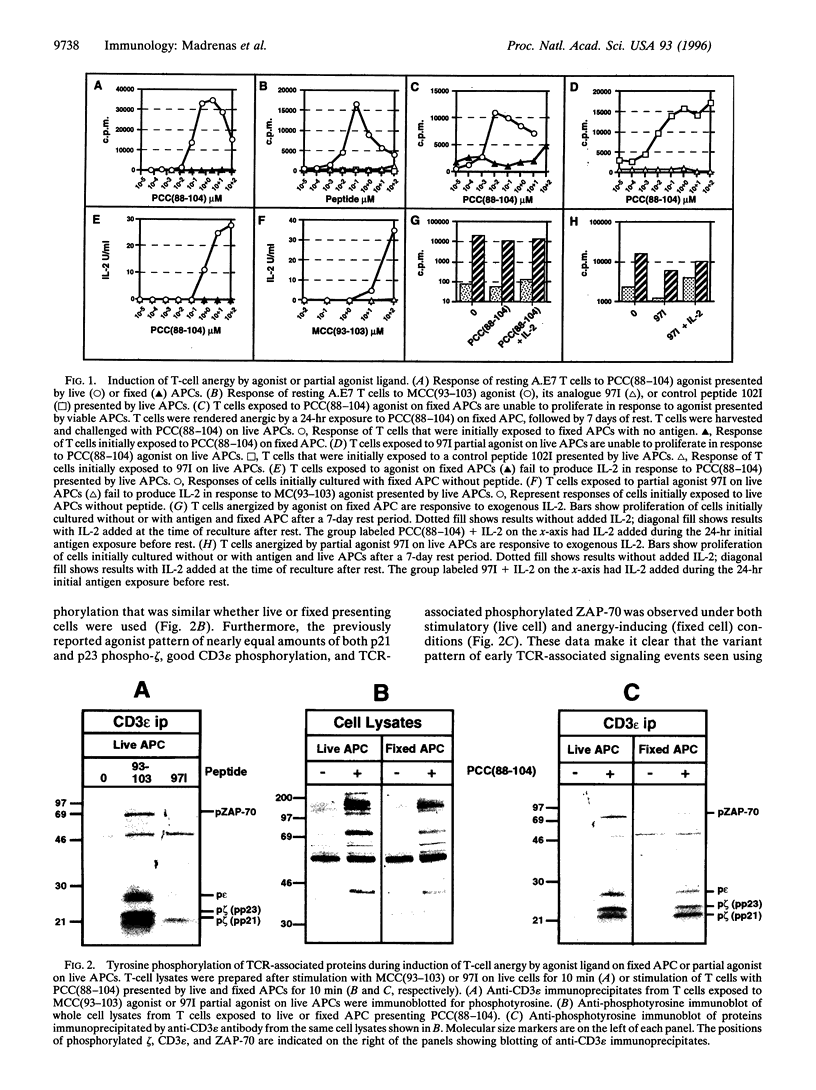
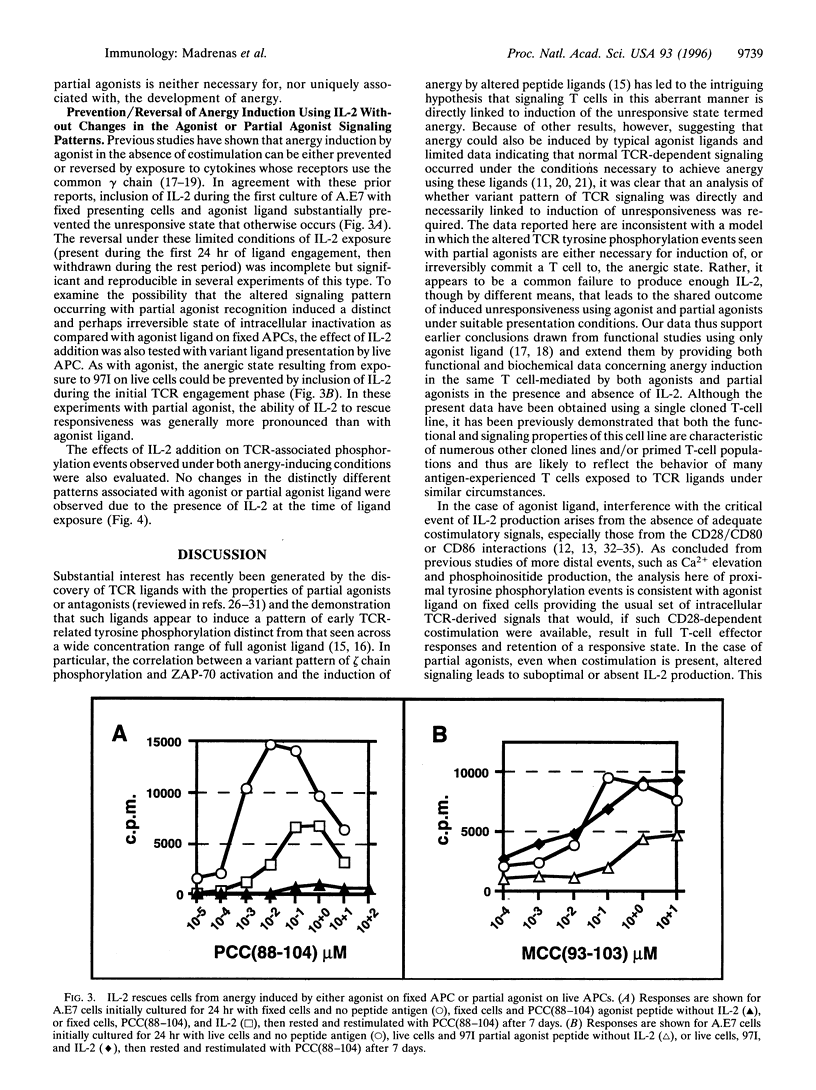
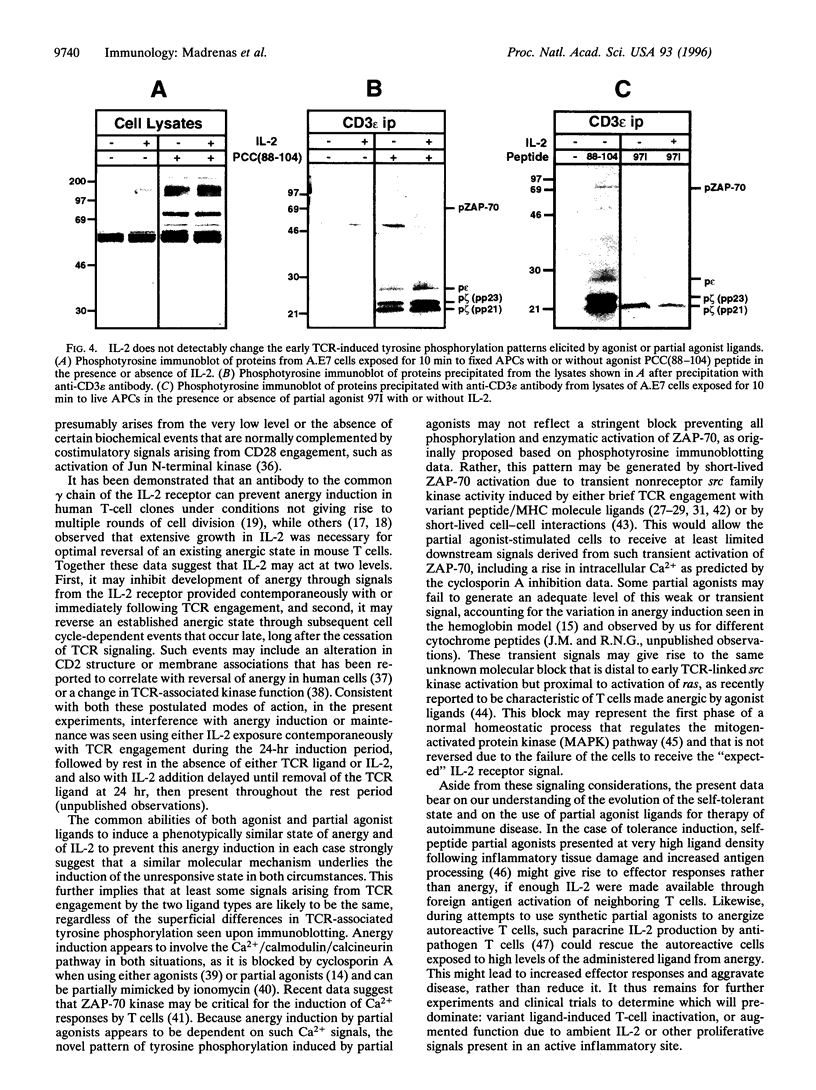
Abstract
Full activation of T cells requires signaling through the T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) and additional surface molecules interacting with ligands on the antigen-presenting cell. TCR recognition of agonist ligands in the absence of accessory signals frequently results in the induction of a state of unresponsiveness termed anergy. However, even in the presence of costimulation, anergy can be induced by TCR partial agonists. The unique pattern of early receptor-induced tyrosine phosphorylation events induced by partial agonists has led to the hypothesis that altered TCR signaling is directly responsible for the development of anergy. Here we show that anergy induction is neither correlated with nor irreversibly determined by the pattern of early TCR-induced phosphorylation. Rather, it appears to result from the absence of downstream events related to interleukin 2 receptor occupancy and/or cell division. This implies that the anergic state can be manipulated independently of the precise pattern of early biochemical changes following TCR occupancy, a finding with implications for understanding the induction of self-tolerance and the use of partial agonist ligands in the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beverly B., Kang S. M., Lenardo M. J., Schwartz R. H. Reversal of in vitro T cell clonal anergy by IL-2 stimulation. Int Immunol. 1992 Jun;4(6):661–671. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.6.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boussiotis V. A., Barber D. L., Nakarai T., Freeman G. J., Gribben J. G., Bernstein G. M., D'Andrea A. D., Ritz J., Nadler L. M. Prevention of T cell anergy by signaling through the gamma c chain of the IL-2 receptor. Science. 1994 Nov 11;266(5187):1039–1042. doi: 10.1126/science.7973657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boussiotis V. A., Freeman G. J., Griffin J. D., Gray G. S., Gribben J. G., Nadler L. M. CD2 is involved in maintenance and reversal of human alloantigen-specific clonal anergy. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1665–1673. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkly L. C., Lo D., Kanagawa O., Brinster R. L., Flavell R. A. T-cell tolerance by clonal anergy in transgenic mice with nonlymphoid expression of MHC class II I-E. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):564–566. doi: 10.1038/342564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho E. A., Riley M. P., Sillman A. L., Quill H. Altered protein tyrosine phosphorylation in anergic Th1 cells. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 1;151(1):20–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchfield J. M., Racke M. K., Zúiga-Pflücker J. C., Cannella B., Raine C. S., Goverman J., Lenardo M. J. T cell deletion in high antigen dose therapy of autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1139–1143. doi: 10.1126/science.7509084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRESSER D. W. Specific inhibition of antibody production. II. Paralysis induced in adult mice by small quantities of protein antigen. Immunology. 1962 May;5:378–388. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSilva D. R., Urdahl K. B., Jenkins M. K. Clonal anergy is induced in vitro by T cell receptor occupancy in the absence of proliferation. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 15;147(10):3261–3267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding L., Linsley P. S., Huang L. Y., Germain R. N., Shevach E. M. IL-10 inhibits macrophage costimulatory activity by selectively inhibiting the up-regulation of B7 expression. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 1;151(3):1224–1234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evavold B. D., Sloan-Lancaster J., Allen P. M. Tickling the TCR: selective T-cell functions stimulated by altered peptide ligands. Immunol Today. 1993 Dec;14(12):602–609. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90200-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields P. E., Gajewski T. F., Fitch F. W. Blocked Ras activation in anergic CD4+ T cells. Science. 1996 Mar 1;271(5253):1276–1278. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5253.1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman G. J., Borriello F., Hodes R. J., Reiser H., Gribben J. G., Ng J. W., Kim J., Goldberg J. M., Hathcock K., Laszlo G. Murine B7-2, an alternative CTLA4 counter-receptor that costimulates T cell proliferation and interleukin 2 production. J Exp Med. 1993 Dec 1;178(6):2185–2192. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.6.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand E. W., Weinberg K., Mazer B. D., Kadlecek T. A., Weiss A. Absence of ZAP-70 prevents signaling through the antigen receptor on peripheral blood T cells but not on thymocytes. J Exp Med. 1995 Oct 1;182(4):1057–1065. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.4.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimmi C. D., Freeman G. J., Gribben J. G., Gray G., Nadler L. M. Human T-cell clonal anergy is induced by antigen presentation in the absence of B7 costimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6586–6590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimmi C. D., Freeman G. J., Gribben J. G., Sugita K., Freedman A. S., Morimoto C., Nadler L. M. B-cell surface antigen B7 provides a costimulatory signal that induces T cells to proliferate and secrete interleukin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6575–6579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding F. A., McArthur J. G., Gross J. A., Raulet D. H., Allison J. P. CD28-mediated signalling co-stimulates murine T cells and prevents induction of anergy in T-cell clones. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):607–609. doi: 10.1038/356607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathcock K. S., Laszlo G., Dickler H. B., Bradshaw J., Linsley P., Hodes R. J. Identification of an alternative CTLA-4 ligand costimulatory for T cell activation. Science. 1993 Nov 5;262(5135):905–907. doi: 10.1126/science.7694361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht T. T., Longo D. L., Matis L. A. The relationship between immune interferon production and proliferation in antigen-specific, MHC-restricted T cell lines and clones. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1049–1055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson S. C., Bevan M. J. T cell receptor antagonists and partial agonists. Immunity. 1995 Jan;2(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins M. K., Ashwell J. D., Schwartz R. H. Allogeneic non-T spleen cells restore the responsiveness of normal T cell clones stimulated with antigen and chemically modified antigen-presenting cells. