Abstract
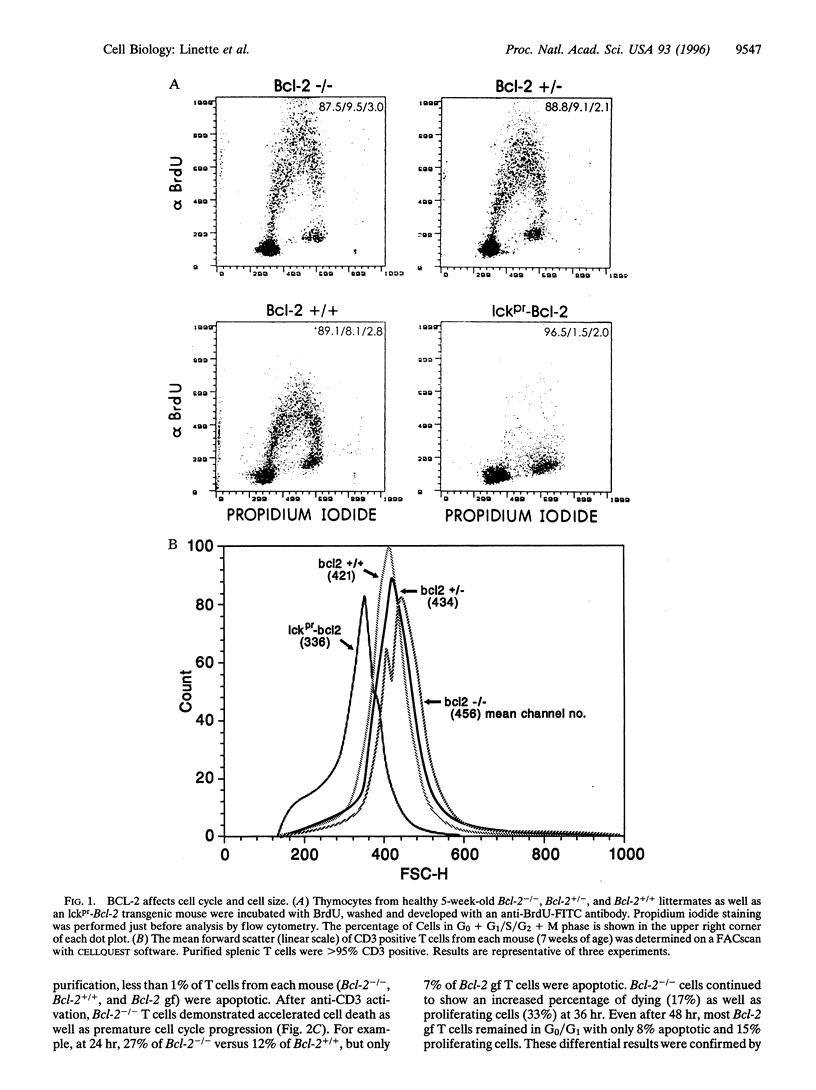
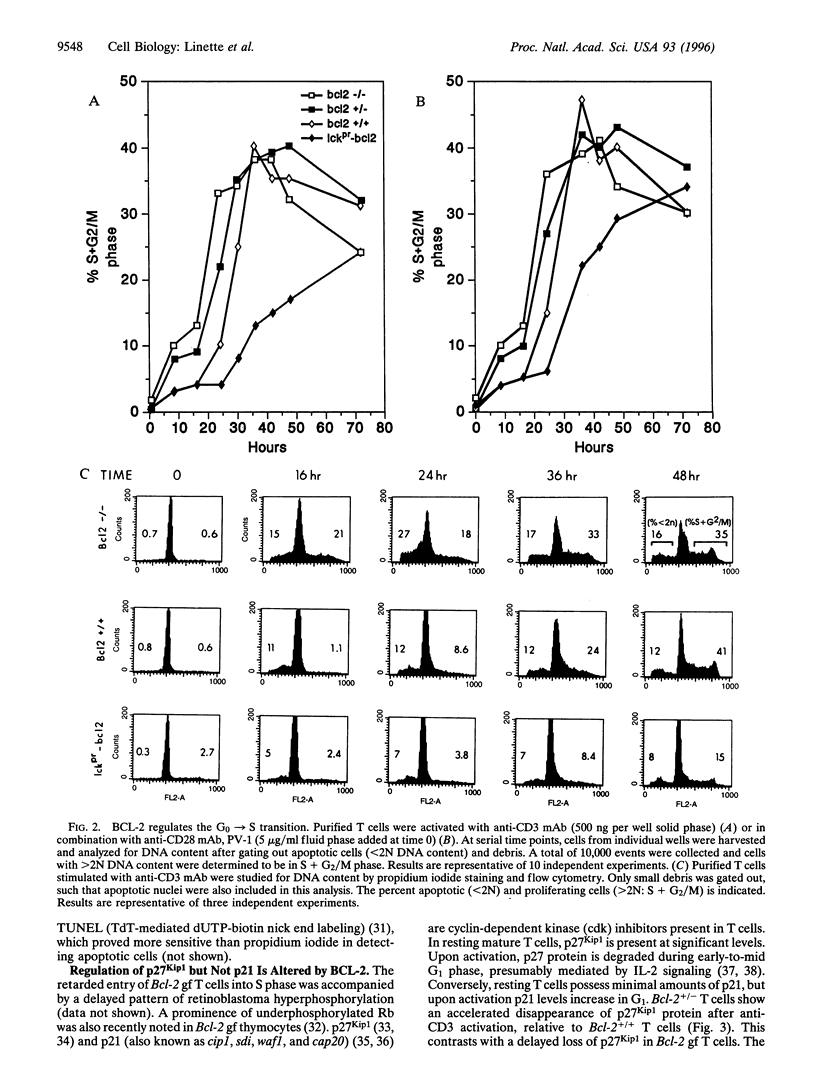
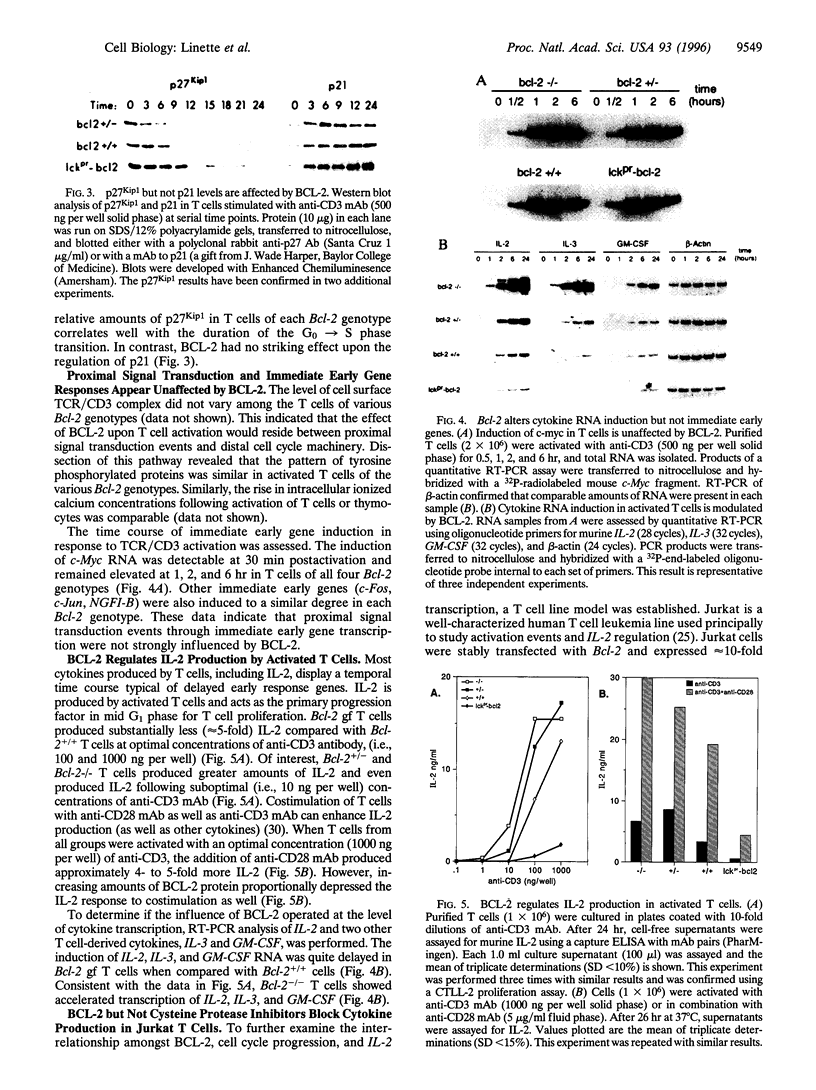
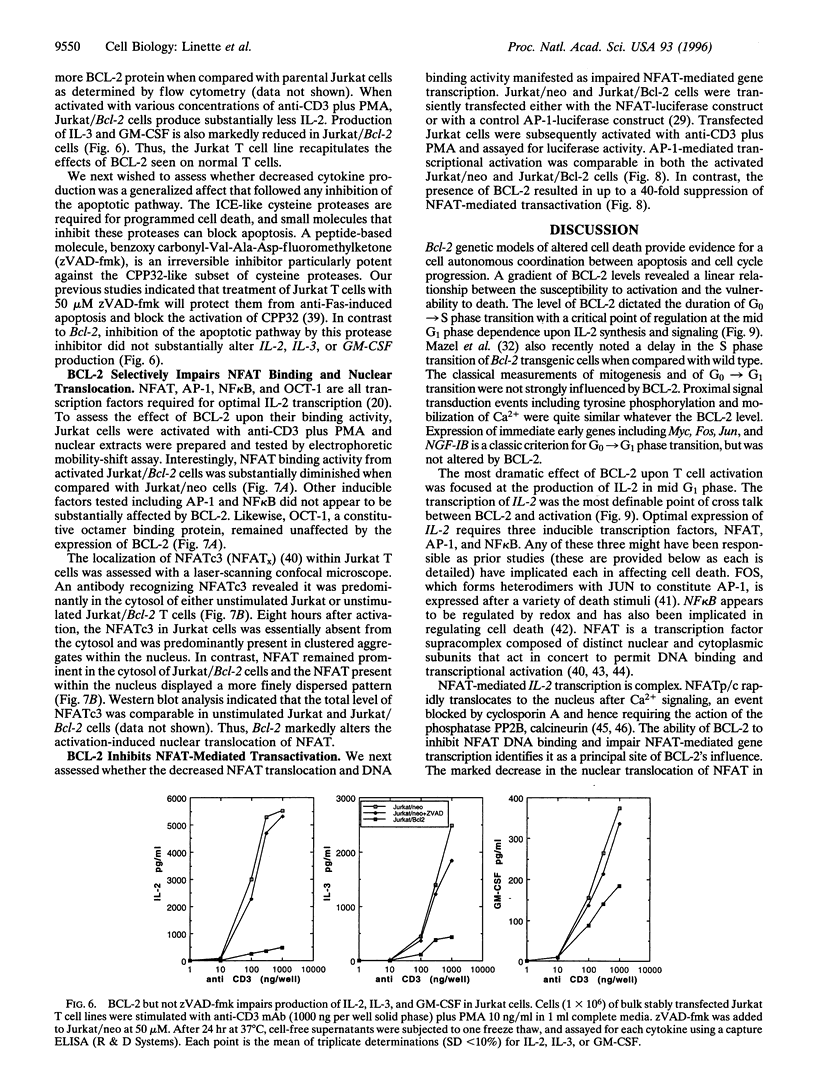
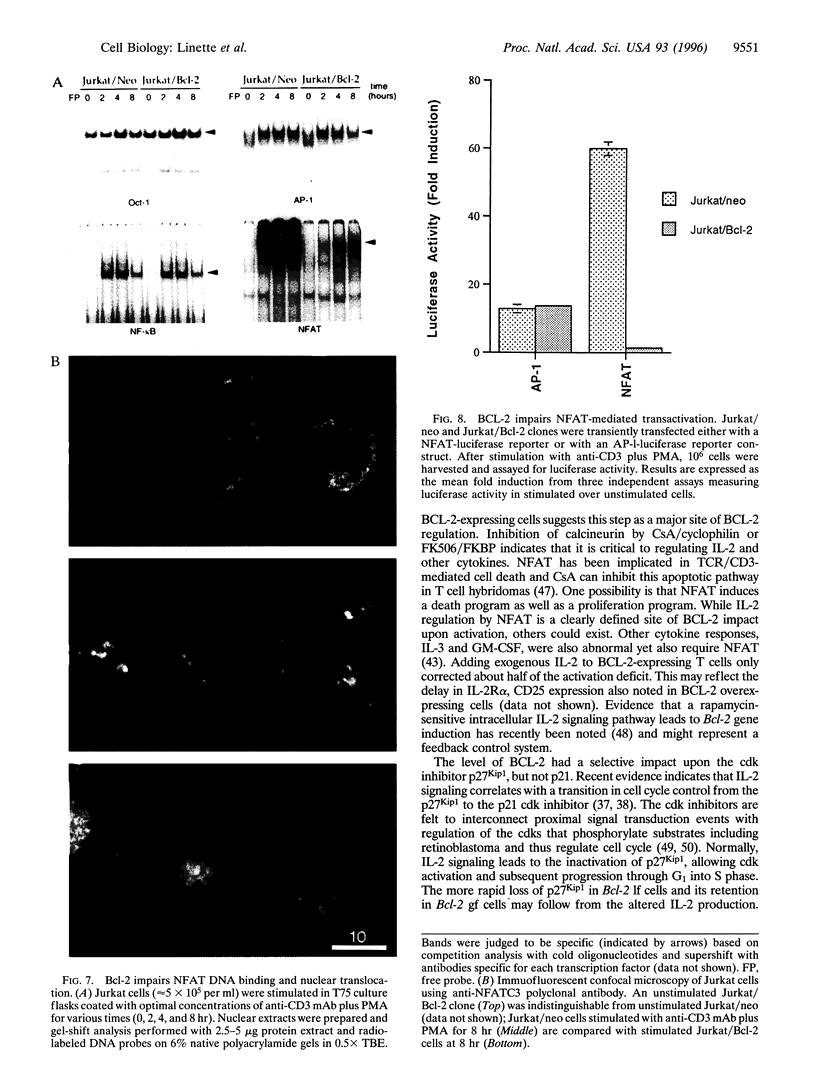
BCL-2-deficient T cells demonstrate accelerated cell cycle progression and increased apoptosis following activation. Increasing the levels of BCL-2 retarded the G0-->S transition, sustained the levels of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1, and repressed postactivation death. Proximal signal transduction events and immediate early gene transcription were unaffected. However, the transcription and synthesis of interleukin 2 and other delayed early cytokines were markedly attenuated by BCL-2. In contrast, a cysteine protease inhibitor that also blocks apoptosis had no substantial affect upon cytokine production. InterleUkin 2 expression requires several transcription factors of which nuclear translocation of NFAT (nuclear factor of activated T cells) and NFAT-mediated transactivation were impaired by BCL-2. Thus, select genetic aberrations in the apoptotic pathway reveal a cell autonomous coregulation of activation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe R., Vandenberghe P., Craighead N., Smoot D. S., Lee K. P., June C. H. Distinct signal transduction in mouse CD4+ and CD8+ splenic T cells after CD28 receptor ligation. J Immunol. 1995 Feb 1;154(3):985–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. C., Aja T., Xiang J., Gaur S., Krebs J. F., Hoang K., Bai X., Korsmeyer S. J., Karanewsky D. S., Fritz L. C. Fas-induced activation of the cell death-related protease CPP32 Is inhibited by Bcl-2 and by ICE family protease inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jul 12;271(28):16850–16855. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.28.16850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakhshi A., Jensen J. P., Goldman P., Wright J. J., McBride O. W., Epstein A. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Cloning the chromosomal breakpoint of t(14;18) human lymphomas: clustering around JH on chromosome 14 and near a transcriptional unit on 18. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):899–906. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carayon P., Bord A. Identification of DNA-replicating lymphocyte subsets using a new method to label the bromo-deoxyuridine incorporated into the DNA. