Abstract
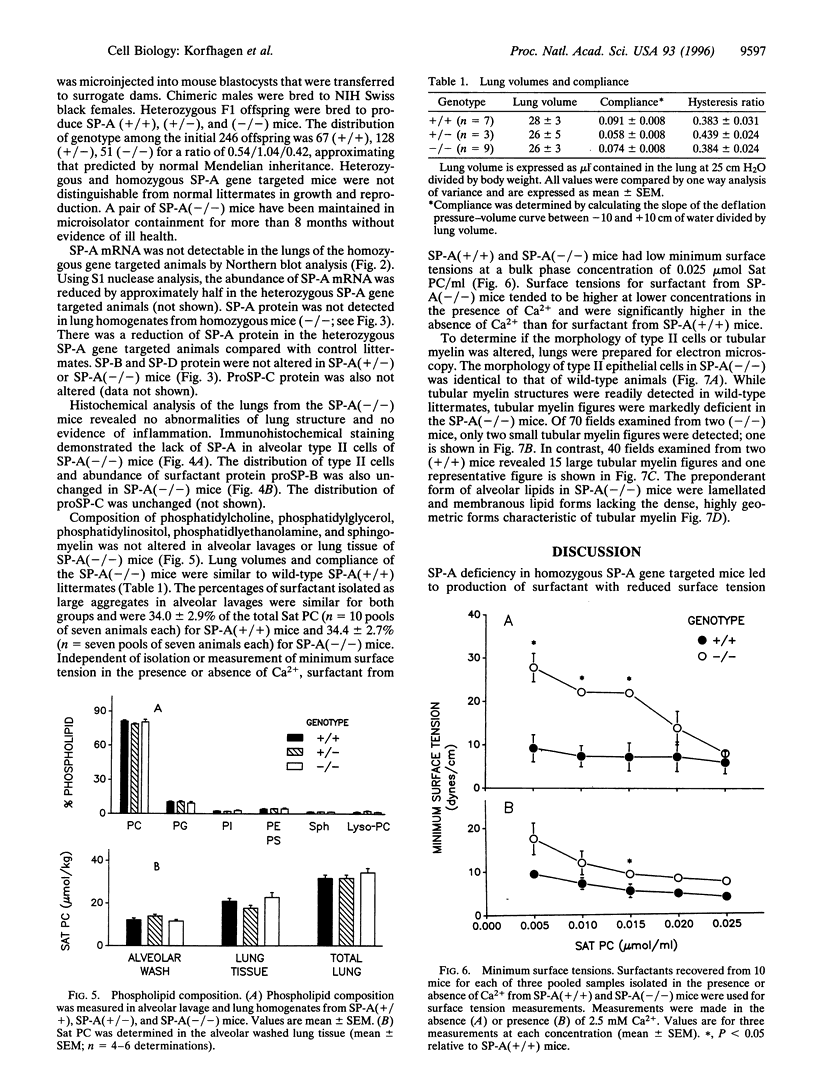
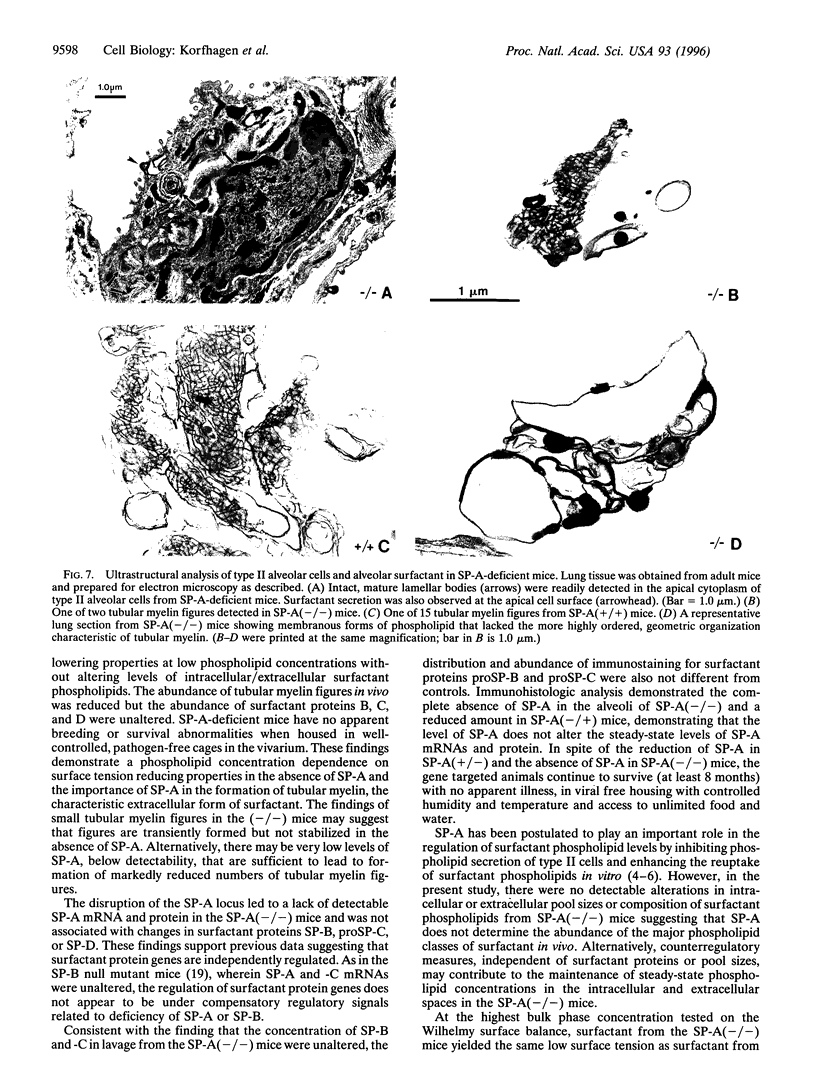
The surfactant protein A (SP-A) gene was disrupted by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells that were used to generate homozygous SP-A-deficient mice. SP-A mRNA and protein were not detectable in the lungs of SP-A(-/-) mice, and perinatal survival of SP-A(-/-) mice was not altered compared with wild-type mice. Lung morphology, surfactant proteins B-D, lung tissue, alveolar phospholipid pool sizes and composition, and lung compliance in SP-A(-/-) mice were unaltered. At the highest concentration tested, surfactant from SP-A(-/-) mice produced the same surface tension as (+/+) mice. At lower concentrations, minimum surface tensions were higher for SP-A(-/-) mice. At the ultrastructural level, type II cell morphology was the same in SP-A(+/+) and (-/-) mice. While alveolar phospholipid pool sizes were unperturbed, tubular myelin figures were decreased in the lungs of SP-A(-/-) mice. A null mutation of the murine SP-A gene interferes with the formation of tubular myelin without detectably altering postnatal survival or pulmonary function.
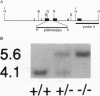
Full text
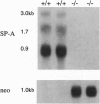
PDF


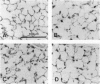
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastacky J., Lee C. Y., Goerke J., Koushafar H., Yager D., Kenaga L., Speed T. P., Chen Y., Clements J. A. Alveolar lining layer is thin and continuous: low-temperature scanning electron microscopy of rat lung. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1995 Nov;79(5):1615–1628. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1995.79.5.1615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. C., Wert S. E., Bachurski C. J., Stahlman M. T., Stripp B. R., Weaver T. E., Whitsett J. A. Targeted disruption of the surfactant protein B gene disrupts surfactant homeostasis, causing respiratory failure in newborn mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 15;92(17):7794–7798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockshutt A. M., Weitz J., Possmayer F. Pulmonary surfactant-associated protein A enhances the surface activity of lipid extract surfactant and reverses inhibition by blood proteins in vitro. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 11;29(36):8424–8429. doi: 10.1021/bi00488a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs L. G., Wright J. R., Hawgood S., Gonzalez R., Venstrom K., Nellenbogen J. Pulmonary surfactant and its components inhibit secretion of phosphatidylcholine from cultured rat alveolar type II cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1010–1014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dranoff G., Crawford A. D., Sadelain M., Ream B., Rashid A., Bronson R. T., Dickersin G. R., Bachurski C. J., Mark E. L., Whitsett J. A. Involvement of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in pulmonary homeostasis. Science. 1994 Apr 29;264(5159):713–716. doi: 10.1126/science.8171324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor C. D., McCormack F. X., Voelker D. R., McGowan S. E., Schlesinger L. S. Pulmonary surfactant protein A mediates enhanced phagocytosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by a direct interaction with human macrophages. J Immunol. 