Abstract
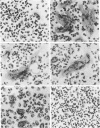
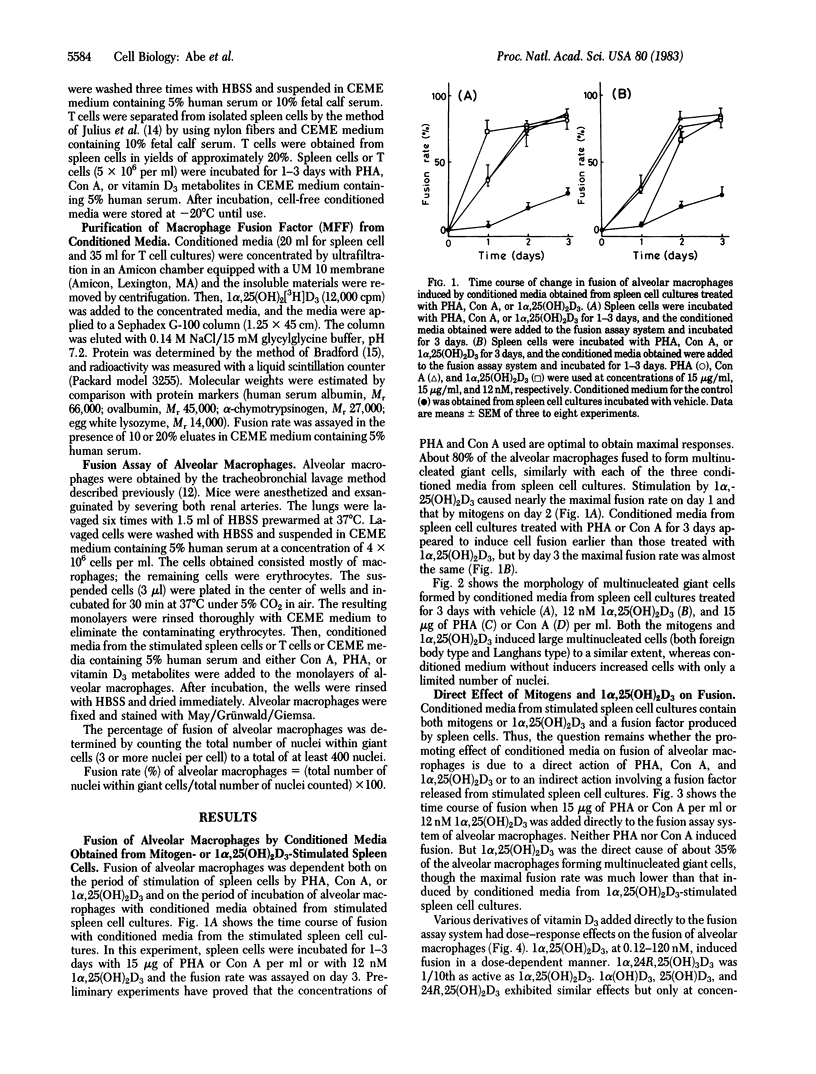
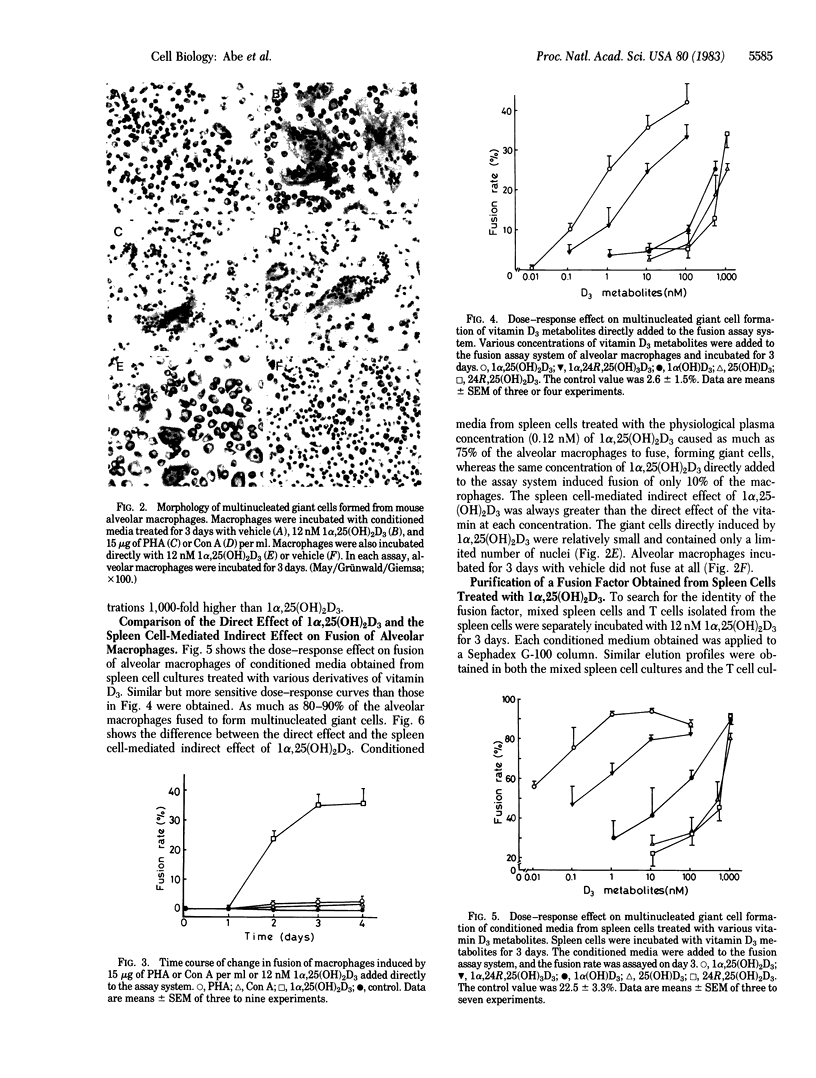
Extensive fusion was induced in mouse alveolar macrophages by treatment with conditioned media obtained from spleen cell cultures treated with 15 micrograms of phytohemagglutinin or concanavalin A per ml or with 12 nM 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1 alpha,25(OH)2D3]. The fusion rate was 80-90% on day 3. In addition, 1 alpha,25(OH)2D3 added directly to alveolar macrophages induced fusion of about 35% of the cells on day 3, whereas direct addition of phytohemagglutinin and concanavalin A did not enhance fusion at all. When conditioned media from spleen cell or T cell cultures treated with 12 nM 1 alpha,25(OH)2D3 were applied to a Sephadex G-100 column, a fusion factor (Mr 37,000-70,000) could be separated from 1 alpha,25(OH)2D3. 1 alpha,25(OH)2D3 induced fusion at 0.012-120 nM in a dose-dependent manner both by direct action and by spleen cell-mediated indirect action, but the fusion rate was always much greater in the latter than in the former at each concentration of the vitamin. Of the vitamin D3 derivatives tested, 1 alpha,25(OH)2D3 was the most potent, followed successively by 1 alpha,24R,25-trihydroxyvitamin D3, 1 alpha-hydroxyvitamin D3, 25-hydroxyvitamin D3, and 24R,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. These results clearly indicate that 1 alpha,25(OH)2D3 induces fusion of mouse alveolar macrophages by both a direct and an indirect mechanism, the latter mediated by spleen cells, probably by T cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe E., Miyaura C., Sakagami H., Takeda M., Konno K., Yamazaki T., Yoshiki S., Suda T. Differentiation of mouse myeloid leukemia cells induced by 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4990–4994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. O. The granulomatous inflammatory response. A review. Am J Pathol. 1976 Jul;84(1):164–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumbaugh P. F., Haussler M. R. 1 Alpha,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol receptors in intestine. I. Association of 1 alpha,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol with intestinal mucosa chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1251–1257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger E. H., Van der Meer J. W., van de Gevel J. S., Gribnau J. C., Thesingh G. W., van Furth R. In vitro formation of osteoclasts from long-term cultures of bone marrow mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1604–1614. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLSSON A. Tracer experiments on the effect of vitamin D on the skeletal metabolism of calcium and phosphorus. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952 Sep 10;26(2-3):212–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1952.tb00904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J. Multinucleate giant cells. J Pathol. 