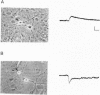
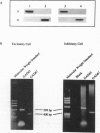
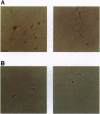
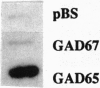
Abstract
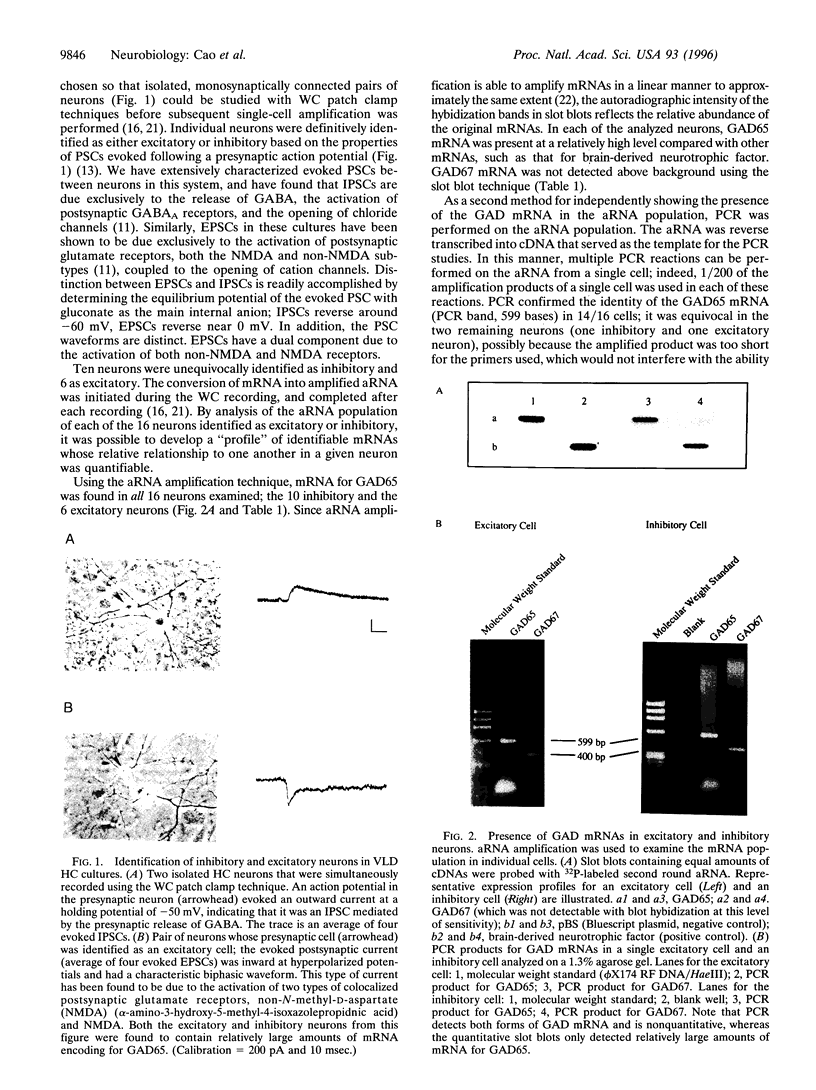
Neurons in very low density hippocampal cultures that are physiologically identified as either GABAergic inhibitory or glutamatergic excitatory all contain mRNA for the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) synthetic enzyme, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD), as detected by single cell mRNA amplification and PCR. However, consistent with the physiology, immunocytochemistry revealed that only a subset of the neurons stain for either GAD protein or GABA. A similar fraction hybridize with RNA probes for GAD65 and GAD67. Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons in slice preparations, which are traditionally thought to be excitatory, also contain mRNA for GAD65 and GAD67. Hippocampal neurons in culture did not contain mRNA for two other neurotransmitter synthesizing enzymes, tyrosine hydroxylase, and choline acetyl transferase. These data suggest that in some neurons, presumably the excitatory neurons, GAD mRNA is selectively regulated at the level of translation. We propose that neurotransmitter phenotype may be posttranscriptionally regulated and neurons may exhibit transient phenotypic plasticity in response to environmental influences.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. M., Verma M. Analytical procedures for a cryptic messenger RNA that mediates translational control of prostaglandin synthase by glucocorticoids. Anal Biochem. 1991 Jul;196(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90110-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchhalter J. R., Dichter M. A. Electrophysiological comparison of pyramidal and stellate nonpyramidal neurons in dissociated cell culture of rat hippocampus. Brain Res Bull. 1991 Mar;26(3):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(91)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. J., Takada M., Hattori T. Co-localization of tyrosine hydroxylase and glutamate decarboxylase in a subpopulation of single nigrotectal projection neurons. Brain Res. 1991 Sep 6;558(2):239–244. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90774-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberwine J., Yeh H., Miyashiro K., Cao Y., Nair S., Finnell R., Zettel M., Coleman P. Analysis of gene expression in single live neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3010–3014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlander M. G., Tillakaratne N. J., Feldblum S., Patel N., Tobin A. J. Two genes encode distinct glutamate decarboxylases. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90077-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlander M. G., Tobin A. J. The structural and functional heterogeneity of glutamic acid decarboxylase: a review. Neurochem Res. 1991 Mar;16(3):215–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00966084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esclapez M., Tillakaratne N. J., Kaufman D. L., Tobin A. J., Houser C. R. Comparative localization of two forms of glutamic acid decarboxylase and their mRNAs in rat brain supports the concept of functional differences between the forms. J Neurosci. 1994 Mar;14(3 Pt 2):1834–1855. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-03-01834.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esclapez M., Tillakaratne N. J., Tobin A. J., Houser C. R. Comparative localization of mRNAs encoding two forms of glutamic acid decarboxylase with nonradioactive in situ hybridization methods. J Comp Neurol. 1993 May 15;331(3):339–362. doi: 10.1002/cne.903310305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldblum S., Erlander M. G., Tobin A. J. Different distributions of GAD65 and GAD67 mRNAs suggest that the two glutamate decarboxylases play distinctive functional roles. J Neurosci Res. 1993 Apr 15;34(6):689–706. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490340612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frotscher M. Mossy fiber synapses on glutamate decarboxylase-immunoreactive neurons: evidence for feed-forward inhibition in the CA3 region of the hippocampus. Exp Brain Res. 1989;75(2):441–445. doi: 10.1007/BF00247950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houser C. R., Esclapez M. Localization of mRNAs encoding two forms of glutamic acid decarboxylase in the rat hippocampal formation. Hippocampus. 1994 Oct;4(5):530–545. doi: 10.1002/hipo.450040503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. A comparative study of the peroxidase-antiperoxidase method and an avidin-biotin complex method for studying polypeptide hormones with radioimmunoassay antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 May;75(5):734–738. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/75.5.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J. F., Legay F., Dumas S., Tappaz M., Mallet J. Molecular cloning, expression and in situ hybridization of rat brain glutamic acid decarboxylase messenger RNA. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jan 14;73(2):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. L., Houser C. R., Tobin A. J. Two forms of the gamma-aminobutyric acid synthetic enzyme glutamate decarboxylase have distinct intraneuronal distributions and cofactor interactions. J Neurochem. 1991 Feb;56(2):720–723. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langdon R. B., Johnson J. W., Barrionuevo G. Asynchrony of mossy fibre inputs and excitatory postsynaptic currents in rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1993 Dec;472:157–176. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legido A., Reichlin S., Dichter M. A., Buchhalter J. Expression of somatostatin and GABA immunoreactivity in cultures of rat hippocampus. Peptides. 1990 Jan-Feb;11(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(90)90117-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackler S. A., Brooks B. P., Eberwine J. H. Stimulus-induced coordinate changes in mRNA abundance in single postsynaptic hippocampal CA1 neurons. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):539–548. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90191-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackler S. A., Eberwine J. H. Diversity of glutamate receptor subunit mRNA expression within live hippocampal CA1 neurons. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;44(2):308–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madtes P., Jr, Redburn D. A. GABA as a trophic factor during development. Life Sci. 1983 Sep 5;33(10):979–984. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90754-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki R., Robinson M. B., Dichter M. A. The glutamate uptake inhibitor L-trans-pyrrolidine-2,4-dicarboxylate depresses excitatory synaptic transmission via a presynaptic mechanism in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 1994 Nov;14(11 Pt 1):6754–6762. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-11-06754.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. L., Rimvall K. Regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid synthesis in the brain. J Neurochem. 1993 Feb;60(2):395–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson M. P., Kater S. B. Development and selective neurodegeneration in cell cultures from different hippocampal regions. Brain Res. 1989 Jun 19;490(1):110–125. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90436-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashiro K., Dichter M., Eberwine J. On the nature and differential distribution of mRNAs in hippocampal neurites: implications for neuronal functioning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):10800–10804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura H., Bérod A., Julien J. F., Geffard M., Kitahama K., Mallet J., Bobillier P. Demonstration of GABAergic cell bodies in the suprachiasmatic nucleus: in situ hybridization of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) mRNA and immunocytochemistry of GAD and GABA. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Jul 31;102(2-3):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. S., Sun Y., Vaidyanathan U., Landis S. C., Zigmond R. E. Regulation of substance P is similar to that of vasoactive intestinal peptide after axotomy or explantation of the rat superior cervical ganglion. J Neurobiol. 1993 May;24(5):571–580. doi: 10.1002/neu.480240504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribak C. E., Vaughn J. E., Saito K., Barber R., Roberts E. Immunocytochemical localization of glutamate decarboxylase in rat substantia nigra. Brain Res. 1976 Nov 5;116(2):287–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90906-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimvall K., Martin D. L. GAD and GABA in an enriched population of cultured GABAergic neurons from rat cerebral cortex. Neurochem Res. 1991 Aug;16(8):859–868. doi: 10.1007/BF00965534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler R., Smith A. D. Coexistence of GABA and glutamate in mossy fiber terminals of the primate hippocampus: an ultrastructural study. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Jan 8;303(2):177–192. doi: 10.1002/cne.903030202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spoerri P. E. Neurotrophic effects of GABA in cultures of embryonic chick brain and retina. Synapse. 1988;2(1):11–22. doi: 10.1002/syn.890020104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucher N. J., Brose N., Deitcher D. L., Awobuluyi M., Gasic G. P., Bading H., Cepko C. L., Greenberg M. E., Jahn R., Heinemann S. F. Expression of endogenous NMDAR1 transcripts without receptor protein suggests post-transcriptional control in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22299–22304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surmeier D. J., Eberwine J., Wilson C. J., Cao Y., Stefani A., Kitai S. T. Dopamine receptor subtypes colocalize in rat striatonigral neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10178–10182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White W. F., Snodgrass S. R., Dichter M. Identification of GABA neurons in rat cortical cultures by GABA uptake autoradiography. Brain Res. 1980 May 19;190(1):139–152. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox K. S., Buchhalter J., Dichter M. A. Properties of inhibitory and excitatory synapses between hippocampal neurons in very low density cultures. Synapse. 1994 Oct;18(2):128–151. doi: 10.1002/syn.890180206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox K. S., Dichter M. A. Paired pulse depression in cultured hippocampal neurons is due to a presynaptic mechanism independent of GABAB autoreceptor activation. J Neurosci. 1994 Mar;14(3 Pt 2):1775–1788. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-03-01775.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodson W., Nitecka L., Ben-Ari Y. Organization of the GABAergic system in the rat hippocampal formation: a quantitative immunocytochemical study. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Feb 8;280(2):254–271. doi: 10.1002/cne.902800207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuenschell C. W., Fisher R. S., Kaufman D. L., Tobin A. J. In situ hybridization to localize mRNA encoding the neurotransmitter synthetic enzyme glutamate decarboxylase in mouse cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6193–6197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafra F., Castrén E., Thoenen H., Lindholm D. Interplay between glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid transmitter systems in the physiological regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor synthesis in hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10037–10041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurn A. Fibroblast growth factor differentially modulates the neurotransmitter phenotype of cultured sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci. 1992 Nov;12(11):4195–4201. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-11-04195.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]