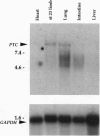
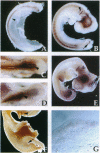
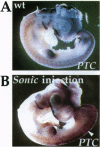
Abstract
Ventral cell fates in the central nervous system are induced by Sonic hedgehog, a homolog of hedgehog, a secreted Drosophila protein. In the central nervous system, Sonic hedgehog has been identified as the signal inducing floor plate, motor neurons, and dopaminergic neurons. Sonic hedgehog is also involved in the induction of ventral cell type in the developing somites. ptc is a key gene in the Drosophila hedgehog signaling pathway where it is involved in transducing the hedgehog signal and is also a transcriptional target of the signal. PTC, a vertebrate homolog of this Drosophila gene, is genetically downstream of Sonic hedgehog (Shh) in the limb bud. We analyze PTC expression during chicken neural and somite development and find it expressed in all regions of these tissues known to be responsive to Sonic hedgehog signal. As in the limb bud, ectopic expression of Sonic hedgehog leads to ectopic induction of PTC in the neural tube and paraxial mesoderm. This conservation of regulation allows us to use PTC as a marker for Sonic hedgehog response. The pattern of PTC expression suggests that Sonic hedgehog may play an inductive role in more dorsal regions of the neural tube than have been previously demonstrated. Examination of the pattern of PTC expression also suggests that PTC may act in a negative feedback loop to attenuate hedgehog signaling.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basler K., Edlund T., Jessell T. M., Yamada T. Control of cell pattern in the neural tube: regulation of cell differentiation by dorsalin-1, a novel TGF beta family member. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):687–702. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90249-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basler K., Struhl G. Compartment boundaries and the control of Drosophila limb pattern by hedgehog protein. Nature. 1994 Mar 17;368(6468):208–214. doi: 10.1038/368208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand-Saberi B., Ebensperger C., Wilting J., Balling R., Christ B. The ventralizing effect of the notochord on somite differentiation in chick embryos. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1993 Sep;188(3):239–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00188215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bumcrot D. A., Takada R., McMahon A. P. Proteolytic processing yields two secreted forms of sonic hedgehog. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;15(4):2294–2303. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.4.2294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capdevila J., Estrada M. P., Sánchez-Herrero E., Guerrero I. The Drosophila segment polarity gene patched interacts with decapentaplegic in wing development. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):71–82. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06236.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capdevila J., Guerrero I. Targeted expression of the signaling molecule decapentaplegic induces pattern duplications and growth alterations in Drosophila wings. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 3;13(19):4459–4468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06768.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. T., López A., von Kessler D. P., Chiang C., Simandl B. K., Zhao R., Seldin M. F., Fallon J. F., Beachy P. A. Products, genetic linkage and limb patterning activity of a murine hedgehog gene. Development. 1994 Nov;120(11):3339–3353. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.11.3339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echelard Y., Epstein D. J., St-Jacques B., Shen L., Mohler J., McMahon J. A., McMahon A. P. Sonic hedgehog, a member of a family of putative signaling molecules, is implicated in the regulation of CNS polarity. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1417–1430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90627-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Tessier-Lavigne M. Patterning of mammalian somites by surface ectoderm and notochord: evidence for sclerotome induction by a hedgehog homolog. Cell. 1994 Dec 30;79(7):1175–1186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekete D. M., Cepko C. L. Replication-competent retroviral vectors encoding alkaline phosphatase reveal spatial restriction of viral gene expression/transduction in the chick embryo. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2604–2613. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich L. V., Johnson R. L., Milenkovic L., McMahon J. A., Scott M. P. Conservation of the hedgehog/patched signaling pathway from flies to mice: induction of a mouse patched gene by Hedgehog. Genes Dev. 1996 Feb 1;10(3):301–312. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.3.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heemskerk J., DiNardo S. Drosophila hedgehog acts as a morphogen in cellular patterning. Cell. 1994 Feb 11;76(3):449–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo A., Ingham P. Cell patterning in the Drosophila segment: spatial regulation of the segment polarity gene patched. Development. 1990 Sep;110(1):291–301. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.1.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper J. E., Scott M. P. The Drosophila patched gene encodes a putative membrane protein required for segmental patterning. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):751–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M., Porter J. A., Chiang C., Chang D., Tessier-Lavigne M., Beachy P. A., Rosenthal A. Induction of midbrain dopaminergic neurons by Sonic hedgehog. Neuron. 1995 Jul;15(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W. Localized hedgehog activity controls spatial limits of wingless transcription in the Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):560–562. doi: 10.1038/366560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W., Taylor A. M., Nakano Y. Role of the Drosophila patched gene in positional signalling. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):184–187. doi: 10.1038/353184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. L., Grenier J. K., Scott M. P. patched overexpression alters wing disc size and pattern: transcriptional and post-transcriptional effects on hedgehog targets. Development. 1995 Dec;121(12):4161–4170. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.12.4161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. L., Laufer E., Riddle R. D., Tabin C. Ectopic expression of Sonic hedgehog alters dorsal-ventral patterning of somites. Cell. 1994 Dec 30;79(7):1165–1173. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. L., Tabin C. The long and short of hedgehog signaling. Cell. 1995 May 5;81(3):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90381-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss S., Concordet J. P., Ingham P. W. A functionally conserved homolog of the Drosophila segment polarity gene hh is expressed in tissues with polarizing activity in zebrafish embryos. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1431–1444. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90628-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. J., von Kessler D. P., Parks S., Beachy P. A. Secretion and localized transcription suggest a role in positional signaling for products of the segmentation gene hedgehog. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):33–50. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90264-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marigo V., Scott M. P., Johnson R. L., Goodrich L. V., Tabin C. J. Conservation in hedgehog signaling: induction of a chicken patched homolog by Sonic hedgehog in the developing limb. Development. 1996 Apr;122(4):1225–1233. doi: 10.1242/dev.122.4.1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martí E., Bumcrot D. A., Takada R., McMahon A. P. Requirement of 19K form of Sonic hedgehog for induction of distinct ventral cell types in CNS explants. Nature. 1995 May 25;375(6529):322–325. doi: 10.1038/375322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martí E., Takada R., Bumcrot D. A., Sasaki H., McMahon A. P. Distribution of Sonic hedgehog peptides in the developing chick and mouse embryo. Development. 1995 Aug;121(8):2537–2547. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.8.2537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano Y., Guerrero I., Hidalgo A., Taylor A., Whittle J. R., Ingham P. W. A protein with several possible membrane-spanning domains encoded by the Drosophila segment polarity gene patched. Nature. 1989 Oct 12;341(6242):508–513. doi: 10.1038/341508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohno T., Kawakami Y., Ohuchi H., Fujiwara A., Yoshioka H., Noji S. Involvement of the Sonic hedgehog gene in chick feather formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Jan 5;206(1):33–39. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Placzek M., Jessell T. M., Dodd J. Induction of floor plate differentiation by contact-dependent, homeogenetic signals. Development. 1993 Jan;117(1):205–218. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.1.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pourquié O., Coltey M., Teillet M. A., Ordahl C., Le Douarin N. M. Control of dorsoventral patterning of somitic derivatives by notochord and floor plate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5242–5246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle R. D., Johnson R. L., Laufer E., Tabin C. Sonic hedgehog mediates the polarizing activity of the ZPA. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1401–1416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90626-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelink H., Augsburger A., Heemskerk J., Korzh V., Norlin S., Ruiz i Altaba A., Tanabe Y., Placzek M., Edlund T., Jessell T. M. Floor plate and motor neuron induction by vhh-1, a vertebrate homolog of hedgehog expressed by the notochord. Cell. 1994 Feb 25;76(4):761–775. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90514-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelink H., Porter J. A., Chiang C., Tanabe Y., Chang D. T., Beachy P. A., Jessell T. M. Floor plate and motor neuron induction by different concentrations of the amino-terminal cleavage product of sonic hedgehog autoproteolysis. Cell. 1995 May 5;81(3):445–455. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90397-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanicola M., Sekelsky J., Elson S., Gelbart W. M. Drawing a stripe in Drosophila imaginal disks: negative regulation of decapentaplegic and patched expression by engrailed. Genetics. 1995 Feb;139(2):745–756. doi: 10.1093/genetics/139.2.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabata T., Kornberg T. B. Hedgehog is a signaling protein with a key role in patterning Drosophila imaginal discs. Cell. 1994 Jan 14;76(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe Y., Roelink H., Jessell T. M. Induction of motor neurons by Sonic hedgehog is independent of floor plate differentiation. Curr Biol. 1995 Jun 1;5(6):651–658. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. M., Nakano Y., Mohler J., Ingham P. W. Contrasting distributions of patched and hedgehog proteins in the Drosophila embryo. Mech Dev. 1993 Jul;42(1-2):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. Z., Jin P., Bumcrot D. A., Marigo V., McMahon A. P., Wang E. A., Woolf T., Pang K. Induction of dopaminergic neuron phenotype in the midbrain by Sonic hedgehog protein. Nat Med. 1995 Nov;1(11):1184–1188. doi: 10.1038/nm1195-1184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Pfaff S. L., Edlund T., Jessell T. M. Control of cell pattern in the neural tube: motor neuron induction by diffusible factors from notochord and floor plate. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):673–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90248-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Placzek M., Tanaka H., Dodd J., Jessell T. M. Control of cell pattern in the developing nervous system: polarizing activity of the floor plate and notochord. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):635–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90247-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]