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Mar 4;147(2):225–230. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(12)80012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary M. L., Sklar J. Nucleotide sequence of a t(14;18) chromosomal breakpoint in follicular lymphoma and demonstration of a breakpoint-cluster region near a transcriptionally active locus on chromosome 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7439–7443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clipstone N. A., Crabtree G. R. Identification of calcineurin as a key signalling enzyme in T-lymphocyte activation. Nature. 1992 Jun 25;357(6380):695–697. doi: 10.1038/357695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R., Clipstone N. A. Signal transmission between the plasma membrane and nucleus of T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:1045–1083. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.005145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Wyllie A. H., Gilbert C. S., Littlewood T. D., Land H., Brooks M., Waters C. M., Penn L. Z., Hancock D. C. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90123-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiering S., Northrop J. P., Nolan G. P., Mattila P. S., Crabtree G. R., Herzenberg L. A. Single cell assay of a transcription factor reveals a threshold in transcription activated by signals emanating from the T-cell antigen receptor. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1823–1834. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firpo E. J., Koff A., Solomon M. J., Roberts J. M. Inactivation of a Cdk2 inhibitor during interleukin 2-induced proliferation of human T lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4889–4901. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. D., Straus D., Weiss A. Signal transduction events leading to T-cell lymphokine gene expression. Immunol Today. 1993 Jul;14(7):357–362. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90236-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruman D. A., Burakoff S. J., Bierer B. E. Immunophilins in protein folding and immunosuppression. FASEB J. 1994 Apr 1;8(6):391–400. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.6.7513288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavrieli Y., Sherman Y., Ben-Sasson S. A. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):493–501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington E. A., Bennett M. R., Fanidi A., Evan G. I. c-Myc-induced apoptosis in fibroblasts is inhibited by specific cytokines. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3286–3295. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06630.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Thomas D. J., Timmerman L. A., Li X., Francke U., Crabtree G. R. NFATc3, a lymphoid-specific NFATc family member that is calcium-regulated and exhibits distinct DNA binding specificity. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 25;270(34):19898–19907. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.34.19898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D., Nuñez G., Milliman C., Schreiber R. D., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):334–336. doi: 10.1038/348334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Fazeli A., Schmitt E. M., Bronson R. T., Goodell M. A., Weinberg R. A. Effects of an Rb mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):295–300. doi: 10.1038/359295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Fletcher M. C., Ledbetter J. A., Samelson L. E. Increases in tyrosine phosphorylation are detectable before phospholipase C activation after T cell receptor stimulation. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1591–1599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., Chang C. Y., Hu N., Wang Y. C., Lai C. C., Herrup K., Lee W. H., Bradley A. Mice deficient for Rb are nonviable and show defects in neurogenesis and haematopoiesis. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):288–294. doi: 10.1038/359288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linette G. P., Grusby M. J., Hedrick S. M., Hansen T. H., Glimcher L. H., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 is upregulated at the CD4+ CD8+ stage during positive selection and promotes thymocyte differentiation at several control points. Immunity. 1994 Jun;1(3):197–205. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linette G. P., Hess J. L., Sentman C. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma in lckpr-bcl-2 transgenic mice. Blood. 