1995 Dec 1;155(11):5343–5351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawgood S., Benson B. J., Hamilton R. L., Jr Effects of a surfactant-associated protein and calcium ions on the structure and surface activity of lung surfactant lipids. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):184–190. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawgood S., Clements J. A. Pulmonary surfactant and its apoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI114670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami M., Jobe A., Glatz T. Surface activity following natural surfactant treatment in premature lambs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Aug;51(2):306–312. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.2.306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami M., Lewis J. F., Tabor B., Rider E. D., Jobe A. H. Surfactant protein A metabolism in preterm ventilated lambs. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 1):L765–L772. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.6.L765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami M., Ueda T., Hull W., Whitsett J. A., Mulligan R. C., Dranoff G., Jobe A. H. Surfactant metabolism in transgenic mice after granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor ablation. Am J Physiol. 1996 Apr;270(4 Pt 1):L650–L658. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1996.270.4.L650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobe A., Kirkpatrick E., Gluck L. Labeling of phospholipids in the surfactant and subcellular fractions of rabbit lung. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3810–3816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoor A., Stahlman M. T., Gray M. E., Whitsett J. A. Temporal-spatial distribution of SP-B and SP-C proteins and mRNAs in developing respiratory epithelium of human lung. J Histochem Cytochem. 1994 Sep;42(9):1187–1199. doi: 10.1177/42.9.8064126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korfhagen T. R., Bruno M. D., Glasser S. W., Ciraolo P. J., Whitsett J. A., Lattier D. L., Wikenheiser K. A., Clark J. C. Murine pulmonary surfactant SP-A gene: cloning, sequence, and transcriptional activity. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 1):L546–L554. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.263.5.L546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. J., Nellenbogen J., Clements J. A. Isolation of disaturated phosphatidylcholine with osmium tetroxide. J Lipid Res. 1976 May;17(3):281–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. J., D'Amore-Bruno M. A., Korfhagen T. R., Glasser S. W., Whitsett J. A., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Chromosomal localization of three pulmonary surfactant protein genes in the mouse. Genomics. 1992 Feb;12(2):388–393. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90389-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardell E. A., Brody J. S. Determinants of mechanical properties of rat lung during postnatal development. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Jul;53(1):140–148. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.1.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pison U., Max M., Neuendank A., Weissbach S., Pietschmann S. Host defence capacities of pulmonary surfactant: evidence for 'non-surfactant' functions of the surfactant system. Eur J Clin Invest. 