Abstract
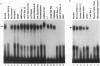
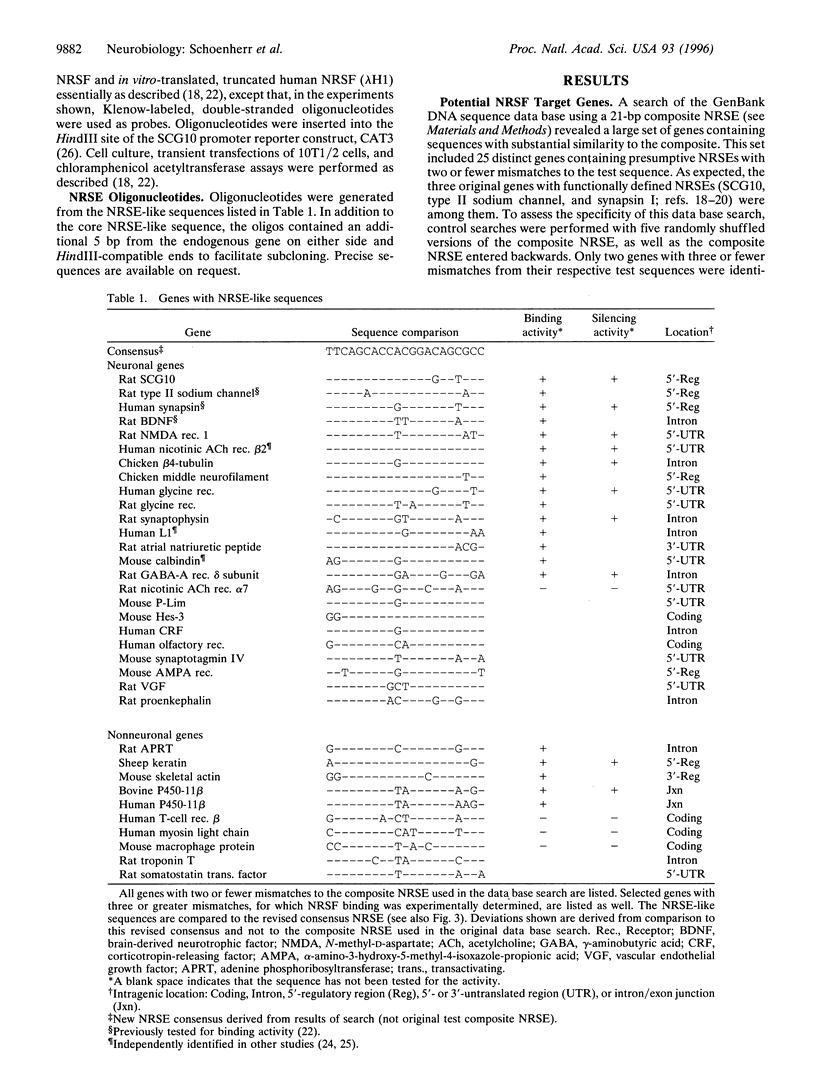
The neuron-restrictive silencer factor (NRSF) represses transcription of several neuronal genes in nonneuronal cells by binding to a 21-bp element called the neuron-restrictive silencer element (NRSE). We have performed data base searches with a composite NRSE to identify additional candidate NRSF target genes. Twenty-two more genes, 17 of which are expressed mainly in neurons, were found to contain NRSE-like sequences. Many of these putative NRSEs bound NRSF in vitro and repressed transcription in vivo. Most of the neuronal genes identified contribute to the basic structural or functional properties of neurons. However, two neuronal transcription factor genes contain NRSEs, suggesting that NRSF may repress neuronal differentiation both directly and indirectly. Functional NRSEs were also found in several nonneuronal genes, implying that NRSF may play a broader role than originally anticipated.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach I., Rhodes S. J., Pearse R. V., 2nd, Heinzel T., Gloss B., Scully K. M., Sawchenko P. E., Rosenfeld M. G. P-Lim, a LIM homeodomain factor, is expressed during pituitary organ and cell commitment and synergizes with Pit-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2720–2724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessis A., Salmon A. M., Zoli M., Le Novère N., Picciotto M., Changeux J. P. Promoter elements conferring neuron-specific expression of the beta 2-subunit of the neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor studied in vitro and in transgenic mice. Neuroscience. 1995 Dec;69(3):807–819. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00303-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong J. A., Tapia-Ramírez J., Kim S., Toledo-Aral J. J., Zheng Y., Boutros M. C., Altshuller Y. M., Frohman M. A., Kraner S. D., Mandel G. REST: a mammalian silencer protein that restricts sodium channel gene expression to neurons. Cell. 1995 Mar 24;80(6):949–957. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreiro B., Kintner C., Zimmerman K., Anderson D., Harris W. A. XASH genes promote neurogenesis in Xenopus embryos. Development. 1994 Dec;120(12):3649–3655. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.12.3649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grueneberg D. A., Natesan S., Alexandre C., Gilman M. Z. Human and Drosophila homeodomain proteins that enhance the DNA-binding activity of serum response factor. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1089–1095. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemot F., Lo L. C., Johnson J. E., Auerbach A., Anderson D. J., Joyner A. L. Mammalian achaete-scute homolog 1 is required for the early development of olfactory and autonomic neurons. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):463–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90381-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamelin M., Scott I. M., Way J. C., Culotti J. G. The mec-7 beta-tubulin gene of Caenorhabditis elegans is expressed primarily in the touch receptor neurons. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2885–2893. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Albert V. R., Chen R. P., Crenshaw 3d E. B., Elsholtz H. P., He X., Kapiloff M. S., Mangalam H. J., Swanson L. W., Treacy M. N. A family of POU-domain and Pit-1 tissue-specific transcription factors in pituitary and neuroendocrine development. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:773–791. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.004013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T. Transcriptional regulation. Converting an activator into a repressor. Curr Biol. 1995 Jan 1;5(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro H., Kim K. T., Joh T. H., Kim K. S. Neuron-specific expression of the human dopamine beta-hydroxylase gene requires both the cAMP-response element and a silencer region. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17987–17994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Genetic control of cell fate specification in Drosophila peripheral nervous system. Annu Rev Genet. 1994;28:373–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.28.120194.002105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. E., Birren S. J., Saito T., Anderson D. J. DNA binding and transcriptional regulatory activity of mammalian achaete-scute homologous (MASH) proteins revealed by interaction with a muscle-specific enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3596–3600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallunki P., Jenkinson S., Edelman G. M., Jones F. S. Silencer elements modulate the expression of the gene for the neuron-glia cell adhesion molecule, Ng-CAM. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 8;270(36):21291–21298. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.36.21291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraner S. D., Chong J. A., Tsay H. J., Mandel G. Silencing the type II sodium channel gene: a model for neural-specific gene regulation. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90218-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. E., Hollenberg S. M., Snider L., Turner D. L., Lipnick N., Weintraub H. Conversion of Xenopus ectoderm into neurons by NeuroD, a basic helix-loop-helix protein. Science. 1995 May 12;268(5212):836–844. doi: 10.1126/science.7754368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Suzuki T., Mori N., Greengard P. Identification of a functional silencer element involved in neuron-specific expression of the synapsin I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1460–1464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Rawson E. J., Simmons D. M., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Dwarf locus mutants lacking three pituitary cell types result from mutations in the POU-domain gene pit-1. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):528–533. doi: 10.1038/347528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maue R. A., Kraner S. D., Goodman R. H., Mandel G. Neuron-specific expression of the rat brain type II sodium channel gene is directed by upstream regulatory elements. Neuron. 1990 Feb;4(2):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90097-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori N., Schoenherr C., Vandenbergh D. J., Anderson D. J. A common silencer element in the SCG10 and type II Na+ channel genes binds a factor present in nonneuronal cells but not in neuronal cells. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori N., Stein R., Sigmund O., Anderson D. J. A cell type-preferred silencer element that controls the neural-specific expression of the SCG10 gene. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):583–594. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90116-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak B. G., Neumann J. C., Croyle M. L., Lingrel J. B. The presence of both negative and positive elements in the 5'-flanking sequence of the rat Na,K-ATPase alpha 3 subunit gene are required for brain expression in transgenic mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Nov 11;22(22):4748–4755. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.22.4748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of a five-finger GLI-DNA complex: new perspectives on zinc fingers. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1701–1707. doi: 10.1126/science.8378770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive sequence comparison with FASTP and FASTA. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:63–98. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83007-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasai Y., Kageyama R., Tagawa Y., Shigemoto R., Nakanishi S. Two mammalian helix-loop-helix factors structurally related to Drosophila hairy and Enhancer of split. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2620–2634. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenherr C. J., Anderson D. J. Silencing is golden: negative regulation in the control of neuronal gene transcription. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995 Oct;5(5):566–571. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(95)80060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenherr C. J., Anderson D. J. The neuron-restrictive silencer factor (NRSF): a coordinate repressor of multiple neuron-specific genes. Science. 1995 Mar 3;267(5202):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.7871435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Evans R. M. Cross-coupling of signal transduction pathways: zinc finger meets leucine zipper. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):377–381. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90259-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Barale J. C., Marcinkiewicz M., Mattei M. G., Day R., Chrétien M. The mouse homeoprotein mLIM-3 is expressed early in cells derived from the neuroepithelium and persists in adult pituitary. DNA Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;13(12):1163–1180. doi: 10.1089/dna.1994.13.1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. Positive and negative regulators of neural fate. Neuron. 1995 Oct;15(4):739–742. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida T., Ensini M., Morton S. B., Baldassare M., Edlund T., Jessell T. M., Pfaff S. L. Topographic organization of embryonic motor neurons defined by expression of LIM homeobox genes. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):957–970. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. L., Weintraub H. Expression of achaete-scute homolog 3 in Xenopus embryos converts ectodermal cells to a neural fate. Genes Dev. 1994 Jun 15;8(12):1434–1447. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.12.1434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valarché I., Tissier-Seta J. P., Hirsch M. R., Martinez S., Goridis C., Brunet J. F. The mouse homeodomain protein Phox2 regulates Ncam promoter activity in concert with Cux/CDP and is a putative determinant of neurotransmitter phenotype. Development. 1993 Nov;119(3):881–896. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.3.881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Chalfie M. mec-3, a homeobox-containing gene that specifies differentiation of the touch receptor neurons in C. elegans. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):5–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90174-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood I. C., Roopra A., Buckley N. J. Neural specific expression of the m4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor gene is mediated by a RE1/NRSE-type silencing element. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jun 14;271(24):14221–14225. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.24.14221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue D., Tu Y., Chalfie M. Cooperative interactions between the Caenorhabditis elegans homeoproteins UNC-86 and MEC-3. Science. 1993 Sep 3;261(5126):1324–1328. doi: 10.1126/science.8103239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman K., Shih J., Bars J., Collazo A., Anderson D. J. XASH-3, a novel Xenopus achaete-scute homolog, provides an early marker of planar neural induction and position along the mediolateral axis of the neural plate. Development. 1993 Sep;119(1):221–232. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.1.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]