1995 Aug 15;86(4):1255–1260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma A., Pena J. C., Chang B., Margosian E., Davidson L., Alt F. W., Thompson C. B. Bclx regulates the survival of double-positive thymocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):4763–4767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.4763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvel J., Perkins G. R., Lopez Rivas A., Collins M. K. Growth factor starvation of bcl-2 overexpressing murine bone marrow cells induced refractoriness to IL-3 stimulation of proliferation. Oncogene. 1994 Apr;9(4):1117–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattila P. S., Ullman K. S., Fiering S., Emmel E. A., McCutcheon M., Crabtree G. R., Herzenberg L. A. The actions of cyclosporin A and FK506 suggest a novel step in the activation of T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4425–4433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07893.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazel S., Burtrum D., Petrie H. T. Regulation of cell division cycle progression by bcl-2 expression: a potential mechanism for inhibition of programmed cell death. J Exp Med. 1996 May 1;183(5):2219–2226. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.5.2219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Deane N., Platt F. M., Nunez G., Jaeger U., McKearn J. P., Korsmeyer S. J. bcl-2-immunoglobulin transgenic mice demonstrate extended B cell survival and follicular lymphoproliferation. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Korsmeyer S. J. Progression from lymphoid hyperplasia to high-grade malignant lymphoma in mice transgenic for the t(14; 18). Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):254–256. doi: 10.1038/349254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki T., Liu Z. J., Kawahara A., Minami Y., Yamada K., Tsujimoto Y., Barsoumian E. L., Permutter R. M., Taniguchi T. Three distinct IL-2 signaling pathways mediated by bcl-2, c-myc, and lck cooperate in hematopoietic cell proliferation. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery R. A., Dallman M. J. Analysis of cytokine gene expression during fetal thymic ontogeny using the polymerase chain reaction. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):554–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motoyama N., Wang F., Roth K. A., Sawa H., Nakayama K., Nakayama K., Negishi I., Senju S., Zhang Q., Fujii S. Massive cell death of immature hematopoietic cells and neurons in Bcl-x-deficient mice. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1506–1510. doi: 10.1126/science.7878471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nourse J., Firpo E., Flanagan W. M., Coats S., Polyak K., Lee M. H., Massague J., Crabtree G. R., Roberts J. M. Interleukin-2-mediated elimination of the p27Kip1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor prevented by rapamycin. Nature. 1994 Dec 8;372(6506):570–573. doi: 10.1038/372570a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuñez G., London L., Hockenbery D., Alexander M., McKearn J. P., Korsmeyer S. J. Deregulated Bcl-2 gene expression selectively prolongs survival of growth factor-deprived hemopoietic cell lines. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3602–3610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe S. J., Tamura J., Kincaid R. L., Tocci M. J., O'Neill E. A. FK-506- and CsA-sensitive activation of the interleukin-2 promoter by calcineurin. Nature. 1992 Jun 25;357(6380):692–694. doi: 10.1038/357692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):603–608. doi: 10.1126/science.2683075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyak K., Lee M. H., Erdjument-Bromage H., Koff A., Roberts J. M., Tempst P., Massagué J. Cloning of p27Kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor and a potential mediator of extracellular antimitogenic signals. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90572-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin X. Q., Livingston D. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr, Adams P. D. Deregulated transcription factor E2F-1 expression leads to S-phase entry and p53-mediated apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):10918–10922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. Social controls on cell survival and cell death. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):397–400. doi: 10.1038/356397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao A. NF-ATp: a transcription factor required for the co-ordinate induction of several cytokine genes. Immunol Today. 1994 Jun;15(6):274–281. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shan B., Lee W. H. Deregulated expression of E2F-1 induces S-phase entry and leads to apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;14(12):8166–8173. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.8166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Roberts J. M. Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev. 1995 May 15;9(10):1149–1163. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.10.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeyne R. J., Vendrell M., Hayward M., Baker S. J., Miao G. G., Schilling K., Robertson L. M., Curran T., Morgan J. I. Continuous c-fos expression precedes programmed cell death in vivo. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):166–169. doi: 10.1038/363166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser A., Harris A. W., Cory S. E mu-bcl-2 transgene facilitates spontaneous transformation of early pre-B and immunoglobulin-secreting cells but not T cells. Oncogene. 1993 Jan;8(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Lindsten T., Ledbetter J. A., Kunkel S. L., Young H. A., Emerson S. G., Leiden J. M., June C. H. CD28 activation pathway regulates the production of multiple T-cell-derived lymphokines/cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1333–1337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima H., Hunter T. p27, a novel inhibitor of G1 cyclin-Cdk protein kinase activity, is related to p21. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90573-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Gorham J., Cossman J., Jaffe E., Croce C. M. The t(14;18) chromosome translocations involved in B-cell neoplasms result from mistakes in VDJ joining. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1390–1393. doi: 10.1126/science.3929382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Cory S., Adams J. M. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):440–442. doi: 10.1038/335440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veis D. J., Sorenson C. M., Shutter J. R., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2-deficient mice demonstrate fulminant lymphoid apoptosis, polycystic kidneys, and hypopigmented hair. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):229–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80065-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell. 1995 May 5;81(3):323–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Stobo J. D. Requirement for the coexpression of T3 and the T cell antigen receptor on a malignant human T cell line. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1284–1299. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]