Abstract
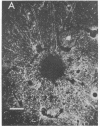
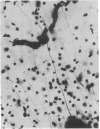
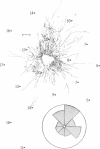
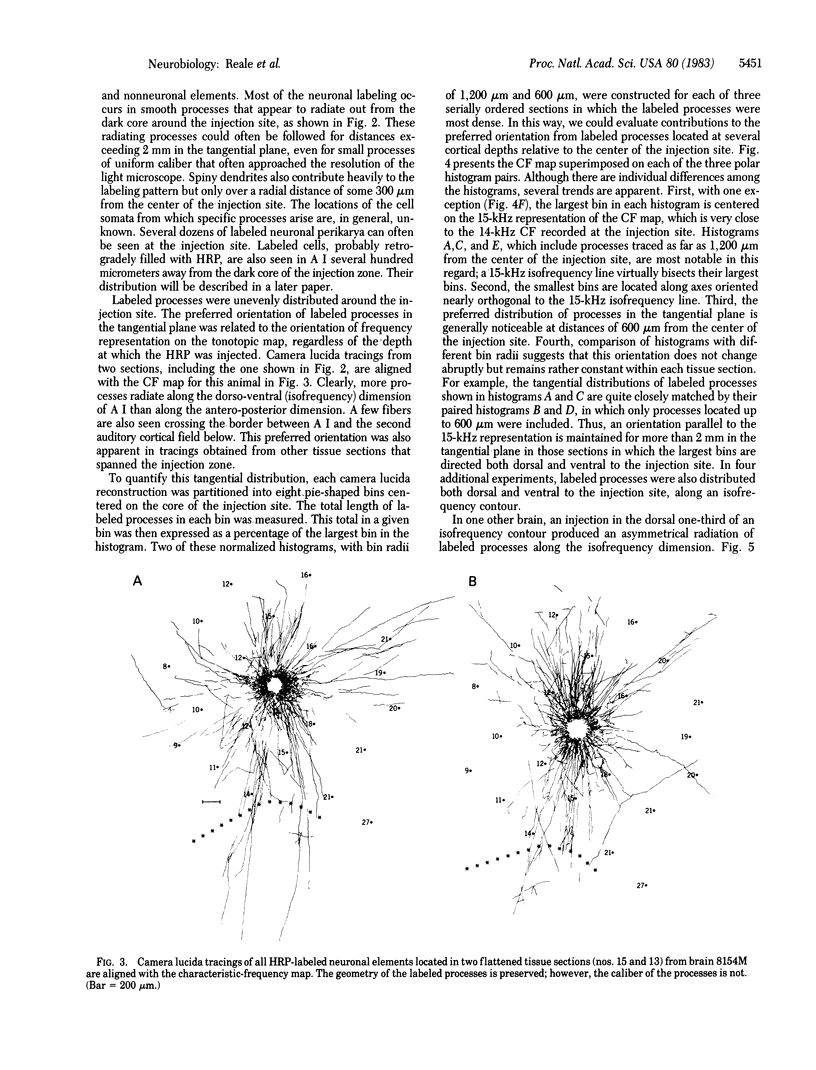
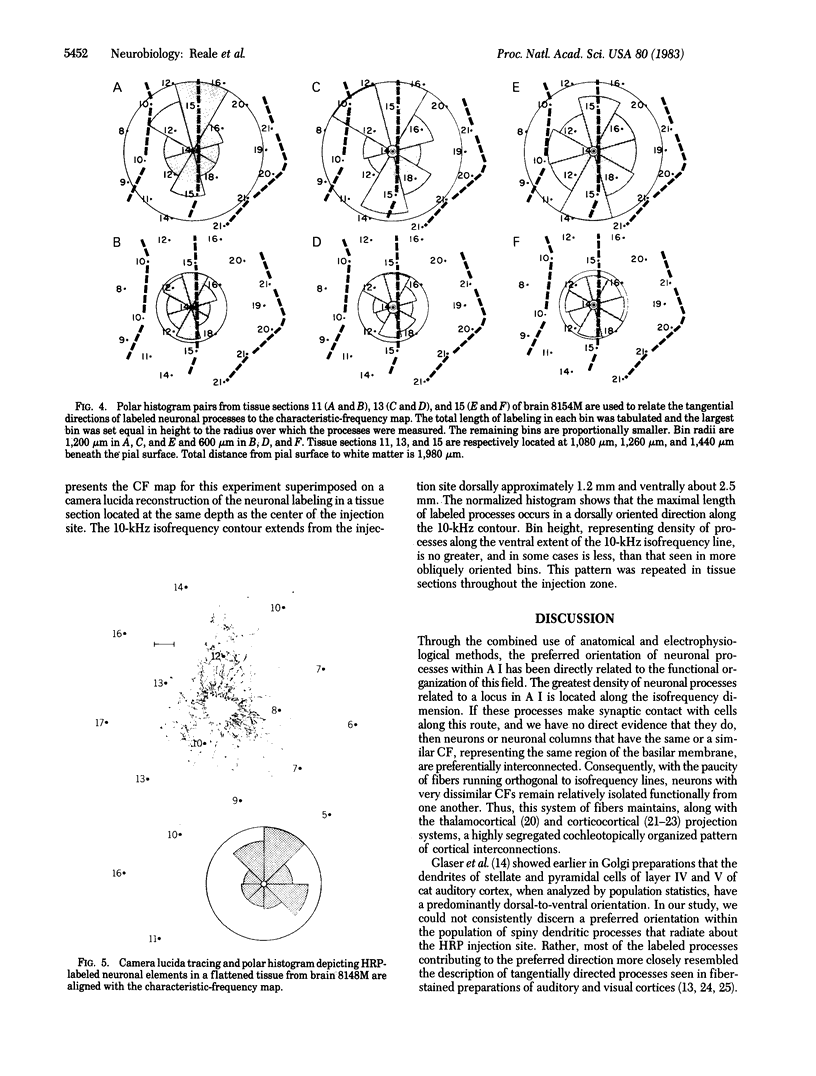
Microelectrode mapping and horseradish peroxidase oxidase histochemistry were combined to study the relationship between the characteristic-frequency representation and the intrinsic connectivity of the primary auditory cortex in the cat. Small extracellular iontophoretic injections of horseradish peroxidase within the characteristic-frequency map resulted in labeling of neuronal processes that, in the tangential plane, radiated out asymmetrically from the injection site over distances of several millimeters. The heaviest concentration of labeled fibers was along an axis parallel with the orientation of the isofrequency line within which the injection had been made. Thus, primary field neurons that have the same or a similar characteristic frequency have the potential of being preferentially interconnected.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. C. Technical considerations on the use of horseradish peroxidase as a neuronal marker. Neuroscience. 1977;2(1):141–145. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitkin L. M., Anderson D. J., Brugge J. F. Tonotopic organization and discharge characteristics of single neurons in nuclei of the lateral lemniscus of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1970 May;33(3):421–440. doi: 10.1152/jn.1970.33.3.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen R. A., Snyder R. L., Merzenich M. M. The topographic organization of corticocollicular projections from physiologically identified loci in the AI, AII, and anterior auditory cortical fields of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Jun;191(3):479–494. doi: 10.1002/cne.901910310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asanuma H., Rosén I. Spread of mono- and polysynaptic connections within cat's motor cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1973 Mar 19;16(5):507–520. doi: 10.1007/BF00234477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLONNIER M. THE TANGENTIAL ORGANIZATION OF THE VISUAL CORTEX. J Anat. 1964 Jul;98:327–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonnier M., Sas E. An anterograde degeneration study of the tangential spread of axons in cortical areas 17 and 18 of the squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus). J Comp Neurol. 1978 May 15;179(2):245–262. doi: 10.1002/cne.901790202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykes R. W. The anatomy and physiology of the somatic sensory cortical regions. Prog Neurobiol. 1978;10(1):33–88. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(78)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisken R. A., Garey L. J., Powell T. P. Patterns of degeneration after intrinsic lesions of the visual cortex (area 17) of the monkey. Brain Res. 1973 Apr 13;53(1):208–213. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90782-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatter K. C., Sloper J. J., Powell T. P. The intrinsic connections of the cortex of area 4 of the monkey. Brain. 1978 Sep;101(3):513–541. doi: 10.1093/brain/101.3.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert C. D., Wiesel T. N. Clustered intrinsic connections in cat visual cortex. J Neurosci. 1983 May;3(5):1116–1133. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-05-01116.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser E. M., Van der Loos H., Gissler M. Tangential orientation and spatial order in dendrites of cat auditory cortex: a computer microscope study of Golgi-impregnated material. Exp Brain Res. 1979 Aug 1;36(3):411–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00238513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein M. H., Jr, Abeles M., Daly R. L., McIntosh J. Functional architecture in cat primary auditory cortex: tonotopic organization. J Neurophysiol. 1970 Jan;33(1):188–197. doi: 10.1152/jn.1970.33.1.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imig T. J., Adrián H. O. Binaural columns in the primary field (A1) of cat auditory cortex. Brain Res. 1977 Dec 16;138(2):241–257. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90743-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imig T. J., Brugge J. F. Sources and terminations of callosal axons related to binaural and frequency maps in primary auditory cortex of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Dec 15;182(4):637–660. doi: 10.1002/cne.901820406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imig T. J., Reale R. A. Ipsilateral corticocortical projections related to binaural columns in cat primary auditory cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Nov 20;203(1):1–14. doi: 10.1002/cne.902030102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imig T. J., Reale R. A. Patterns of cortico-cortical connections related to tonotopic maps in cat auditory cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Jul 15;192(2):293–332. doi: 10.1002/cne.901920208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imig T. J., Ruggero M. A., Kitzes L. M., Javel E., Brugge J. F. Organization of auditory cortex in the owl monkey (Aotus trivirgatus). J Comp Neurol. 1977 Jan 1;171(1):111–128. doi: 10.1002/cne.901710108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaVail J. H., LaVail M. M. The retrograde intraaxonal transport of horseradish peroxidase in the chick visual system: a light and electron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol. 1974 Oct 1;157(3):303–357. doi: 10.1002/cne.901570304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merzenich M. M., Brugge J. F. Representation of the cochlear partition of the superior temporal plane of the macaque monkey. Brain Res. 1973 Feb 28;50(2):275–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90731-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merzenich M. M., Kaas J. H., Roth G. L. Auditory cortex in the grey squirrel: tonotopic organization and architectonic fields. J Comp Neurol. 