Abstract
Protein tyrosine phosphorylation and dephosphorylation are key regulatory events in T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling. We investigated the role of the tyrosine phosphatase SHPTP1 in TCR signaling by analysis of TCR signal transduction in motheaten (me/me) mice, which lack SHPTP1 expression. As revealed by flow cytometric analysis, thymocyte development was normal in me/me mice. However, me/me thymocytes hyperproliferated (3-to 5-fold) in response to TCR stimulation, whereas their response to interleukin 2 stimulation was unchanged compared with normal thymocytes. TCR-induced hyperproliferation of me/me thymocytes was reproduced in purified single-positive thymocytes. Moreover, me/me thymocytes produced increased amounts of interleukin 2 production upon TCR stimulation. Biochemical analysis revealed that, in response to TCR or TCR/CD4 stimulation, thymocytes lacking SHPTP1 showed increased tyrosyl phosphorylation of several cellular substrates, which correlated with increased activation of the src-family kinases Lck and Fyn. Taken together, our data suggest that SHPTP1 is an important negative regulator of TCR signaling, acting at least in part to inactivate Lck and Fyn.
Full text
PDF



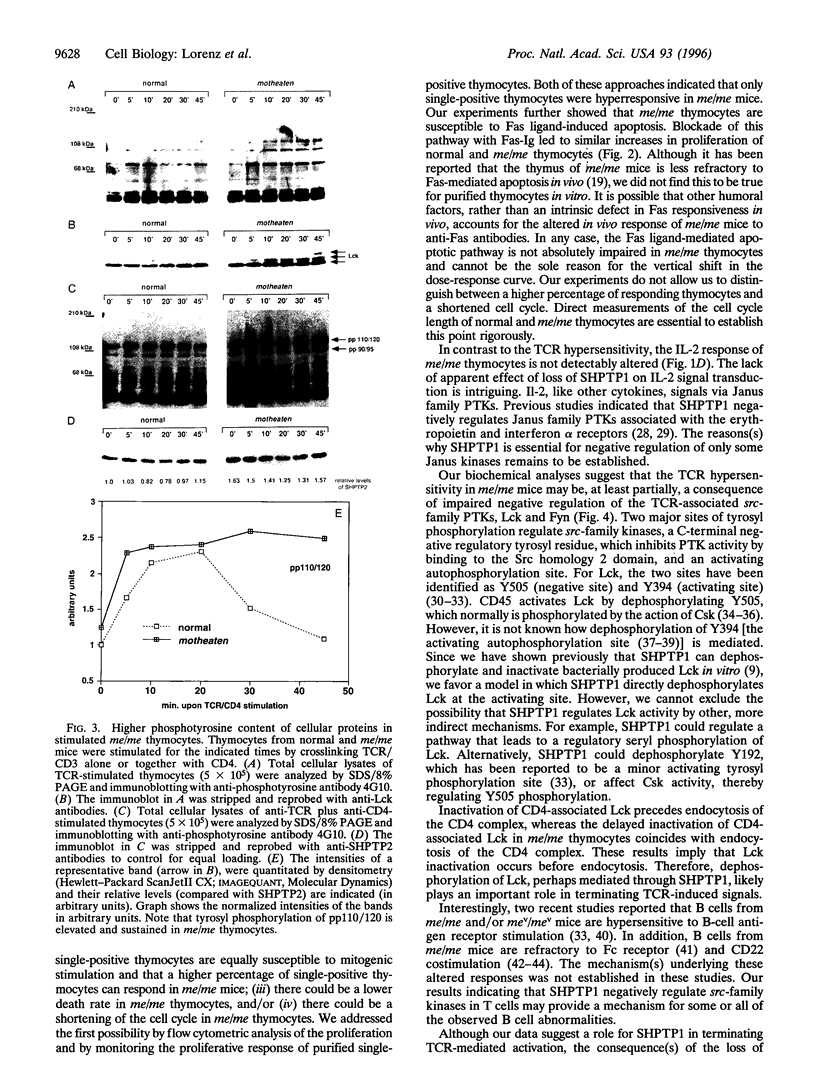

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham K. M., Levin S. D., Marth J. D., Forbush K. A., Perlmutter R. M. Delayed thymocyte development induced by augmented expression of p56lck. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1421–1432. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham K. M., Levin S. D., Marth J. D., Forbush K. A., Perlmutter R. M. Thymic tumorigenesis induced by overexpression of p56lck. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3977–3981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham N., Veillette A. Activation of p56lck through mutation of a regulatory carboxy-terminal tyrosine residue requires intact sites of autophosphorylation and myristylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5197–5206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adachi M., Fischer E. H., Ihle J., Imai K., Jirik F., Neel B., Pawson T., Shen S., Thomas M., Ullrich A. Mammalian SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatases. Cell. 1996 Apr 5;85(1):15–15. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amrein K. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of a site of tyrosine phosphorylation in the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase, p56lck, reveals its oncogenic potential in fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4247–4251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. J., Levin S. D., Perlmutter R. M. Involvement of the protein tyrosine kinase p56lck in T cell signaling and thymocyte development. Adv Immunol. 1994;56:151–178. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60451-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. J., Perlmutter R. M. A signaling pathway governing early thymocyte maturation. Immunol Today. 1995 Feb;16(2):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner T., Mogil R. J., LaFace D., Yoo N. J., Mahboubi A., Echeverri F., Martin S. J., Force W. R., Lynch D. H., Ware C. F. Cell-autonomous Fas (CD95)/Fas-ligand interaction mediates activation-induced apoptosis in T-cell hybridomas. Nature. 1995 Feb 2;373(6513):441–444. doi: 10.1038/373441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. A., Klinman N. R. Phosphotyrosine-dependent association between CD22 and protein tyrosine phosphatase 1C. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Jun;25(6):1573–1579. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke M. P., Abraham K. M., Forbush K. A., Perlmutter R. M. Regulation of T cell receptor signaling by a src family protein-tyrosine kinase (p59fyn). Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90162-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couture C., Baier G., Oetken C., Williams S., Telford D., Marie-Cardine A., Baier-Bitterlich G., Fischer S., Burn P., Altman A. Activation of p56lck by p72syk through physical association and N-terminal tyrosine phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;14(8):5249–5258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ambrosio D., Hippen K. L., Minskoff S. A., Mellman I., Pani G., Siminovitch K. A., Cambier J. C. Recruitment and activation of PTP1C in negative regulation of antigen receptor signaling by Fc gamma RIIB1. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):293–297. doi: 10.1126/science.7716523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Chen H. E., Goelz S., Larner A. C., Neel B. G. Differential regulation of the alpha/beta interferon-stimulated Jak/Stat pathway by the SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase SHPTP1. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;15(12):7050–7058. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.12.7050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson W. F., Morse H. C., 3rd, Sharrow S. O., Chused T. M. Phenotypic and functional effects of the motheaten gene on murine B and T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):884–891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhein J., Walczak H., Bäumler C., Debatin K. M., Krammer P. H. Autocrine T-cell suicide mediated by APO-1/(Fas/CD95) Nature. 1995 Feb 2;373(6513):438–441. doi: 10.1038/373438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doody G. M., Justement L. B., Delibrias C. C., Matthews R. J., Lin J., Thomas M. L., Fearon D. T. A role in B cell activation for CD22 and the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP. Science. 1995 Jul 14;269(5221):242–244. doi: 10.1126/science.7618087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajewski T. F., Qian D., Fields P., Fitch F. W. Anergic T-lymphocyte clones have altered inositol phosphate, calcium, and tyrosine kinase signaling pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):38–42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. C., Shultz L. D. Motheaten, an immunodeficient mutant of the mouse. I. Genetics and pathology. J Hered. 1975 Sep-Oct;66(5):250–258. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a108625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greiner D. L., Goldschneider I., Komschlies K. L., Medlock E. S., Bollum F. J., Schultz L. Defective lymphopoiesis in bone marrow of motheaten (me/me) and viable motheaten (mev/mev) mutant mice. I. Analysis of development of prothymocytes, early B lineage cells, and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-positive cells. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1129–1144. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haar J. L., Popp J. D., Shultz L. D. Defective in vitro migratory capacity of bone marrow cells from viable motheaten mice in response to normal thymus culture supernatants. Exp Hematol. 1989 Jan;17(1):21–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr Thymic selection: two pathways to life and two to death. Immunity. 1994 Apr;1(1):3–6. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju S. T., Panka D. J., Cui H., Ettinger R., el-Khatib M., Sherr D. H., Stanger B. Z., Marshak-Rothstein A. Fas(CD95)/FasL interactions required for programmed cell death after T-cell activation. Nature. 1995 Feb 2;373(6513):444–448. doi: 10.1038/373444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingmüller U., Lorenz U., Cantley L. C., Neel B. G., Lodish H. F. Specific recruitment of SH-PTP1 to the erythropoietin receptor causes inactivation of JAK2 and termination of proliferative signals. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo G. C., Manyak C. L., Dasch J., Ellingsworth L., Shultz L. D. Suppressive effects of monocytic cells and transforming growth factor-beta on natural killer cell differentiation in autoimmune viable motheaten mutant mice. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1194–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lankester A. C., van Schijndel G. M., van Lier R. A. Hematopoietic cell phosphatase is recruited to CD22 following B cell antigen receptor ligation. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 1;270(35):20305–20308. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.35.20305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz U., Ravichandran K. S., Pei D., Walsh C. T., Burakoff S. J., Neel B. G. Lck-dependent tyrosyl phosphorylation of the phosphotyrosine phosphatase SH-PTP1 in murine T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1824–1834. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Cooper J. A., King C. S., Ziegler S. F., Tinker D. A., Overell R. W., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. Neoplastic transformation induced by an activated lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (pp56lck). Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):540–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Lewis D. B., Cooke M. P., Mellins E. D., Gearn M. E., Samelson L. E., Wilson C. B., Miller A. D., Perlmutter R. M. Lymphocyte activation provokes modification of a lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (p56lck). J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2430–2437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. J., Bowne D. B., Flores E., Thomas M. L. Characterization of hematopoietic intracellular protein tyrosine phosphatases: description of a phosphatase containing an SH2 domain and another enriched in proline-, glutamic acid-, serine-, and threonine-rich sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2396–2405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Altman A. Dephosphorylation and activation of the T cell tyrosine kinase pp56lck by the leukocyte common antigen (CD45). Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):809–813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Golstein P. The Fas death factor. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1449–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.7533326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard H. L., Shackelford D. A., Hurley T. R., Johnson P., Hyman R., Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S. Expression of CD45 alters phosphorylation of the lck-encoded tyrosine protein kinase in murine lymphoma T-cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8959–8963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pani G., Kozlowski M., Cambier J. C., Mills G. B., Siminovitch K. A. Identification of the tyrosine phosphatase PTP1C as a B cell antigen receptor-associated protein involved in the regulation of B cell signaling. J Exp Med. 1995 Jun 1;181(6):2077–2084. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.6.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plutzky J., Neel B. G., Rosenberg R. D. Isolation of a src homology 2-containing tyrosine phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1123–1127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. H., Bastien L., Posner B. I., Chrétien P. A protein-tyrosine phosphatase with sequence similarity to the SH2 domain of the protein-tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):736–739. doi: 10.1038/352736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shultz L. D., Schweitzer P. A., Rajan T. V., Yi T., Ihle J. N., Matthews R. J., Thomas M. L., Beier D. R. Mutations at the murine motheaten locus are within the hematopoietic cell protein-tyrosine phosphatase (Hcph) gene. Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1445–1454. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90369-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shultz L. D., Sidman C. L. Genetically determined murine models of immunodeficiency. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:367–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. L., Shultz L. D., Unanue E. R. The mouse mutant "motheaten." II. Functional studies of the immune system. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2399–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan-Lancaster J., Shaw A. S., Rothbard J. B., Allen P. M. Partial T cell signaling: altered phospho-zeta and lack of zap70 recruitment in APL-induced T cell anergy. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):913–922. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotirellis N., Johnson T. M., Hibbs M. L., Stanley I. J., Stanley E., Dunn A. R., Cheng H. C. Autophosphorylation induces autoactivation and a decrease in the Src homology 2 domain accessibility of the Lyn protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 15;270(50):29773–29780. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.50.29773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su X., Zhou T., Wang Z., Yang P., Jope R. S., Mountz J. D. Defective expression of hematopoietic cell protein tyrosine phosphatase (HCP) in lymphoid cells blocks Fas-mediated apoptosis. Immunity. 1995 Apr;2(4):353–362. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Superti-Furga G., Fumagalli S., Koegl M., Courtneidge S. A., Draetta G. Csk inhibition of c-Src activity requires both the SH2 and SH3 domains of Src. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2625–2634. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05923.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge I. S., Thomas M. L. CD45: an emerging role as a protein tyrosine phosphatase required for lymphocyte activation and development. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:85–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsui H. W., Siminovitch K. A., de Souza L., Tsui F. W. Motheaten and viable motheaten mice have mutations in the haematopoietic cell phosphatase gene. Nat Genet. 1993 Jun;4(2):124–129. doi: 10.1038/ng0693-124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Fournel M. The CD4 associated tyrosine protein kinase p56lck is positively regulated through its site of autophosphorylation. Oncogene. 1990 Oct;5(10):1455–1462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil R., Veillette A. Intramolecular and extramolecular mechanisms repress the catalytic function of p56lck in resting T-lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 9;269(36):22830–22838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Littman D. R. Signal transduction by lymphocyte antigen receptors. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. T cell antigen receptor signal transduction: a tale of tails and cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):209–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90221-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi T. L., Cleveland J. L., Ihle J. N. Protein tyrosine phosphatase containing SH2 domains: characterization, preferential expression in hematopoietic cells, and localization to human chromosome 12p12-p13. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):836–846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva A. J., Janssen O., Rudd C. E. T cell receptor zeta/CD3-p59fyn(T)-associated p120/130 binds to the SH2 domain of p59fyn(T). J Exp Med. 1993 Dec 1;178(6):2107–2113. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.6.2107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]