Abstract
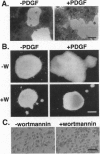
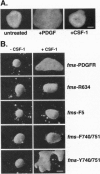
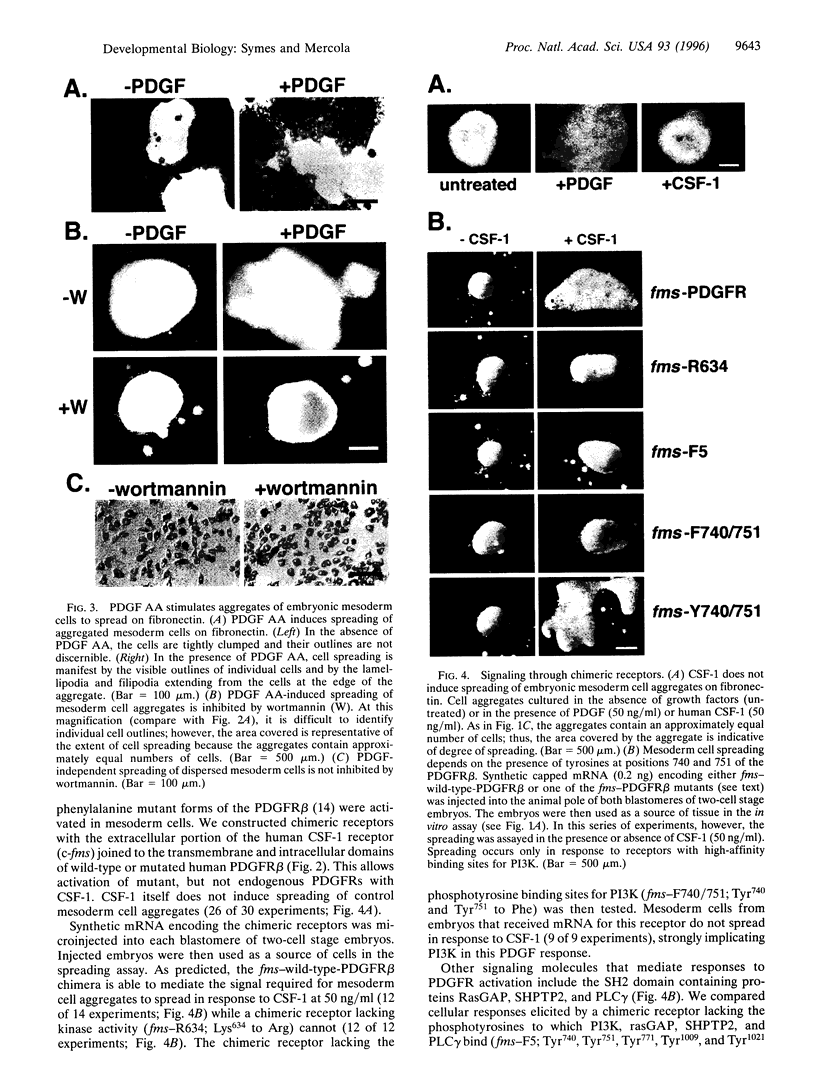
Abnormal mesoderm movement, leading to defects in axial organization, is observed in mouse and Xenopus laevis embryos deprived of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) AA signaling. However, neither the cellular response to PDGF nor the signaling pathways involved are understood. Herein we describe an in vitro assay to examine the direct effect of PDGF AA on aggregates of Xenopus embryonic mesoderm cells. We find that PDGF AA stimulates aggregates to spread on fibronectin. This behavior is similar to that of migrating mesoderm cells in vivo that spread and form lamellipodia and filipodia on contact with fibronectin-rich extracellular matrix. We go on to show two lines of evidence that implicate phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) as an important component of PDGF-induced mesoderm cell spreading. (i) The fungal metabolite wortmannin, which inhibits signaling by PI3K, blocks mesoderm spreading in response to PDGF AA. (ii) Activation of a series of receptors with specific tyrosine-to-phenylalanine mutations revealed PDGF-induced spreading of mesoderm cells depends on PI3K but not on other signaling molecules that interact with PDGF receptors including phospholipase C gamma, Ras GTPase-activating protein, and phosphotyrosine phosphatase SHPTP2. These results indicate that a PDGF signal, medicated by PI3K, can facilitate embryonic mesoderm cell spreading on fibronectin. We propose that PDGF, produced by the ectoderm, influences the adhesive properties of the adjacent mesoderm cells during gastrulation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcaro A., Wymann M. P. Wortmannin is a potent phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor: the role of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate in neutrophil responses. Biochem J. 1993 Dec 1;296(Pt 2):297–301. doi: 10.1042/bj2960297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ataliotis P., Symes K., Chou M. M., Ho L., Mercola M. PDGF signalling is required for gastrulation of Xenopus laevis. Development. 1995 Sep;121(9):3099–3110. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.9.3099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornfeldt K. E., Raines E. W., Graves L. M., Skinner M. P., Krebs E. G., Ross R. Platelet-derived growth factor. Distinct signal transduction pathways associated with migration versus proliferation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Sep 7;766:416–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb26691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. L., Duckworth B. C., Auger K. R., Cohen B., Schaffhausen B. S., Cantley L. C. Purification and characterization of phosphoinositide 3-kinase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19704–19711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson-Welsh L. Platelet-derived growth factor receptor signals. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 23;269(51):32023–32026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindarajan V., Ramachandran R. K., George J. M., Shakes D. C., Tomlinson C. R. An ECM-bound, PDGF-like growth factor and a TGF-alpha-like growth factor are required for gastrulation and spiculogenesis in the Lytechinus embryo. Dev Biol. 1995 Dec;172(2):541–551. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.8059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. B., Smith J. C., Gerhart J. C. Slow emergence of a multithreshold response to activin requires cell-contact-dependent sharpening but not prepattern. Development. 1994 Aug;120(8):2271–2278. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.8.2271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. B., Smith J. C. Graded changes in dose of a Xenopus activin A homologue elicit stepwise transitions in embryonic cell fate. Nature. 1990 Sep 27;347(6291):391–394. doi: 10.1038/347391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Eguinoa A., Qiu R. G., Stokoe D., Cooke F. T., Walters R., Wennström S., Claesson-Welsh L., Evans T., Symons M. PDGF stimulates an increase in GTP-Rac via activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Curr Biol. 1995 Apr 1;5(4):393–403. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai F., Ito K., Todaka M., Hayashi H., Kamohara S., Ishii K., Okada T., Hazeki O., Ui M., Ebina Y. Insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation is relevant to the phosphorylation of IRS-1 and the activity of PI3-kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Sep 15;195(2):762–768. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A. Receptor tyrosine kinases and their targets. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):5–14. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinashi T., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T., Takatsu K., Springer T. A. Receptor tyrosine kinase stimulates cell-matrix adhesion by phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase and phospholipase C-gamma 1 pathways. Blood. 1995 Sep 15;86(6):2086–2090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacsovics T. J., Bachelot C., Toker A., Vlahos C. J., Duckworth B., Cantley L. C., Hartwig J. H. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibition spares actin assembly in activating platelets but reverses platelet aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 12;270(19):11358–11366. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.19.11358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. Signal transduction. How receptors turn Ras on. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):15–16. doi: 10.1038/363015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori S., Rönnstrand L., Yokote K., Engström A., Courtneidge S. A., Claesson-Welsh L., Heldin C. H. Identification of two juxtamembrane autophosphorylation sites in the PDGF beta-receptor; involvement in the interaction with Src family tyrosine kinases. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2257–2264. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05879.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle D. L., Martin-DeLeon P., Hough R. B., Bućan M. Structural analysis of chromosomal rearrangements associated with the developmental mutations Ph, W19H, and Rw on mouse chromosome 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):7237–7241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura R., Li W., Kashishian A., Mondino A., Zhou M., Cooper J., Schlessinger J. Two signaling molecules share a phosphotyrosine-containing binding site in the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6889–6896. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Urtreger A., Bedford M. T., Do M. S., Eisenbach L., Lonai P. Developmental expression of the alpha receptor for platelet-derived growth factor, which is deleted in the embryonic lethal Patch mutation. Development. 1992 May;115(1):289–303. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.1.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Urtreger A., Lonai P. Platelet-derived growth factor-A and its receptor are expressed in separate, but adjacent cell layers of the mouse embryo. Development. 1992 Aug;115(4):1045–1058. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.4.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmieri S. L., Payne J., Stiles C. D., Biggers J. D., Mercola M. Expression of mouse PDGF-A and PDGF alpha-receptor genes during pre- and post-implantation development: evidence for a developmental shift from an autocrine to a paracrine mode of action. Mech Dev. 1992 Dec;39(3):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(92)90045-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng H. B. Xenopus laevis: Practical uses in cell and molecular biology. Solutions and protocols. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;36:657–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran R. K., Govindarajan V., Seid C. A., Patil S., Tomlinson C. R. Role for platelet-derived growth factor-like and epidermal growth factor-like signaling pathways in gastrulation and spiculogenesis in the Lytechinus sea urchin embryo. Dev Dyn. 1995 Sep;204(1):77–88. doi: 10.1002/aja.1002040110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J. Membrane ruffling and signal transduction. Bioessays. 1994 May;16(5):321–327. doi: 10.1002/bies.950160506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatteman G. C., Morrison-Graham K., van Koppen A., Weston J. A., Bowen-Pope D. F. Regulation and role of PDGF receptor alpha-subunit expression during embryogenesis. Development. 1992 May;115(1):123–131. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. A., Seldin M. F., Martinez L., Watson M. L., Choudhury G. G., Lalley P. A., Pierce J., Aaronson S., Barker J., Naylor S. L. Mouse platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha gene is deleted in W19H and patch mutations on chromosome 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4811–4815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Slack J. M. Dorsalization and neural induction: properties of the organizer in Xenopus laevis. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1983 Dec;78:299–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Symes K., Hynes R. O., DeSimone D. Mesoderm induction and the control of gastrulation in Xenopus laevis: the roles of fibronectin and integrins. Development. 1990 Feb;108(2):229–238. doi: 10.1242/dev.108.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson D. A., Mercola M., Anderson E., Wang C. Y., Stiles C. D., Bowen-Pope D. F., Chapman V. M. Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha-subunit gene (Pdgfra) is deleted in the mouse patch (Ph) mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):6–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symes K., Yordán C., Mercola M. Morphological differences in Xenopus embryonic mesodermal cells are specified as an early response to distinct threshold concentrations of activin. Development. 1994 Aug;120(8):2339–2346. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.8.2339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valius M., Kazlauskas A. Phospholipase C-gamma 1 and phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase are the downstream mediators of the PDGF receptor's mitogenic signal. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):321–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90232-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlahos C. J., Matter W. F., Hui K. Y., Brown R. F. A specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, 2-(4-morpholinyl)-8-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (LY294002). J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):5241–5248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennström S., Hawkins P., Cooke F., Hara K., Yonezawa K., Kasuga M., Jackson T., Claesson-Welsh L., Stephens L. Activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase is required for PDGF-stimulated membrane ruffling. Curr Biol. 1994 May 1;4(5):385–393. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennström S., Siegbahn A., Yokote K., Arvidsson A. K., Heldin C. H., Mori S., Claesson-Welsh L. Membrane ruffling and chemotaxis transduced by the PDGF beta-receptor require the binding site for phosphatidylinositol 3' kinase. Oncogene. 1994 Feb;9(2):651–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Downes C. P., Keeler M., Keller T., Cantley L. Type I phosphatidylinositol kinase makes a novel inositol phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):644–646. doi: 10.1038/332644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. A., Melton D. A. Mesodermal patterning by an inducer gradient depends on secondary cell-cell communication. Curr Biol. 1994 Aug 1;4(8):676–686. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00152-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wymann M., Arcaro A. Platelet-derived growth factor-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation mediates actin rearrangements in fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1994 Mar 15;298(Pt 3):517–520. doi: 10.1042/bj2980517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano H., Nakanishi S., Kimura K., Hanai N., Saitoh Y., Fukui Y., Nonomura Y., Matsuda Y. Inhibition of histamine secretion by wortmannin through the blockade of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in RBL-2H3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25846–25856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J. C., Li W., Wang L. M., Uren A., Pierce J. H., Heidaran M. A. Differential requirement of a motif within the carboxyl-terminal domain of alpha-platelet-derived growth factor (alpha PDGF) receptor for PDGF focus forming activity chemotaxis, or growth. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 31;270(13):7033–7036. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.13.7033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]