Abstract
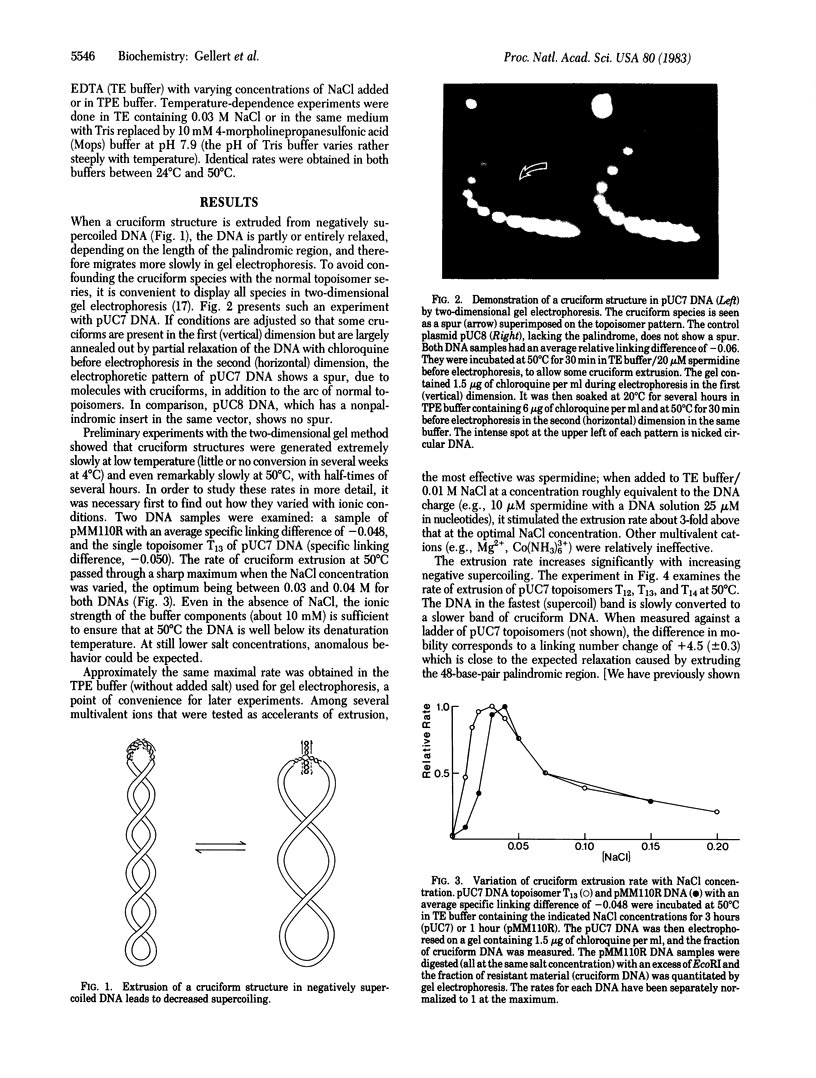
Extrusion of cruciform structures in self-complementary regions of DNA is known to be favored by negative supercoiling of DNA. We show here that, in moderately supercoiled DNA, cruciform extrusion is a very slow process. In plasmid pUC7 DNA, with a 48-base-pair palindrome, the half-time of extrusion at 50 degrees C is typically several hours; rates are even slower at lower temperature. The rates increase significantly with increasing DNA supercoiling but are only slightly faster in DNA species with much longer palindromes. The reabsorption of cruciform arms is also very slow. The equilibrium between cruciform and regular DNA structures is sensitive to changes in the linking number. Measurement of this equilibrium leads to an estimate of 18 kcal/mol (75.3 kJ/mol) for the free energy required to generate a cruciform structure. In bacterial cells, cruciform DNA may be rare, even when it is thermodynamically favored, because of its slow formation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer W. R. Structure and reactions of closed duplex DNA. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:287–313. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.001443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. J. Stable cruciform formation at inverted repeat sequences in supercoiled DNA. Biopolymers. 1982 Mar;21(3):679–696. doi: 10.1002/bip.360210314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Felsenfeld G. Supercoiling energy and nucleosome formation: the role of the arginine-rich histone kernel. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1159–1181. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1159-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. Instability of palindromic DNA in Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):409–416. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depew D. E., Wang J. C. Conformational fluctuations of DNA helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Ohmori H., Tomizawa J. DNA gyrase and DNA supercoiling. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):35–40. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh T. S., Wang J. C. Thermodynamic properties of superhelical DNAs. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 11;14(3):527–535. doi: 10.1021/bi00674a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Determination of the number of superhelical turns in simian virus 40 DNA by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper B., Garabett M. Studies on T4-head maturation. 1. Purification and characterization of gene-49-controlled endonuclease. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar 16;115(1):123–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Mizusawa H., Kakefuda T. Unwinding of double-stranded DNA helix by dehydration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2838–2842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. In vivo consequences of plasmid topology. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):380–382. doi: 10.1038/292380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. The inverted repeat as a recognizable structural feature in supercoiled DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6468–6472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Fisher L. M., O'Dea M. H., Gellert M. DNA gyrase action involves the introduction of transient double-strand breaks into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1847–1851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Kemper B., Hays J., Weisberg R. A. T4 endonuclease VII cleaves holliday structures. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Mizuuchi M., Gellert M. Cruciform structures in palindromic DNA are favored by DNA supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 5;156(2):229–243. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Wells R. D. Cruciform structures in supercoiled DNA. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):466–470. doi: 10.1038/289466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt J. R. POSSIBLE SEPARATION OF INTERTWINED NUCLEIC ACID CHAINS BY TRANSFER-TWIST. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1955 Mar 15;41(3):181–183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.41.3.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Shure M., Tang D., Vinograd J., Vosberg H. P. Action of nicking-closing enzyme on supercoiled and nonsupercoiled closed circular DNA: formation of a Boltzmann distribution of topological isomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4280–4284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler J. R., Tecklenburg M., Betz J. L. Plasmids containing many tandem copies of a synthetic lactose operator. Gene. 1980 Feb;8(3):279–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakakibara Y., Tomizawa J. I. Replication of colicin E1 plasmid DNA in cell extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):802–806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Pulleyblank D. E., Vinograd J. The problems of eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA packaging and in vivo conformation posed by superhelix density heterogeneity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1183–1205. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden R. R., Broyles S. S., Pettijohn D. E. Perfect palindromic lac operator DNA sequence exists as a stable cruciform structure in supercoiled DNA in vitro but not in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1797–1801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton C. K., Wells R. D. Relationship between superhelical density and cruciform formation in plasmid pVH51. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6292–6295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vologodskii A. V., Lukashin A. V., Anshelevich V. V., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Fluctuations in superhelical DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Mar;6(3):967–982. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.3.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]