1978 Nov;126(3):125–148. doi: 10.1002/path.1711260302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P., Trummel C., Horton J., Baker J. J., Oppenheim J. J. Production of osteoclast-activating factor by normal human peripheral blood rosetting and nonrosetting lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Oct;6(10):732–736. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830061014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca H. F., Schnoes H. K. Metabolism and mechanism of action of vitamin D. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:631–666. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez J. H., Mundy G. R. Monocytes mediate osteoclastic bone resorption by prostaglandin production. Calcif Tissue Int. 1980;31(1):29–34. doi: 10.1007/BF02407164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galindo B., Lazdins J., Castillo R. Fusion of normal rabbit alveolar macrophages induced by supernatant fluids from BCG-sensitized lymph node cells after elicitation by antigen. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):212–216. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.212-216.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A. J., Simmons D. J. Investigation of cell lineage in bone using a chimaera of chick and quial embryonic tissue. Nature. 1975 Nov 27;258(5533):325–327. doi: 10.1038/258325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A. J., Stewart C. C., Teitelbaum S. L. Contact-mediated bone resorption by human monocytes in vitro. Science. 1978 Mar 3;199(4332):988–990. doi: 10.1126/science.622581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasukabe T., Honma Y., Hozumi M. Induction of lysosomal enzyme activities with glucocorticoids during differentiation of cultured mouse myeloid leukemia cells. Gan. 1977 Dec;68(6):765–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko J. S., Bernard G. W. Osteoclast formation in vitro from bone marrow mononuclear cells in osteoclast-free bone. Am J Anat. 1981 Aug;161(4):415–425. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001610407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luben R. A., Mundy G. R., Trummel C. L., Raisz L. G. Partial purification of osteoclast-activating factor from phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1473–1480. doi: 10.1172/JCI107696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundy G. R., Luben R. A., Raisz L. G., Oppenheim J. J., Buell D. N. Bone-resorbing activity in supernatants from lymphoid cell lines. N Engl J Med. 1974 Apr 18;290(16):867–871. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197404182901601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundy G. R., Raisz L. G., Shapiro J. L., Bandelin J. G., Turcotte R. J. Big and little forms of osteoclast activating factor. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):122–128. doi: 10.1172/JCI108748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Remold H. G., David J. R. Characterization of a lymphocyte factor which alters macrophage functions. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):275–290. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks D. E., Weiser R. S. The role of phagocytosis and natural lymphokines in the fusion of alveolar macrophages to form Langhans giant cells. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1975 Apr;17(4):219–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Jackson B. K., Beachey E. H., Kang A. H. Formation of multinucleated giant cells from human monocyte precursors. Mediation by a soluble protein from antigen-and mitogen-stimulated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):168–178. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raisz L. G., Trummel C. L., Holick M. F., DeLuca H. F. 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol: a potent stimulator of bone resorption in tissue culture. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):768–769. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold H. G., David R. A., David J. R. Characterization of migration inhibitory factor (MIF) from guinea pig lymphocytes stimulated with concanavalin A. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):578–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold H. G., Mednis A. D. Two migration inhibitory factors with different chromatographic behavior and isoelectric points. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2015–2019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiina Y., Abe E., Miyaura C., Tanaka H., Yamada S., Ohmori M., Nakayama K., Takayama H., Matsunaga I., Nishii Y. Biological activity of 24,24-difluoro-1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-26,23-lactone in inducing differentiation of human myeloid leukemia cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jan;220(1):90–94. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone S., Bucana C., Hoyer L. C., Fidler I. J. Kinetics and ultrastructural studies of the induction of rat alveolar macrophage fusion by mediators released from mitogen-stimulated lymphocytes. Am J Pathol. 1981 May;103(2):234–246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka H., Abe E., Miyaura C., Kuribayashi T., Konno K., Nishii Y., Suda T. 1 alpha,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol and a human myeloid leukaemia cell line (HL-60). Biochem J. 1982 Jun 15;204(3):713–719. doi: 10.1042/bj2040713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada S., Ohmori M., Takayama H., Takasaki Y., Suda T. Isolation and identification of 1 alpha- and 23-hydroxylated metabolites of 25-hydroxy-24-oxovitamin D3 from in vitro incubates of chick kidney homogenates. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):457–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]