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3324–3330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins M. K., Pardoll D. M., Mizuguchi J., Chused T. M., Schwartz R. H. Molecular events in the induction of a nonresponsive state in interleukin 2-producing helper T-lymphocyte clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5409–5413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins M. K., Schwartz R. H. Antigen presentation by chemically modified splenocytes induces antigen-specific T cell unresponsiveness in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):302–319. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty K. J., Cunningham A. J. A new analysis of allogeneic interactions. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1975 Feb;53(1):27–42. doi: 10.1038/icb.1975.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J. Interleukin-2 programs mouse alpha beta T lymphocytes for apoptosis. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):858–861. doi: 10.1038/353858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W., Whaley C. D., Mondino A., Mueller D. L. Blocked signal transduction to the ERK and JNK protein kinases in anergic CD4+ T cells. Science. 1996 Mar 1;271(5253):1272–1276. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5253.1272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Clark E. A., Ledbetter J. A. T-cell antigen CD28 mediates adhesion with B cells by interacting with activation antigen B7/BB-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5031–5035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madrenas J., Germain R. N. Variant TCR ligands: new insights into the molecular basis of antigen-dependent signal transduction and T-cell activation. Semin Immunol. 1996 Apr;8(2):83–101. doi: 10.1006/smim.1996.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madrenas J., Wange R. L., Wang J. L., Isakov N., Samelson L. E., Germain R. N. Zeta phosphorylation without ZAP-70 activation induced by TCR antagonists or partial agonists. Science. 1995 Jan 27;267(5197):515–518. doi: 10.1126/science.7824949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Lo D., Brinster R., Palmiter R., Burkly L., Flavell R. H., Kappler J. The effect of thymus environment on T cell development and tolerance. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):627–634. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90578-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui K., Boniface J. J., Steffner P., Reay P. A., Davis M. M. Kinetics of T-cell receptor binding to peptide/I-Ek complexes: correlation of the dissociation rate with T-cell responsiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12862–12866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller D. L., Jenkins M. K., Chiodetti L., Schwartz R. H. An intracellular calcium increase and protein kinase C activation fail to initiate T cell proliferation in the absence of a costimulatory signal. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):3701–3709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller D. L., Jenkins M. K., Schwartz R. H. An accessory cell-derived costimulatory signal acts independently of protein kinase C activation to allow T cell proliferation and prevent the induction of unresponsiveness. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;142(8):2617–2628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller D. L., Jenkins M. K., Schwartz R. H. Clonal expansion versus functional clonal inactivation: a costimulatory signalling pathway determines the outcome of T cell antigen receptor occupancy. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:445–480. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.002305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin S. X., Wise M., Cobbold S. P., Leong L., Kong Y. C., Parnes J. R., Waldmann H. Induction of tolerance in peripheral T cells with monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Dec;20(12):2737–2745. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronchese F., Schwartz R. H., Germain R. N. Functionally distinct subsites on a class II major histocompatibility complex molecule. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):254–256. doi: 10.1038/329254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salemi S., Caporossi A. P., Boffa L., Longobardi M. G., Barnaba V. HIVgp120 activates autoreactive CD4-specific T cell responses by unveiling of hidden CD4 peptides during processing. J Exp Med. 1995 Jun 1;181(6):2253–2257. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.6.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H. Acquisition of immunologic self-tolerance. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1073–1081. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sette A., Alexander J., Ruppert J., Snoke K., Franco A., Ishioka G., Grey H. M. Antigen analogs/MHC complexes as specific T cell receptor antagonists. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:413–431. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.002213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan-Lancaster J., Allen P. M. Significance of T-cell stimulation by altered peptide ligands in T cell biology. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995 Feb;7(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(95)80035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan-Lancaster J., Evavold B. D., Allen P. M. Induction of T-cell anergy by altered T-cell-receptor ligand on live antigen-presenting cells. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):156–159. doi: 10.1038/363156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan-Lancaster J., Shaw A. S., Rothbard J. B., Allen P. M. Partial T cell signaling: altered phospho-zeta and lack of zap70 recruitment in APL-induced T cell anergy. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):913–922. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su B., Jacinto E., Hibi M., Kallunki T., Karin M., Ben-Neriah Y. JNK is involved in signal integration during costimulation of T lymphocytes. Cell. 1994 Jun 3;77(5):727–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valitutti S., Dessing M., Aktories K., Gallati H., Lanzavecchia A. Sustained signaling leading to T cell activation results from prolonged T cell receptor occupancy. Role of T cell actin cytoskeleton. J Exp Med. 1995 Feb 1;181(2):577–584. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb S., Morris C., Sprent J. Extrathymic tolerance of mature T cells: clonal elimination as a consequence of immunity. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1249–1256. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90420-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wucherpfennig K. W., Strominger J. L. Molecular mimicry in T cell-mediated autoimmunity: viral peptides activate human T cell clones specific for myelin basic protein. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):695–705. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90348-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]