Abstract
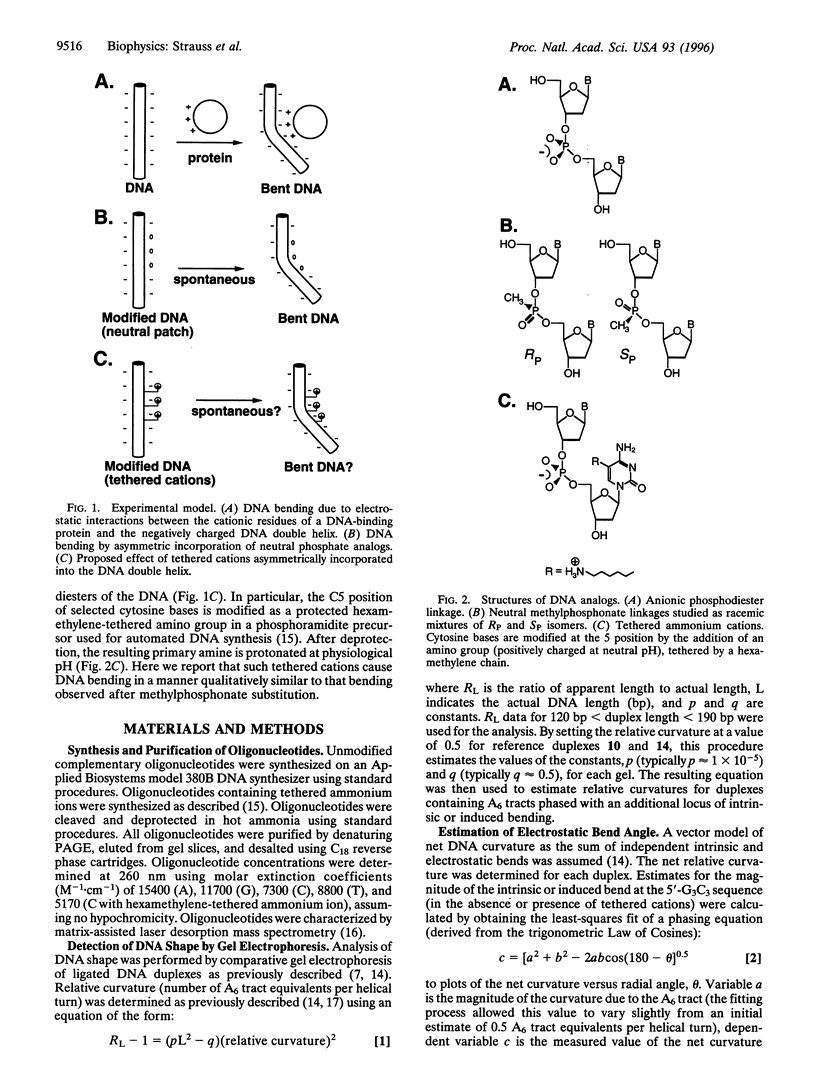
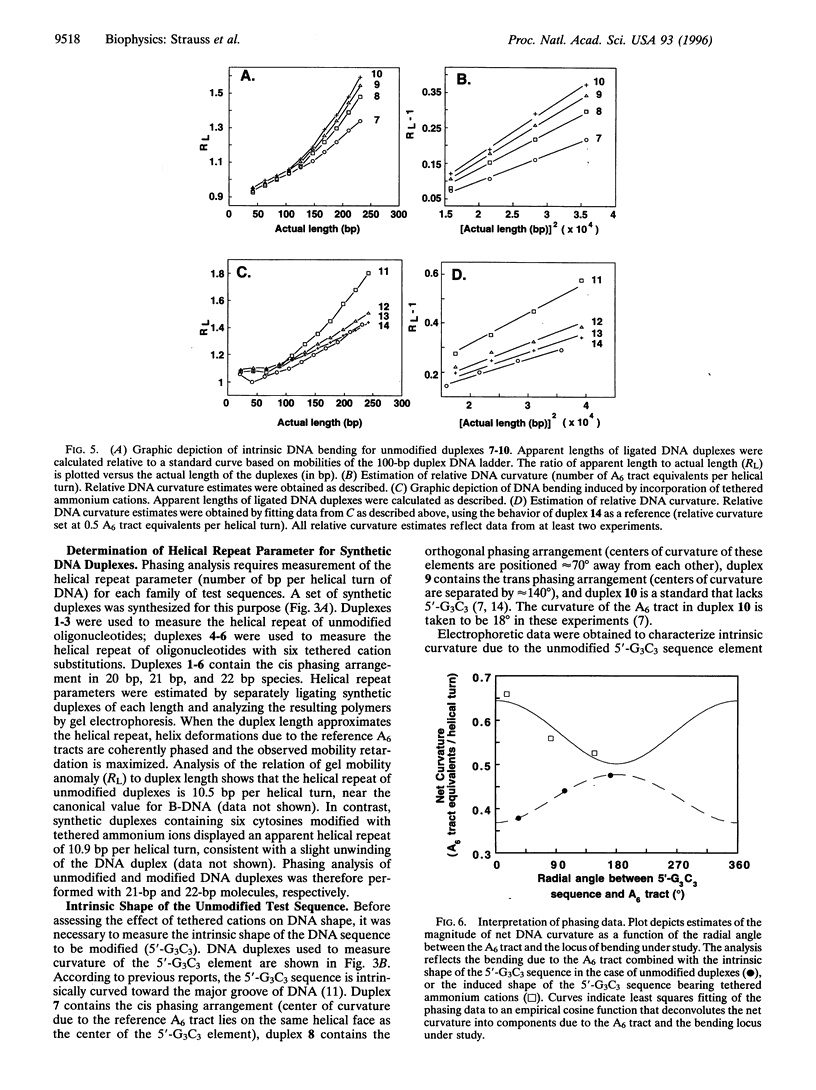
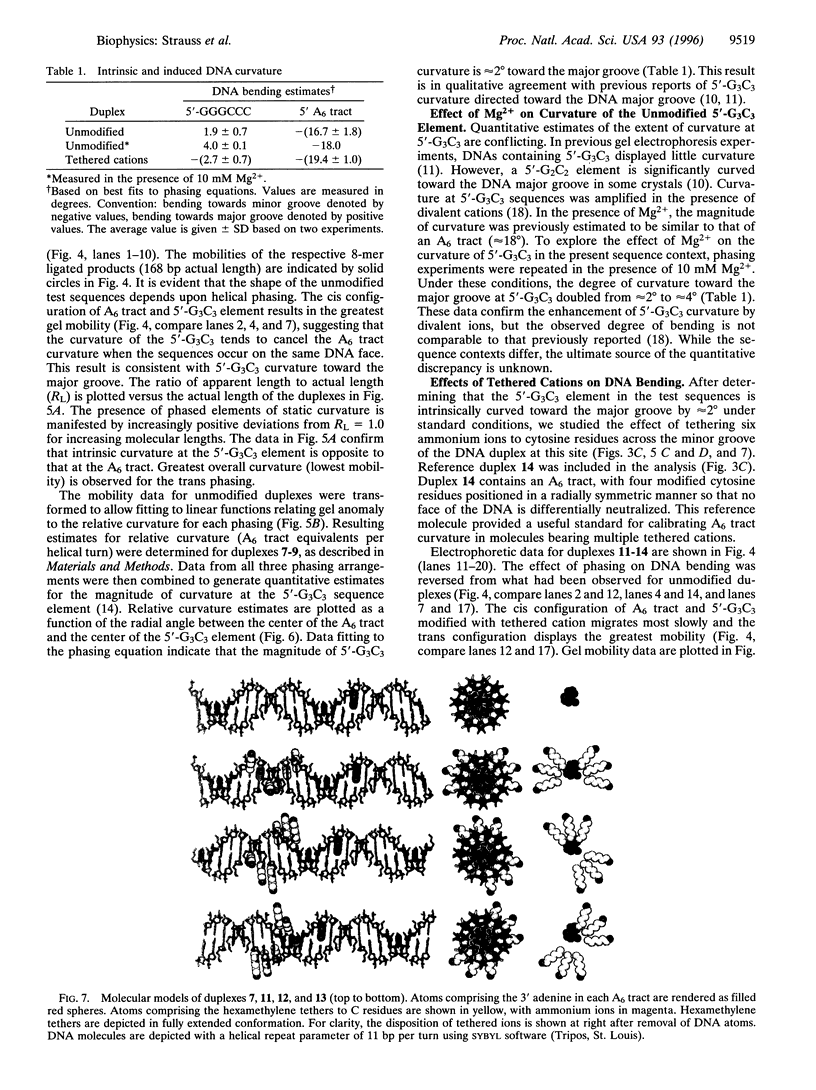
DNA is bent when complexed with certain proteins. We are exploring the hypothesis that asymmetric neutralization of phosphate charges will cause the DNA double helix to collapse toward the neutralized face. We have previously shown that DNA spontaneously bends toward one face of the double helix when it is partially substituted with neutral methylphosphonate linkages. We have now synthesized DNA duplexes in which cations are tethered by hexamethylene chains near specific phosphates. Electrophoretic phasing experiments demonstrate that tethering six ammonium ions on one helical face causes DNA to bend by approximately 5 degrees toward that face, in qualitative agreement with predictions. Ion pairing between tethered cations and DNA phosphates provides a new model for simulating the electrostatic consequences of phosphate neutralization by proteins.
Full text
PDF
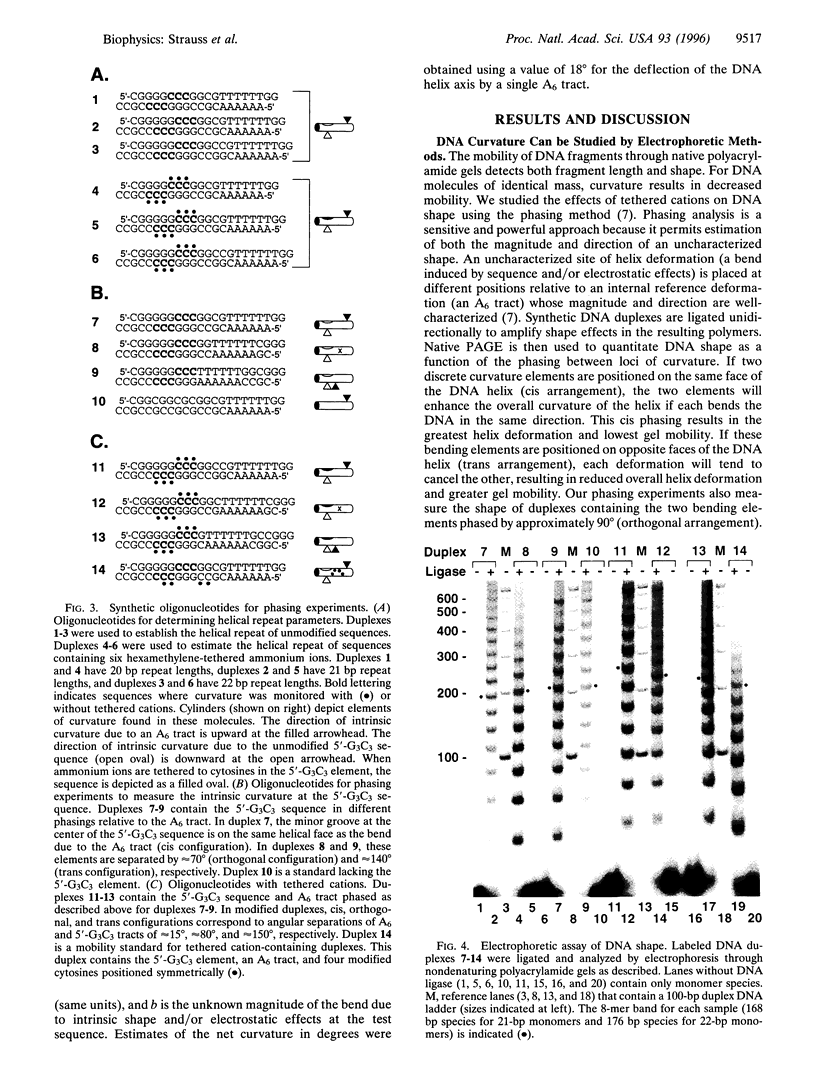

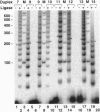
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutel B. A., Gold L. In vitro evolution of intrinsically bent DNA. J Mol Biol. 1992 Dec 5;228(3):803–812. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90865-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brukner I., Dlakic M., Savic A., Susic S., Pongor S., Suck D. Evidence for opposite groove-directed curvature of GGGCCC and AAAAA sequence elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 25;21(4):1025–1029. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.4.1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brukner I., Susic S., Dlakic M., Savic A., Pongor S. Physiological concentration of magnesium ions induces a strong macroscopic curvature in GGGCCC-containing DNA. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 11;236(1):26–32. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brukner I., Sánchez R., Suck D., Pongor S. Sequence-dependent bending propensity of DNA as revealed by DNase I: parameters for trinucleotides. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 18;14(8):1812–1818. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Drak J. Global features of DNA structure by comparative gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1992;212:46–71. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)12005-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodsell D. S., Kopka M. L., Cascio D., Dickerson R. E. Crystal structure of CATGGCCATG and its implications for A-tract bending models. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2930–2934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Flexibility of DNA. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:265–286. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haran T. E., Kahn J. D., Crothers D. M. Sequence elements responsible for DNA curvature. J Mol Biol. 1994 Nov 25;244(2):135–143. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. L., Nikolov D. B., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of a TATA element. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):520–527. doi: 10.1038/365520a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y., Geiger J. H., Hahn S., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of a yeast TBP/TATA-box complex. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):512–520. doi: 10.1038/365512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Crothers D. M. Calibration of DNA curvature and a unified description of sequence-directed bending. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1763–1767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love J. J., Li X., Case D. A., Giese K., Grosschedl R., Wright P. E. Structural basis for DNA bending by the architectural transcription factor LEF-1. Nature. 1995 Aug 31;376(6543):791–795. doi: 10.1038/376791a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S., Ebralidse K. K., Mirzabekov A. D., Rich A. An estimate of the extent of folding of nucleosomal DNA by laterally asymmetric neutralization of phosphate groups. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1989 Apr;6(5):877–889. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1989.10506519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirzabekov A. D., Rich A. Asymmetric lateral distribution of unshielded phosphate groups in nucleosomal DNA and its role in DNA bending. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1118–1121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini L., Tan S., Richmond T. J. Structure of serum response factor core bound to DNA. Nature. 1995 Aug 10;376(6540):490–498. doi: 10.1038/376490a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieles U., Zürcher W., Schär M., Moser H. E. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry: a powerful tool for the mass and sequence analysis of natural and modified oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3191–3196. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. C., Shields G. C., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure of a CAP-DNA complex: the DNA is bent by 90 degrees. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1001–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.1653449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss J. K., Maher L. J., 3rd DNA bending by asymmetric phosphate neutralization. Science. 1994 Dec 16;266(5192):1829–1834. doi: 10.1126/science.7997878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulyanov N. B., Zhurkin V. B. Sequence-dependent anisotropic flexibility of B-DNA. A conformational study. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1984 Oct;2(2):361–385. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1984.10507573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]