health Res. 2008;1:139–49. [Google Scholar]
- 101.Jain S, Shrivastava S, Nayak S, Sumbhate S. Recent trends in Curcuma longa Linn. Pharmacog Rev. 2007;1:119–28. [Google Scholar]
- 102.Joe B, Vijaykumar M, Lokesh BR. Biological properties of curcumin-cellular and molecular mechanisms of action. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2004;44:97–111. doi: 10.1080/10408690490424702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Akram M, Shahab-uddin, Ahmed A, Usmanghani K, Hannan A, Mohiuddin E, et al. Curcuma longa and curcumin: A review article. Rom J Biol-Plant Biol. 2010;55:65–70. [Google Scholar]
- 104.Kunchandy F, Rao MN. Oxygen radical scavenging activity of curcumin. Int J Pharm. 1990;58:237–40. [Google Scholar]
- 105.Chainani-Wu N. Safety and anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin: A component of turmeric (Curcuma longa) J Altern Complement Med. 2003;9:61–8. doi: 10.1089/107555303321223035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Chattopadhyay I, Biswas K, Bandyopadhyay U, Banerjee RK. Turmeric and curcumin: Biological actions and medicinal applications. Curr Sci. 2004;87:44–53. [Google Scholar]
- 107.Simon A, Allais DP, Duroux JL, Basly JP, Durand-Fontanier S, Delage C. Inhibitory effect of curcuminoids on MCF-7 cell proliferation and structure-activity relationships. Cancer Lett. 1998;129:111–6. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(98)00092-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Sreejayan, Rao MN. Nitric oxide scavenging by curcuminoids. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1997;49:105–7. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1997.tb06761.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Daniel S, Limson JL, Dairam A, Watkins GM, Daya S. Through metal binding, curcumin protects against lead- and cadmium-induced lipid peroxidation in rat brain homogenates and against lead-induced tissue damage in rat brain. J Inorg Biochem. 2004;98:266–75. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2003.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Ghoneim AI, Abdel-Naim AB, Khalifa AE, El-Denshary ES. Protective effects of curcumin against ischaemia/reperfusion insult in rat forebrain. Pharmacol Res. 2002;46:273–9. doi: 10.1016/s1043-6618(02)00123-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Vajragupta O, Boonchoong P, Watanabe H, Tohda M, Kummasud N, Sumanont Y. Manganese complexes of curcumin and its derivatives: Evaluation for the radical scavenging ability and neuroprotective activity. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003;35:1632–44. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2003.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Thiyagarajan M, Sharma SS. Neuroprotective effect of curcumin in middle cerebral artery occlusion induced focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Life Sci. 2004;74:969–85. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2003.06.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Frautschy SA, Hu W, Kim P, Miller SA, Chu T, Harris-White ME, et al. Phenolic anti-inflammatory antioxidant reversal of Abeta-induced cognitive deficits and neuropathology. Neurobiol Aging. 2001;22:993–1005. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(01)00300-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Kumar P, Padi SS, Naidu PS, Kumar A. Possible neuroprotective mechanisms of curcumin in attenuating 3-nitropropionic acid-induced neurotoxicity. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2007;29:19–25. doi: 10.1358/mf.2007.29.1.1063492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Nah SY, Kim DH, Rhim H. Ginsenosides: Are any of them candidates for drugs acting on central nervous system. CNS Drug Rev. 2007;13:381–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3458.2007.00023.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Lu JM, Yao Q, Chen C. Ginseng compounds: An update on their molecular mechanisms and medical applications. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2009;7:293–302. doi: 10.2174/157016109788340767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Liu CX, Xiao PG. Recent advances on ginseng research in China. J Ethnopharmacol. 1992;36:27–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-8741(92)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Rausch WD, Liu S, Gille G, Radad K. Neuroprotective effects of ginsenosides. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 2006;66:369–75. doi: 10.55782/ane-2006-1625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Radad K, Gille G, Liu L, Rausch WD. Use of ginseng in medicine with emphasis on neurodegenerative disorders. J Pharmacol Sci. 2006;100:175–86. doi: 10.1254/jphs.crj05010x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Keum YS, Park KK, Lee JM, Chun KS, Park JH, Lee SK, et al. Antioxidant and anti-tumor promoting activities of the methanol extract of heat-processed ginseng. Cancer Lett. 2000;13:41–8. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(99)00369-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Li X, Li SH. Effect of total saponins of Sanchi (Panax pseudoginseng notoginseng) on TNF, NO and its mechanisms. Zhong Cao Yao. 1999;30:514–7. [Google Scholar]
