Abstract
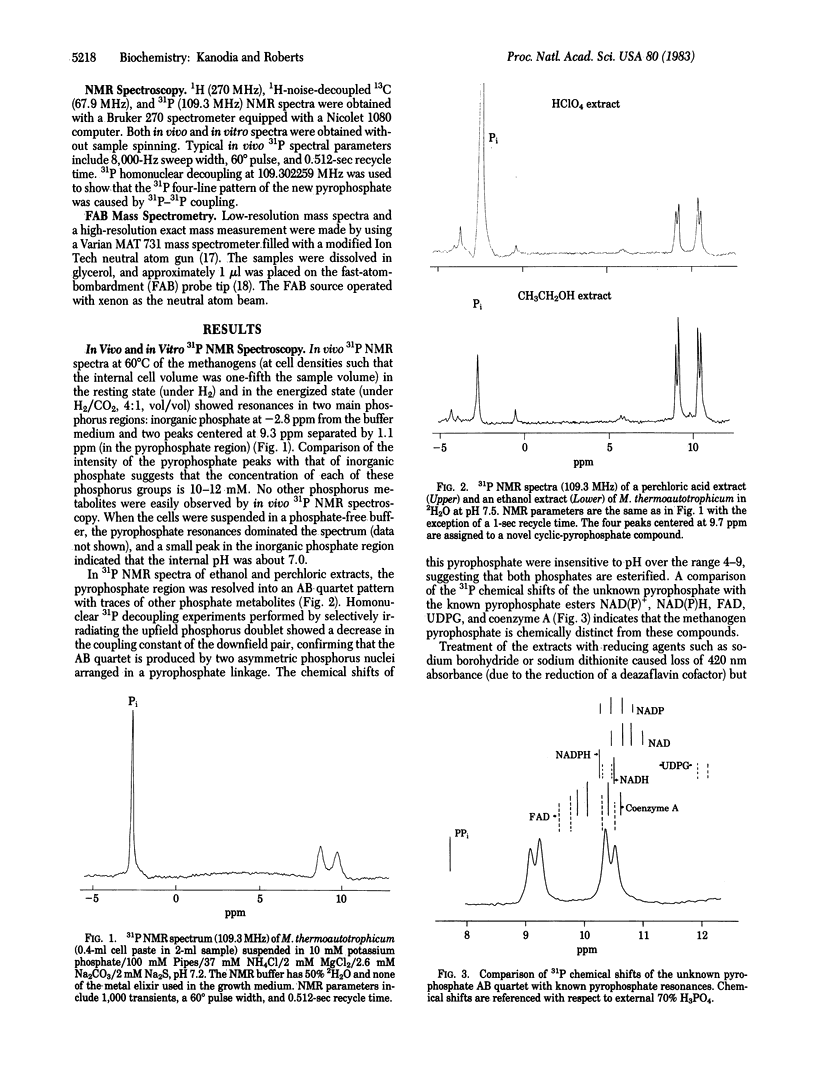
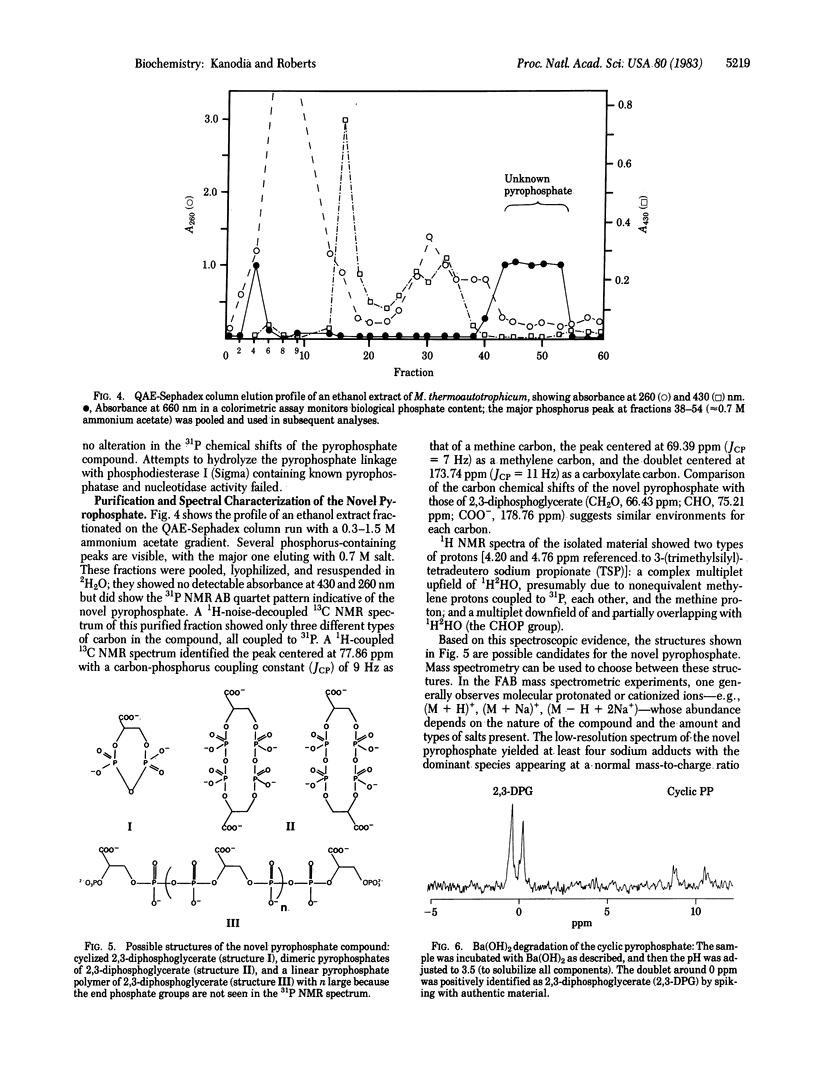
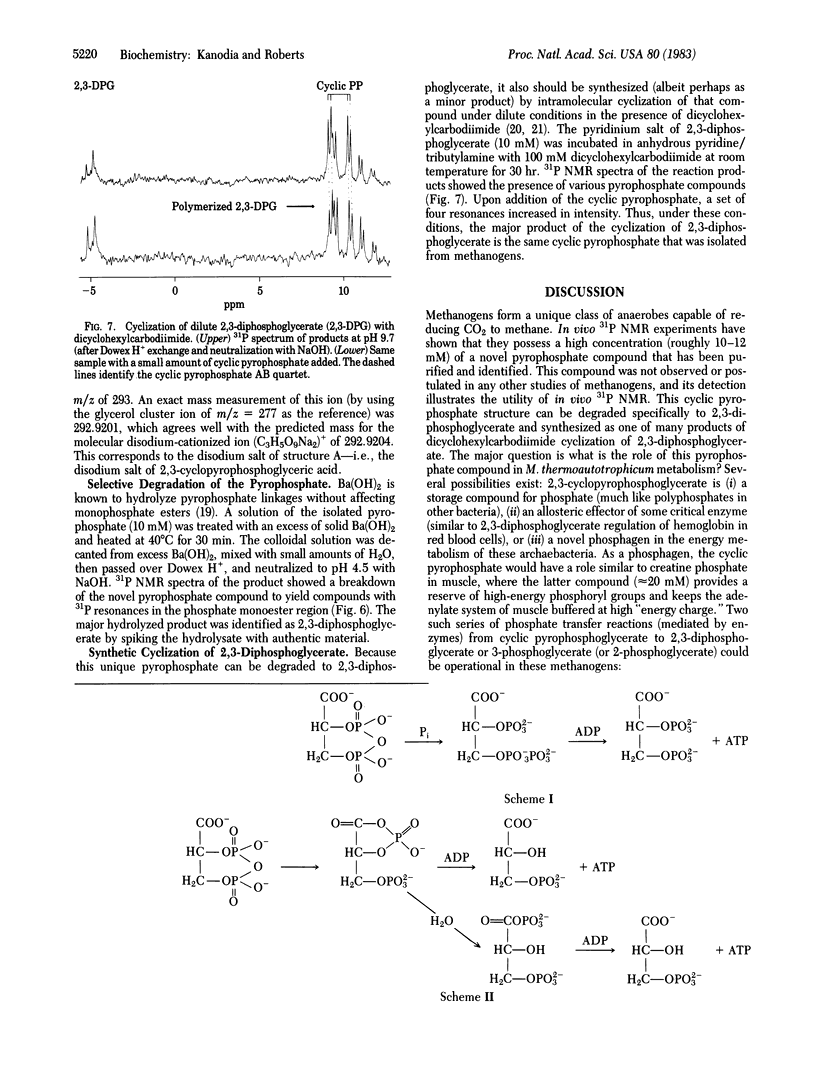
A unique cyclic pyrophosphate compound has been detected at 10-12 mM intracellular concentration in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum by in vivo31P NMR. This compound has been extracted from cells and purified by anion-exchange chromatography. Studies with 1H, 13C, and 31P NMR and fast-atom-bombardment mass spectrometry have identified it as 2,3-cyclopyrophosphoglycerate, an intramolecularly cyclized pyrophosphate of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate. Chemical degradation to 2,3-diphosphoglycerate and synthesis by dicyclohexylcarbodiimide coupling of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate are consistent with this identification. It is suggested that this compound serves as a primary phosphagen in methanogens.
Keywords: methanogens; 31P NMR; 2,3-cyclopyrophosphoglycerate; phosphagen
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burt C. T., Cohen S. M., Bárány M. Analysis with intact tissue with 31P NMR. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1979;8:1–25. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.08.060179.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt C. T., Glonek T., Bárány M. Phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance detection of unexpected phosphodiesters in muscle. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4850–4853. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadian D. G., Radda G. K. NMR studies of tissue metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:69–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies R. J., Ugurbil K., den Hollander J. A., Shulman R. G. 31P NMR studies of intracellular pH and phosphate metabolism during cell division cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2125–2129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASHIMOTO T., YOSHIKAWA H. Further studies on adenylyl 2, 3-diphosphoglyceric acid. J Biochem. 1963 Mar;53:219–226. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon G., Ogawa S., Shulman R. G., Yamane T. High-resolution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance studies of metabolism in aerobic Escherichia coli cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):888–891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon G., Shulman R. G., Yamane T., Eccleshall T. R., Lam K. B., Baronofsky J. J., Marmur J. Phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of wild-type and glycolytic pathway mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4487–4499. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuccitelli R., Webb D. J., Lagier S. T., Matson G. B. 31P NMR reveals increased intracellular pH after fertilization in Xenopus eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4421–4425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salhany J. M., Yamane T., Shulman R. G., Ogawa S. High resolution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance studies of intact yeast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4966–4970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. D., Rouser G. Precise quantitative determination of human blood lipids by thin-layer and triethylaminoethylcellulose column chromatography. II. Plasma lipids. Anal Biochem. 1970 Dec;38(2):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugurbil K., Rottenberg H., Glynn P., Shulman R. G. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance studies of bioenergetics and glycolysis in anaerobic Escherichia coli cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2244–2248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Magrum L. J., Fox G. E. Archaebacteria. J Mol Evol. 1978 Aug 2;11(3):245–251. doi: 10.1007/BF01734485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Wolfe R. S. Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicus sp. n., an anaerobic, autotrophic, extreme thermophile. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):707–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.707-713.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