1976 Apr 15;166(4):387–401. doi: 10.1002/cne.901660402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merzenich M. M., Knight P. L., Roth G. L. Representation of cochlea within primary auditory cortex in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1975 Mar;38(2):231–249. doi: 10.1152/jn.1975.38.2.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrooks J. C., Dykes R. W., Merzenich M. M. Binaural response-specific bands in primary auditory cortex (AI) of the cat: topographical organization orthogonal to isofrequency contours. Brain Res. 1980 Jan 6;181(1):31–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91257-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison G., Crick F. Long axons within the striate cortex: their distribution, orientation, and patterns of connection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3661–3665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. P., Irvine D. R. Responses of single neurons in physiologically defined primary auditory cortex (AI) of the cat: frequency tuning and responses to intensity. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Jan;45(1):48–58. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reale R. A., Imig T. J. Tonotopic organization in auditory cortex of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Jul 15;192(2):265–291. doi: 10.1002/cne.901920207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockland K. S., Lund J. S. Widespread periodic intrinsic connections in the tree shrew visual cortex. Science. 1982 Mar 19;215(4539):1532–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.7063863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosene D. L., Mesulam M. M. Fixation variables in horseradish peroxidase neurohistochemistry. I. The effect of fixation time and perfusion procedures upon enzyme activity. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Jan;26(1):28–39. doi: 10.1177/26.1.413864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUNTURI A. R. Physiological determination of the arrangement of the afferent connections to the middle ectosylvian auditory area in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1950 Sep;162(3):489–502. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1950.162.3.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong W. C. The tangential organization of dendrites and axons in three auditory areas of the cat's cerebral cortex. J Anat. 1967 Jun;101(Pt 3):419–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]