Abstract
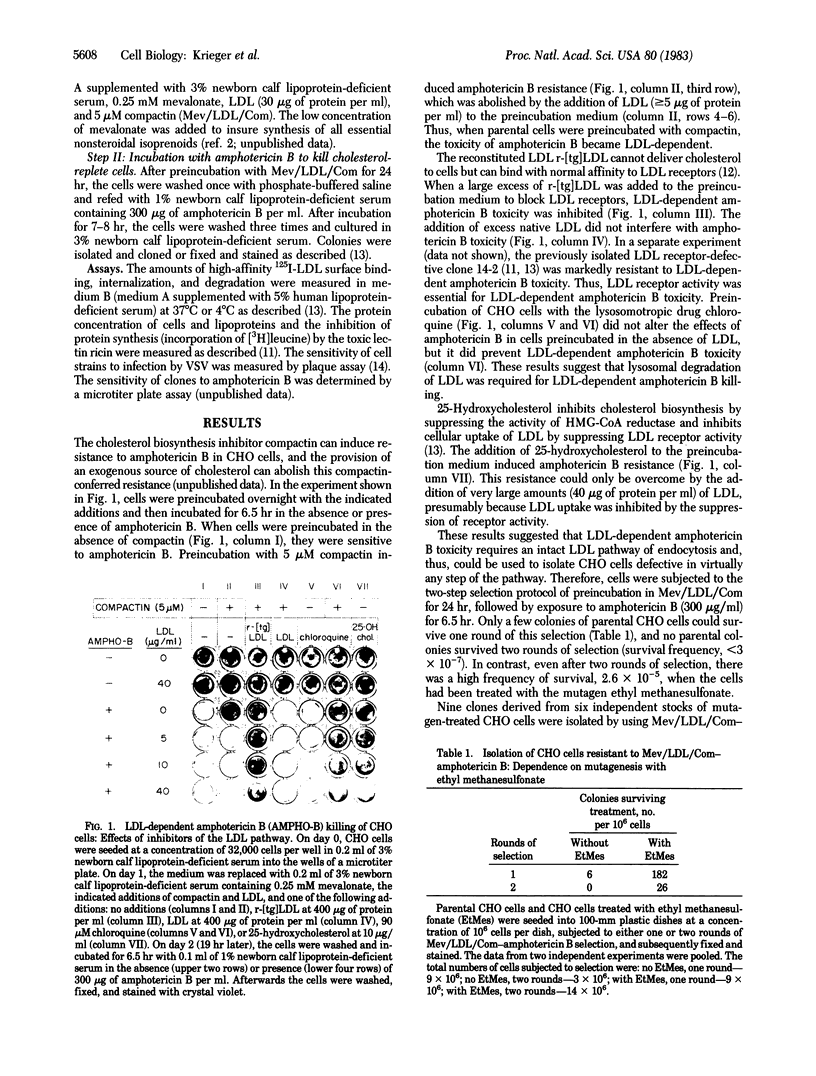
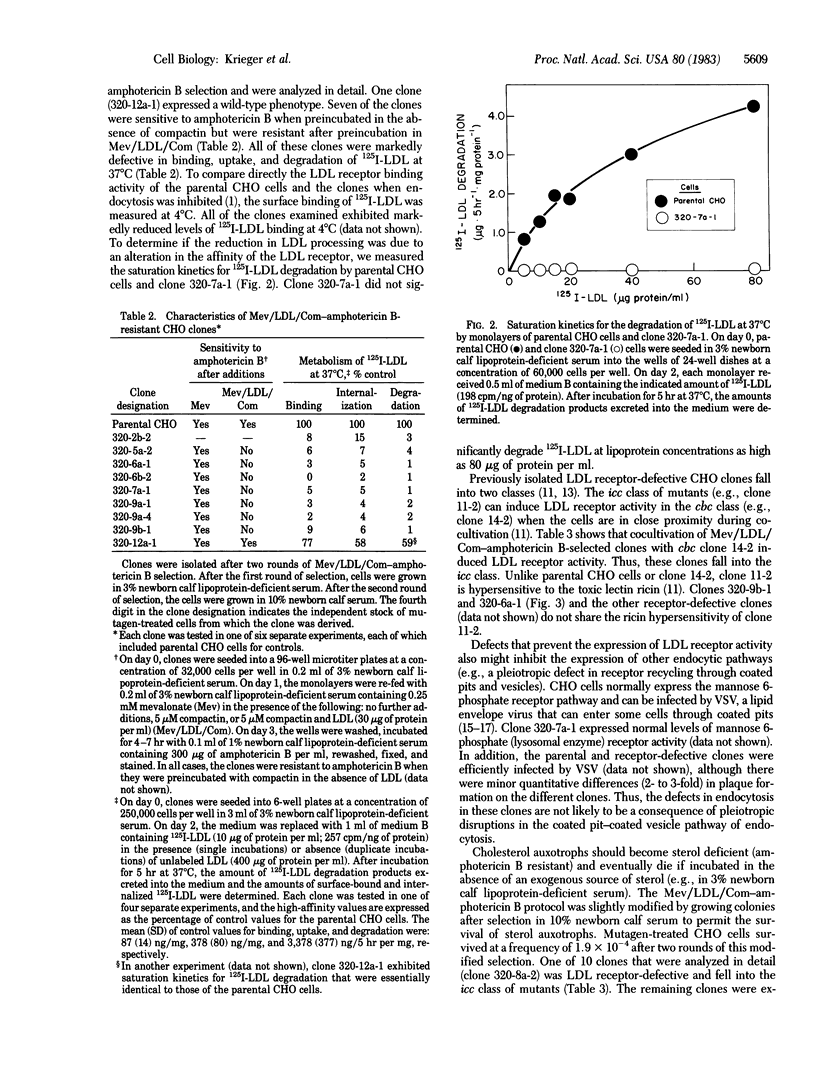
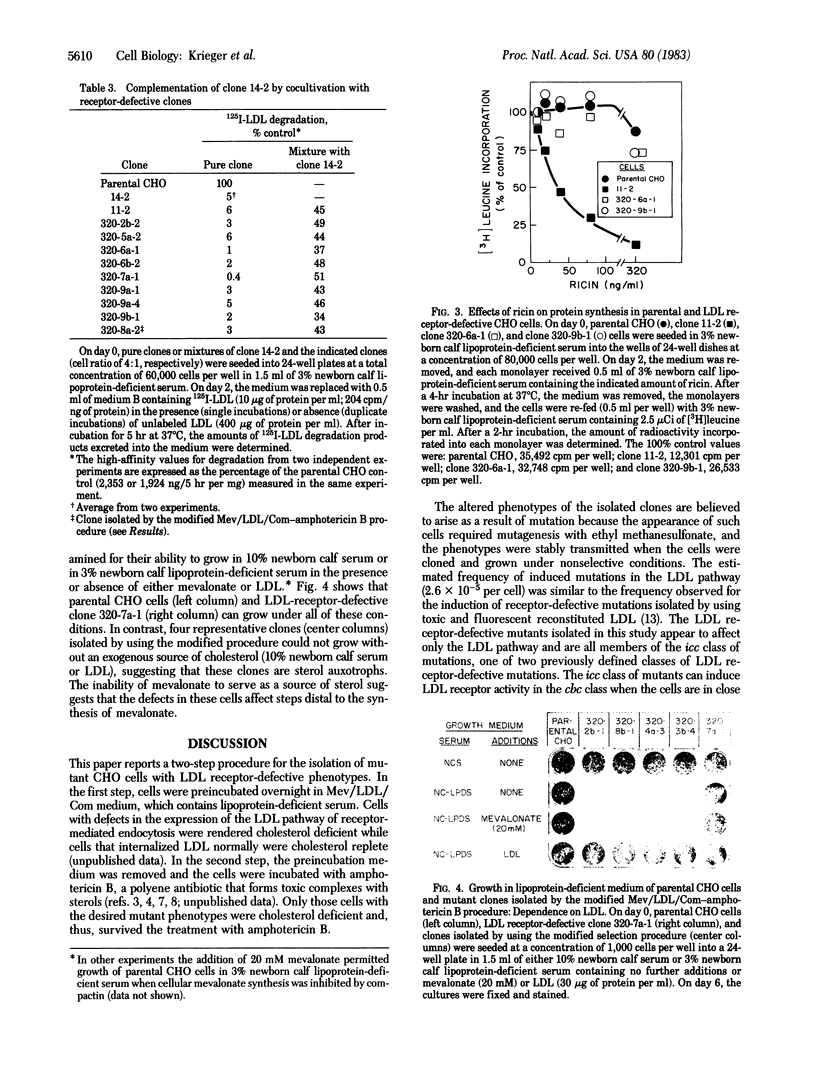
This paper describes a rapid and efficient two-step procedure for the isolation of mutant cells with defects in receptor-mediated endocytosis. The procedure takes advantage of two fungal metabolites, compactin (ML236B), a potent inhibitor of cholesterol biosynthesis, and amphotericin B, a polyene antibiotic that forms toxic complexes with sterols in membranes. Mutagen-treated Chinese hamster ovary cells were preincubated overnight in a medium containing mevalonate, low density lipoprotein (LDL), and compactin (Mev/LDL/Com). At the end of the preincubation period, wild-type cells were cholesterol replete while mutant cells that could not utilize the cholesterol in LDL were cholesterol deficient. Subsequent incubation with amphotericin B for 6 hr killed most of the wild-type cells. After a second round of Mev/LDL/Com-amphotericin B selection, endocytosis-defective clones appeared at a frequency of approximately equal to 2.6 X 10(-5). Some of these clones expressed LDL receptor-defective phenotypes and fell into one of two previously defined classes of mutation. Sensitivity of the mutants to infection by vesicular stomatitis virus suggested that the mutations do not disrupt the coated pit-coated vesicle pathway of endocytosis. Minor modifications in the Mev/LDL/Com-amphotericin B selection permit the isolation of cholesterol auxotrophs and might allow the isolation of conditional-lethal mutations. Because LDL can be coupled to ligands that bind to receptors other than the LDL receptor, Mev/LDL/Com-amphotericin B selection may permit the isolation of mutant cells with defects that specifically disrupt other endocytic pathways.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Multivalent feedback regulation of HMG CoA reductase, a control mechanism coordinating isoprenoid synthesis and cell growth. J Lipid Res. 1980 Jul;21(5):505–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. Y., Chang C. C. Revertants of a Chinese hamster ovary cell mutant resistant to suppression by an analogue of cholesterol: isolation and partial biochemical characterization. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 12;21(21):5316–5323. doi: 10.1021/bi00264a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. B., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. alpha 2-macroglobulin adsorbed to colloidal gold: a new probe in the study of receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1981 Apr;89(1):29–34. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo A., Kuroda M., Tanzawa K. Competitive inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase by ML-236A and ML-236B fungal metabolites, having hypocholesterolemic activity. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 31;72(2):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80996-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Helgeson J. A., Brown M. S. Inhibition of cholesterol synthesis with compactin renders growth of cultured cells dependent on the low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5403–5409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka K., Endo H., Akiyama S., Kuwano M. Isolation and characterization of amphotericin B-resistant cell lines in Chinese hamster cells. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):415–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C. Antibiotic interaction with model membranes. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1970;10:119–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.10.040170.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger M., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Isolation of Chinese hamster cell mutants defective in the receptor-mediated endocytosis of low density lipoprotein. J Mol Biol. 1981 Aug 5;150(2):167–184. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90447-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger M. Complementation of mutations in the LDL pathway of receptor-mediated endocytosis by cocultivation of LDL receptor-defective hamster cell mutants. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90423-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger M., McPhaul M. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Replacement of neutral lipids of low density lipoprotein with esters of long chain unsaturated fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3845–3853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Reggio H., Helenius A., Simons K. Pathway of vesicular stomatitis virus entry leading to infection. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):609–631. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. R., Peng S. S., Marshall J. L. Mutant Chinese hamster ovary cells pleiotropically defective in receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;96(4):1064–1071. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.4.1064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Chou S. M., Silbert D. F. Animal cell mutants defective in sterol metabolism: a specific selection procedure and partial characterization of defects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3730–3734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M., Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Absence of interference during high-multiplicity infection by clonally purified vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1971 Mar;7(3):409–411. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.3.409-411.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruijff B., Gerritsen W. J., Oerlemans A., Demel R. A., van Deenen L. L. Polyene antibiotic-sterol interactions in membranes of Acholeplasma laidlawii cells and lecithin liposomes. I. Specificity of the membrane permeability changes induced by the polyene antibiotics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Feb 26;339(1):30–43. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





