Abstract
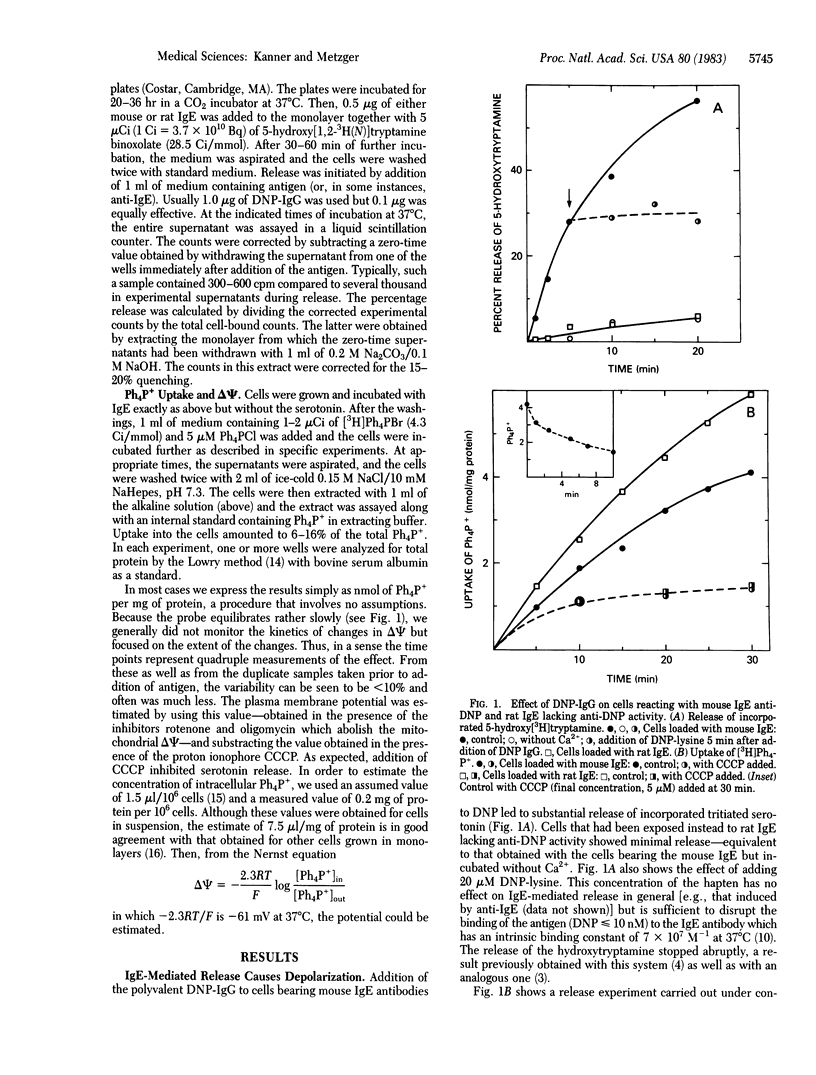
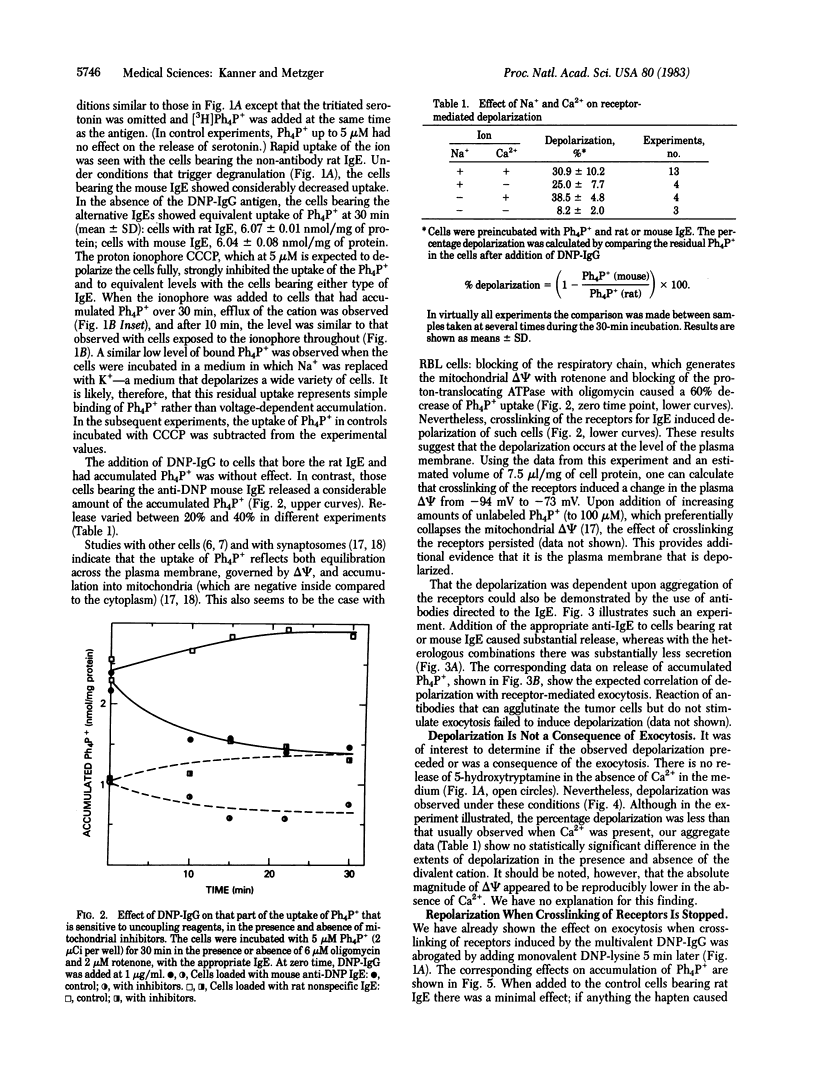
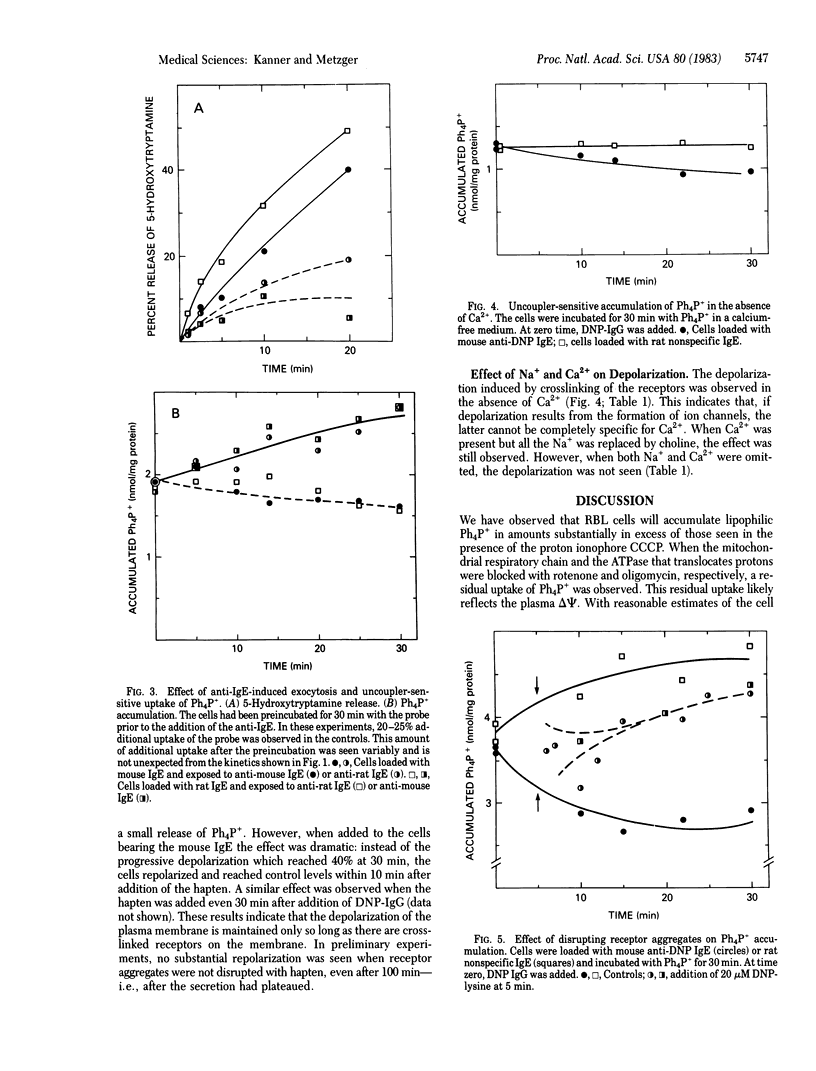
Aggregation of the receptor for IgE on mast cells, basophils, and a tumor analog, rat basophilic leukemia (RBL) cells, induces a calcium-dependent degranulation of the cells. We have measured the membrane potential (delta psi) of RBL cells during this reaction by using the tetraphenylphosphonium ion (Ph4P+) equilibration technique. We observed a 20-45% reduction in ionophore-sensitive Ph4P+ accumulation. The phenomenon persisted under conditions expected to collapse the mitochondrial membrane potential, consistent with the effect being due to a change in delta psi of the plasma membrane. We estimated that the change reflects a depolarization of 20 mV (from -90 to -70 mV, interior negative). Whereas degranulation fails to occur in the absence of external Ca2+, this was not true of the depolarization, indicating that the latter was not a consequence of secretion. When aggregation of the receptor is induced by reaction of the cell-bound IgE with a multivalent antigen, the secretory reaction can be halted by adding a univalent hapten. In this case, complete repolarization occurs. Equivalent depolarization was observed in the absence of Na+ but was diminished when both Ca2+ and Na+ were absent. Together, the data suggest that aggregation of the receptor opens ion channels and that the latter disappear promptly when the receptors are disaggregated. It is plausible that formation of these channels leads to the entry of Ca2+ and is an early and critical consequence of the aggregation of the receptors, thereby leading to degranulation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsumian E. L., Isersky C., Petrino M. G., Siraganian R. P. IgE-induced histamine release from rat basophilic leukemia cell lines: isolation of releasing and nonreleasing clones. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Apr;11(4):317–323. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazin H., Querinjean P., Beckers A., Heremans J. F., Dessy F. Transplantable immunoglobulin-secreting tumours in rats. IV. Sixty-three IgE-secreting immunocytoma tumours. Immunology. 1974 Apr;26(4):713–723. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. Effects of potassium, veratridine, and scorpion venom on calcium accumulation and transmitter release by nerve terminals in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;247(3):617–655. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Johnson E. M., Jr, Needleman P. Calcium-dependent norepinephrine release from presynaptic nerve endings in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2237–2240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews F. T., Morita Y., McGivney A., Hirata F., Siraganian R. P., Axelrod J. IgE-mediated histamine release in rat basophilic leukemia cells: receptor activation, phospholipid methylation, Ca2+ flux, and release of arachidonic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Dec;212(2):561–571. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90399-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holowka D., Metzger H. Further characterization of the beta-component of the receptor for immunoglobulin E. Mol Immunol. 1982 Feb;19(2):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90334-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isersky C., Metzger H., Buell D. N. Cell cycle-associated changes in receptors for IgE during growth and differentiation of a rat basophilic leukemia cell line. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):1147–1162. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T. Biochemical analysis of triggering signals induced by bridging of IgE receptors. Fed Proc. 1982 Jan;41(1):17–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Hirata F., Ishizaka K., Axelrod J. Stimulation of phospholipid methylation, Ca2+ influx, and histamine release by bridging of IgE receptors on rat mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1903–1906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagey-Sobotka A., MacGlashan D. W., Lichtenstein L. M. Role of receptor aggregation in triggering IgE-mediated reactions. Fed Proc. 1982 Jan;41(1):12–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer H., Blume A. J., Kaback H. R. Membrane potential changes during mitogenic stimulation of mouse spleen lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2200–2204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulczycki A., Jr, Metzger H. The interaction of IgE with rat basophilic leukemia cells. II. Quantitative aspects of the binding reaction. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1676–1695. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Holgate S. T., Roberts L. J., 2nd, Maguire J. F., Oates J. A., Austen K. F. Effects of indomethacin on cyclic nucleotide levels and histamine release from rat serosal mast cells. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1663–1668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtshtein D., Kaback H. R., Blume A. J. Use of a lipophilic cation for determination of membrane potential in neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cell suspensions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):650–654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Bohn J. W., Ferry E. L., Yamamoto H., Molinaro C. A., Sherman L. A., Klinman N. R., Katz D. H. Monoclonal dinitrophenyl-specific murine IgE antibody: preparation, isolation, and characterization. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2728–2737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G., Rugolo M., Scott I. G., Meldolesi J. alpha-latrotoxin of black widow spider venom depolarizes the plasma membrane, induces massive calcium influx, and stimulates transmitter release in guinea pig brain synaptosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7924–7928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce F. L. Calcium and histamine secretion from mast cells. Prog Med Chem. 1982;19:59–109. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6468(08)70328-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Grollman E. F., Lazo P. S., Dyer S. A., Habig W. H., Hardegree M. C., Kaback H. R., Kohn L. D. Effect of tetanus toxin on the accumulation of the permeant lipophilic cation tetraphenylphosphonium by guinea pig brain synaptosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4783–4787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivnay B., Wank S. A., Poy G., Metzger H. Phospholipids stabilize the interaction between the alpha and beta subunits of the solubilized receptor for immunoglobulin E. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6922–6927. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Rozengurt E. Na+/H+ antiport in Swiss 3T3 cells: mitogenic stimulation leads to cytoplasmic alkalinization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7778–7782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow C. M., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Mast cell mediator release as a function of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activation. J Exp Med. 1981 Oct 1;154(4):1125–1133. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.4.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Unkeless J. C., Kaback H. R., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage membrane potential changes associated with gamma 2b/gamma 1 Fc receptor-ligand binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1357–1361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Unkeless J. C., Kaback H. R., Cohn Z. A. Mouse macrophage Fc receptor for IgG gamma 2b/gamma 1 in artificial and plasma membrane vesicles functions as a ligand-dependent ionophore. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1636–1640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