1994 Sep;24(9):586–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1994.tb01110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Basset G., Lecossier D., O'Donnell K. M., Pinkston P., Martin P. G., Crystal R. G. Estimation of volume of epithelial lining fluid recovered by lavage using urea as marker of dilution. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Feb;60(2):532–538. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.2.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. R., Ross G. F., Singleton F. M., Dingle S., Whitsett J. A. Surfactant-associated protein inhibits phospholipid secretion from type II cells. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Aug;63(2):692–698. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.2.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. F., Notter R. H., Meuth J., Whitsett J. A. Phospholipid binding and biophysical activity of pulmonary surfactant-associated protein (SAP)-35 and its non-collagenous COOH-terminal domains. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14283–14291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavkin H. C., Johnson R., Oliver P., Bringas P., Jr, Don-Wheeler G., Mayo M., Whitsett J. A. Lamellar body formation precedes pulmonary surfactant apoprotein expression during embryonic mouse lung development in vivo and in vitro. Differentiation. 1989 Sep;41(3):223–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1989.tb00751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Fujita Y., Kogishi K. Reconstitution of tubular myelin from synthetic lipids and proteins associated with pig pulmonary surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Jul;140(1):75–81. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Robinson S. L., Borchelt J., Wright J. R. Human pulmonary surfactant protein (SP-A), a protein structurally homologous to C1q, can enhance FcR- and CR1-mediated phagocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13923–13928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Iwaarden J. F., Pikaar J. C., Storm J., Brouwer E., Verhoef J., Oosting R. S., van Golde L. M., van Strijp J. A. Binding of surfactant protein A to the lipid A moiety of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Biochem J. 1994 Oct 15;303(Pt 2):407–411. doi: 10.1042/bj3030407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorbroker D. K., Profitt S. A., Nogee L. M., Whitsett J. A. Aberrant processing of surfactant protein C in hereditary SP-B deficiency. Am J Physiol. 1995 Apr;268(4 Pt 1):L647–L656. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1995.268.4.L647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R. Scaling of structural and functional variables in the respiratory system. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:147–159. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.001051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. T., Damm D., Miller J., Spratt K., Schilling J., Hawgood S., Benson B., Cordell B. Isolation and characterization of the human pulmonary surfactant apoprotein gene. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):361–363. doi: 10.1038/317361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. R., Wager R. E., Hawgood S., Dobbs L., Clements J. A. Surfactant apoprotein Mr = 26,000-36,000 enhances uptake of liposomes by type II cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2888–2894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]