- 122.Kim YC, Kim SR, Markelonis GJ, Oh TH. Ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg3 protect cultured rat cortical cells from glutamate-induced neurodegeneration. J Neurosci Res. 1998;53:426–32. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19980815)53:4<426::AID-JNR4>3.0.CO;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Kim S, Ahn K, Oh TH, Nah SY, Rhim H. Inhibitory effect of ginsenosides on NMDA receptor-mediated signals in rat hippocampal neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;296:247–54. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(02)00870-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Lian XY, Zhang Z, Stringer JL. Protective effects of ginseng components in a rodent model of neurodegeneration. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:642–8. doi: 10.1002/ana.20450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Kim JH, Kim S, Yoon IS, Lee JH, Jang BJ, Jeong SM, et al. Protective effects of ginseng saponins on 3-nitropropionic acid-induced striatal degeneration in rats. Neuropharmacology. 2005;48:743–56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2004.12.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Wu J, Jeong HK, Bulin SE, Kwon SW, Park JH, Bezprozvanny I. Ginsenosides protect striatal neurons in cellular model of Huntington's disease. J Neurosci Res. 2009;87:1904–12. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Handa SS. Rasaayana Drugs Part-I. Pharm Times. 1993;25:9–15. [Google Scholar]
- 128.Veerendra Kumar MH, Gupta YK. Effect of different extracts of Centella asiatica on cognition and markers of oxidative stress in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2002;79:253–60. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(01)00394-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Wijeweera P, Arnason JT, Koszycki D, Merali Z. Evaluation of anxiolytic properties of Gotukola--(Centella asiatica) extracts and asiaticoside in rat behavioral models. Phytomedicine. 2006;13:668–76. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2006.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Soumyanath A, Zhong YP, Gold SA, Yu X, Koop DR, Bourdette D, et al. Centella asiatica accelerates nerve regeneration upon oral administration and contains multiple active fractions increasing neurite elongation in vitro. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2005;57:1221–9. doi: 10.1211/jpp.57.9.0018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Zainol MK, Abdul-Hamid A, Yusof S, Muse R. Antioxidative activity and total polyphenolic compounds of leaf, root and petiole of four accessions of Centella asiatica (L.) urban. Food Chem. 2003;81:575–81. [Google Scholar]
- 132.Hussin M, Hamid AA, Mohamad S, Saari N, Ismail M, Hair Bejo M. Protective effect of Centella asiatica extract and powder on oxidative stress in rats. Food Chem. 2007;100:535–41. [Google Scholar]
- 133.Singh B, Rastogi RP. A reinvestigation of the triterpenes of Centella asiatica. Phytochemistry. 1969;8:917–21. [Google Scholar]
- 134.Randriamampionona D, Diallo B, Rakotoniriana F, Rabemanantsoa C, Cheuk K, Corbisier AM, et al. Comparitive analysis of active constituents in Centella asiatica samples from Madagascar: Application for ex situ conservation and clonal propagation. Fitoterapia. 2007;78:482–9. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2007.03.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Singh B, Rastogi RP. Chemical examination of Centella asiatica Linn.-III. Phytochemistry. 1968;7:1385–93. [Google Scholar]
- 136.Asakawa Y, Mastuda R, Takemoto T. Monoterpenoids and sesqiterpenoids from Hydrocotyle and Centella species. Phytochemistry. 1982;21:2590–2. [Google Scholar]
- 137.Shinomol GK, Muralidhara Prophylactic neuroprotective property of Centella asiatica against 3-nitropropionic acid induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunctions in brain regions of prepubertal mice. Neurotoxicology. 2008;29:948–57. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2008.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Ren W, Qiao Z, Wang H, Zhu L, Zhang L. Flavonoids: Promising anticancer agents. Med Res Rev. 2003;23:519–34. doi: 10.1002/med.10033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Narayana KR, Reddy MS, Chaluvadi MR, Krishna DR. Bioflavonoids classification, pharmacological, biochemical effects and therapeutic potential. Indian J Pharmacol. 2001;33:2–16. [Google Scholar]
- 140.Bors W, Heller W, Michel C, Saran M. Flavonoids as antioxidants: Determination of radical-scavenging efficiencies. Methods Enzymol. 1990;186:343–55. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)86128-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Coleridge Smith PD, Thomas P, Scurr JH, Dormandy JA. Causes of various ulceration: A new hypothesis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988;296:1726–7. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6638.1726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Prior RL, Cao G, Prior RL, Cao G. Analysis of botanicals and dietary supplements for antioxidant capacity: A review. J AOAC Int. 2000;83:950–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Renugadevi J, Prabu SM. Naringenin protects against cadmium-induced oxidative renal dysfunction in rats. Toxicology. 2009;256:128–34. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2008.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Schroeter H, Boyd C, Spencer JP, Williams RJ, Cadenas E, Rice-Evans C. MAPK signaling in neurodegeneration: Influences of flavonoids and of nitric oxide. Neurobiol Aging. 2001;23:861–80. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(02)00075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Lopez-Lopez G, Moreno L, Cogolludo A, Galisteo M, Ibarra M, Duarte J, et al. Nitric oxide (NO) scavenging and NO protecting effects of quercetin and their biological significance in vascular smooth muscle. Mol Pharmacol. 2004;65:851–9. doi: 10.1124/mol.65.4.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Kumar P, Padi SS, Naidu PS, Kumar A. Cyclooxygenase inhibition attenuates 3-nitropropionic acid-induced neurotoxicity in rats: Possible antioxidant mechanisms. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2007;21:297–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2007.00485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Raso GM, Meli R, Di Carlo G, Pacilio M, Di Carlo R. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by flavonoids in macrophage J774A.1. Life Sci. 2001;68:921–31. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(00)00999-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Ishige K, Schubert D, Sagara Y. Flavonoids protect neuronal cells from oxidative stress by three distinct mechanisms. Free Radic Biol Med. 2001;30:433–46. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(00)00498-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Kumar P, Kumar A. Protective effect of hesperidin and naringin against 3-nitropropionic acid induced Huntington's like symptoms in rats: Possible role of nitric oxide. Behav Brain Res. 2010;206:38–46. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2009.08.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Kumar P, Kalonia H, Kumar A. Protective effect of sesamol against 3-nitropropionic acid-induced cognitive dysfunction and altered glutathione redox balance in rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010;107:577–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2010.00537.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Kumar P, Kumar A. Effect of lycopene and epigallocatechin-3-gallate against 3-nitropropionic acid induced cognitive dysfunction and glutathione depletion in rat: A novel nitric oxide mechanism. Food Chem Toxicol. 2009;47:2522–30. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2009.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Lagoa R, Lopez-Sanchez C, Samhan-Arias AK, Ganan CM, Garcia-Martinez V, Gutierrez-Merino C. Kaempferol protects against rat striatal degeneration induced by 3-nitropropionic acid. J Neurochem. 2009;111:473–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Kumar P, Kumar A. Protective effects of epigallocatechin gallate following 3-nitropropionic acid-induced brain damage: Possible nitric oxide mechanisms. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2009;207:257–70. doi: 10.1007/s00213-009-1652-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Allison AC, Cacabelos R, Lombardi VR, Alvarez XA, Vigo C. Celastrol, a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory drug, as a possible treatment for Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2001;25:1341–57. doi: 10.1016/s0278-5846(01)00192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Kim DH, Shin EK, Kim YH, Lee BW, Jun JG, Park JH, et al. Suppression of inflammatory responses by celastrol, a quinone methide triterpenoid isolated from Celastrus regelii. Eur J Clin Invest. 2009;39:819–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2009.02186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Lee JH, Choi KJ, Seo WD, Jang SY, Kim M, Lee BW, et al. Enhancement of radiation sensitivity in lung cancer cells by celastrol is mediated by inhibition of Hsp90. Int J Mol Med. 2011;27:441–6. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2011.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Avilla J, Teixido A, Velazquez C, Alvarenga N, Ferro E, Canela R. Insecticidal activity of Maytenus species (Celastraceae) nortriterpene quinone methides against codling moth, Cydia pomonella (L.) (Lepidoptera: tortricidae) J Agric Food Chem. 2000;48:88–92. doi: 10.1021/jf990008w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Cleren C, Calingasan NY, Chen J, Beal MF. Celastrol protects against MPTP- and 3-nitropropionic acid-induced neurotoxicity. J Neurochem. 2005;94:995–1004. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Zhang YQ, Sarge KD. Celastrol inhibits polyglutamine aggregation and toxicity though induction of the heat shock response. J Mol Med (Berl) 2007;85:1421–8. doi: 10.1007/s00109-007-0251-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Chen Q, Haddad GG. Role of trehalose phosphate synthase and trehalose during hypoxia: From flies to mammals. J Exp Biol. 2004;207:3125–9. doi: 10.1242/jeb.01133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Kandror O, Bretschneider N, Kreydin E, Cavalieri D, Goldberg AL. Yeast adapt to near-freezing temperatures by STRE/Msn2,4-dependent induction of trehalose synthesis and certain molecular chaperones. Mol Cell. 2004;13:771–81. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(04)00148-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Arora A, Ha C, Park CB. Inhibition of insulin amyloid formation by small stress molecules. FEBS Lett. 2004;564:121–5. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(04)00326-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Liu R, Barkhordarian H, Emadi S, Park CB, Sierks MR. Trehalose differentially inhibits aggregation and neurotoxicity of beta-amyloid 40 and 42. Neurobiol Dis. 2005;20:74–81. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2005.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Tanaka M, Machida Y, Niu S, Ikeda T, Jana NR, Doi H, et al. Trehalose alleviates polyglutamine-mediated pathology in a mouse model of Huntington disease. Nat Med. 2004;10:148–54. doi: 10.1038/nm985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Sarkar S, Davies JE, Huang Z, Tunnacliffe A, Rubinsztein DC. Trehalose, a novel mTOR-independent autophagy enhancer, accelerates the clearance of mutant huntingtin and alpha-synuclein. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:5641–52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M609532200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Visioli F, Riso P, Grande S, Galli C, Porrini M. Protective activity of tomato products on in vivo markers of lipid oxidation. Eur J Nutr. 2003;42:201–6. doi: 10.1007/s00394-003-0415-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Karahan I, Atessahin A, Yilmaz S, Ceribasi AO, Sakin F. Protective effect of lycopene on gentamicin-induced oxidative stress and nephrotoxicity in rats. Toxicology. 2005;215:198–204. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2005.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Tapiero H, Townsend DM, Tew KD. The role of carotenoids in the prevention of human pathologies. Biomed Pharmacother. 2004;58:100–10. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2003.12.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Hsiao G, Fong TH, Tzu NH, Lin KH, Chou DS, Sheu JR. A potent antioxidant, lycopene, affords neuroprotection against microglia activation and focal cerebral ischemia in rats. In Vivo. 2004;18:351–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Rafi MM, Yadav PN, Reyes M. Lycopene inhibits LPS-induced proinflammatory mediator inducible nitric oxide synthase in mouse macrophage cells. J Food Sci. 2007;72:S069–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2006.00219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Gunasekera RS, Sewgobind K, Desai S, Dunn L, Black HS, McKeehan WL, et al. Lycopene and lutein inhibit proliferation in rat prostate carcinoma cells. Nutr Cancer. 2007;58:171–7. doi: 10.1080/01635580701328339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Kuhad A, Sethi R, Chopra K. Lycopene attenuates diabetes-associated cognitive decline in rats. Life Sci. 2008;83:128–34. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2008.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Akbaraly NT, Faure H, Gourlet V, Favier A, Berr C. Plasma carotenoid levels and cognitive performance in an elderly population: Results of the EVA Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2007;62:308–16. doi: 10.1093/gerona/62.3.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Atessahin A, Yilmaz S, Karahan I, Ceribasi AO, Karaoglu A. Effects of lycopene against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats. Toxicology. 2005;212:116–23. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2005.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Kumar P, Kalonia H, Kumar A. Lycopene modulates nitric oxide pathways against 3-nitropropionic acid-induced neurotoxicity. Life Sci. 2009;85:711–8. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2009.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Sankar D, Sambandam G, Ramakrishna Rao M, Pugalendi KV. Modulation of blood pressure, lipid profiles and redox status in hypertensive patients taking different edible oils. Clin Chim Acta. 2005;355:97–104. doi: 10.1016/j.cccn.2004.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Baba NH, Antoniades K, Habbal Z. Effects of dietary canola, olive, and linolenic acid enriched olive oils on plasma lipids, lipid peroxidation and lipoprotein lipase activity in rats. Nutr Res. 1998;49:41–5. [Google Scholar]
- 178.Kapadia GJ, Azuine MA, Tokuda H, Takasaki M, Mukainaka T, Konoshima T, et al. Chemopreventive effect of resveratrol, sesamol, sesame oil and sunflower oil in the Epstein-Barr virus early antigen activation assay and the mouse skin two-stage carcinogenesis. Pharmacol Res. 2002;45:499–505. doi: 10.1006/phrs.2002.0992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Hsu DZ, Chen KT, Li YH, Chuang YC, Liu MY. Sesamol delays mortality and attenuates hepatic injury after cecal ligation and puncture in rats: Role of oxidative stress. Shock. 2006;25:528–32. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000209552.95839.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Kumar P, Kalonia H, Kumar A. Sesamol attenuate 3-nitropropionic acid-induced Huntington-like behavioral, biochemical, and cellular alterations in rats. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2009;11:439–50. doi: 10.1080/10286020902862194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Hsu DZ, Wan CH, Hsu HF, Lin YM, Liu MY. The prophylactic protective effect of sesamol against ferric-nitrilotriacetate-induced acute renal injury in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008;46:2736–41. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2008.04.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Hsu DZ, Chien SP, Chen KT, Liu MY. The effect of sesamol on systemic oxidative stress and hepatic dysfunction in acutely iron-intoxicated mice. Shock. 2007;28:596–601. doi: 10.1097/shk.0b013e31804d4474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


