Abstract
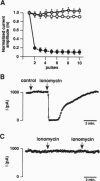
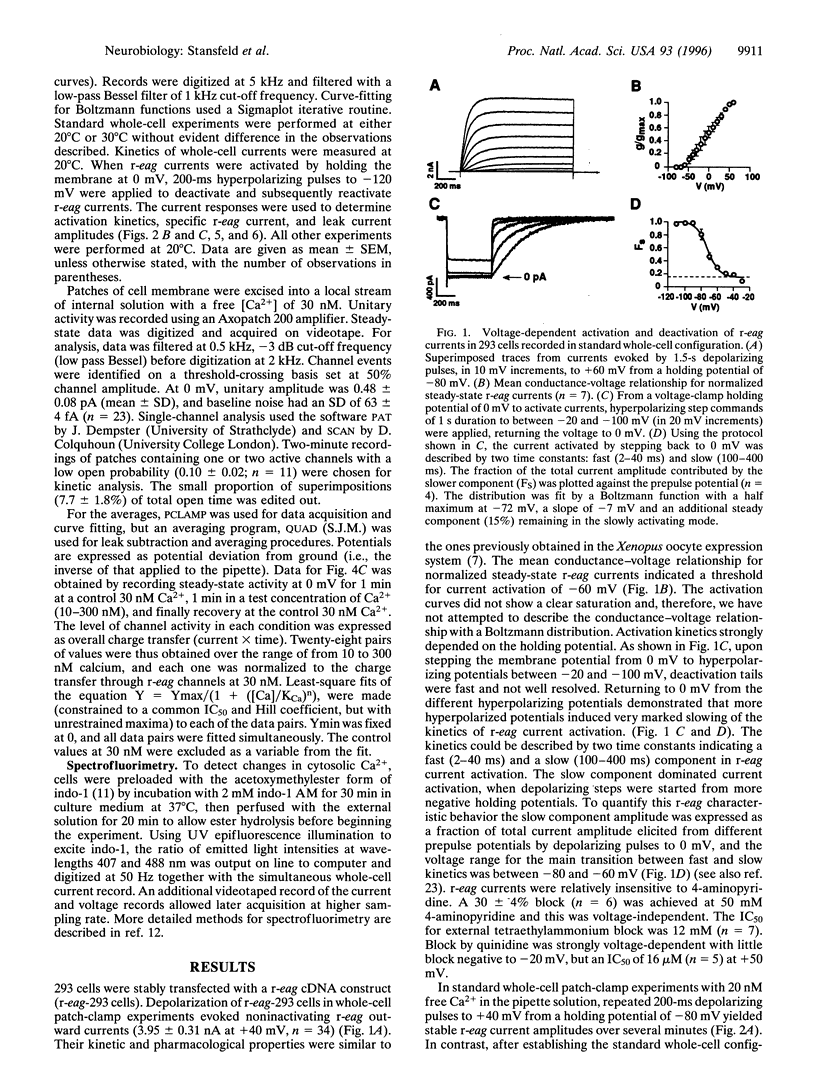
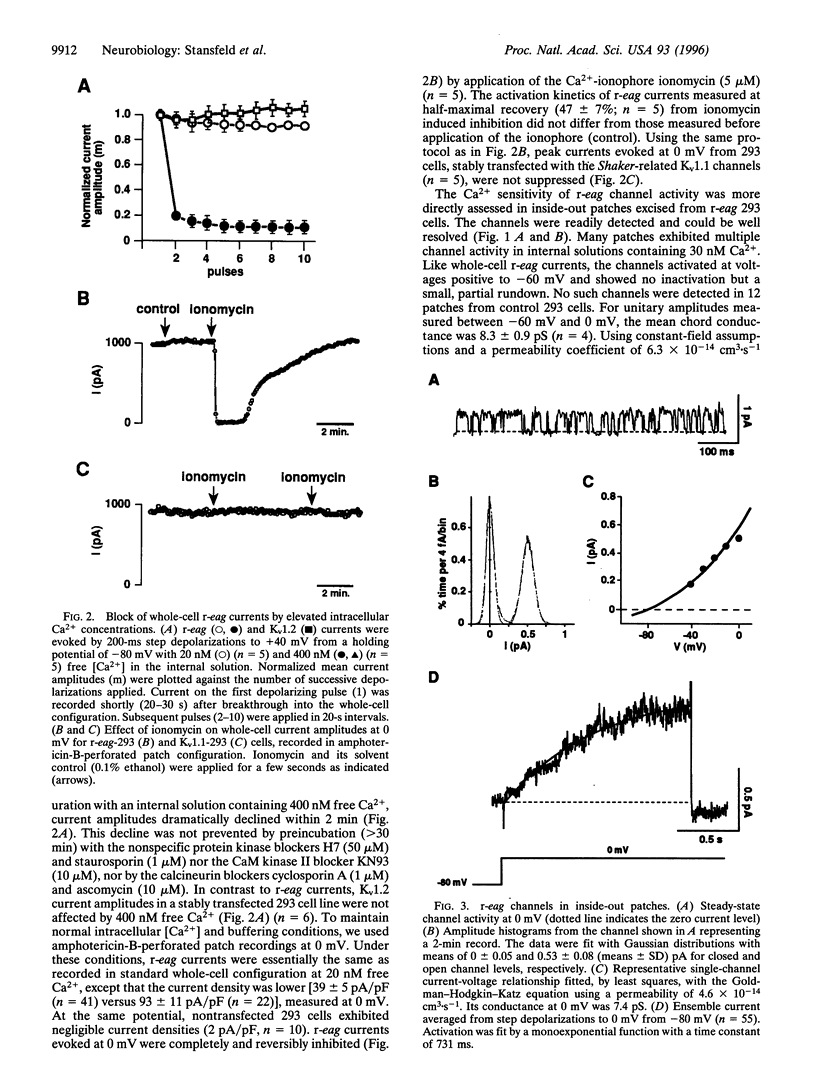
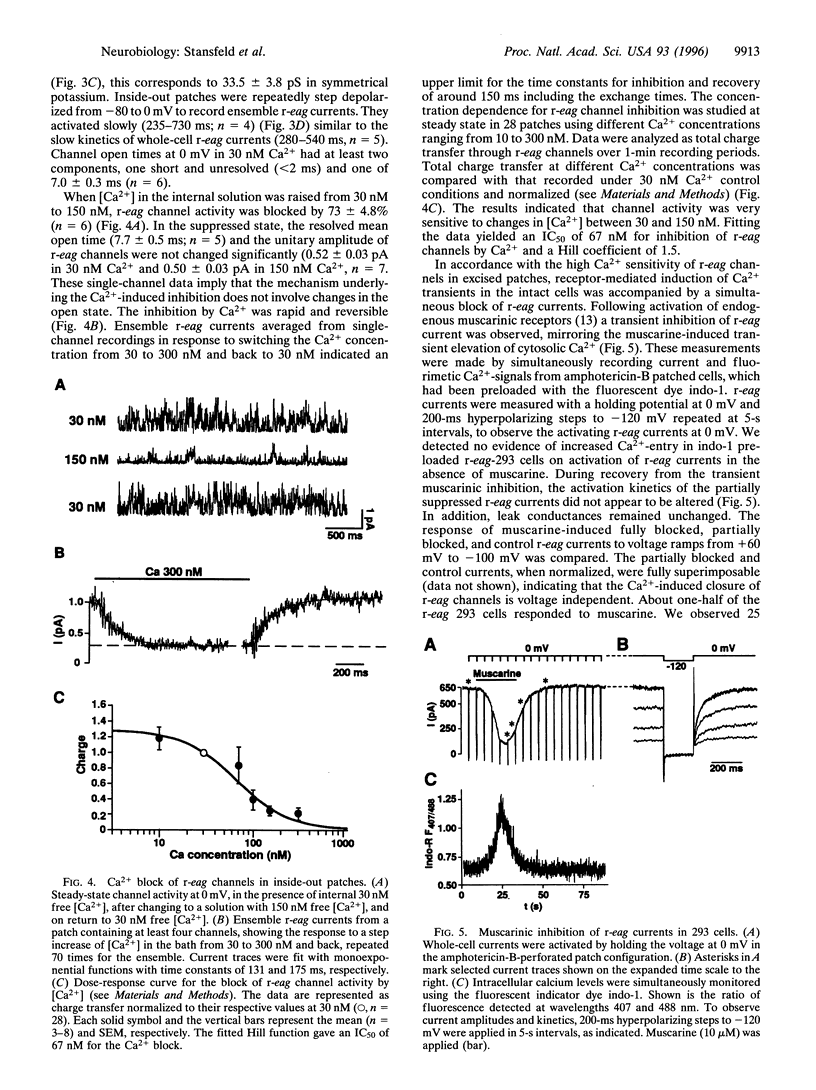
We have studied the properties of r-eag voltage-activated potassium channels in a stably transfected human embryonic kidney cell line. It was found that r-eag channels are rapidly and reversibly inhibited by a rise in intracellular calcium from 30 to 300 nM. The inhibition does not appear to depend on the activity of calcium-dependent kinases and phosphatases. The effect of calcium on r-eag channel activity was studied in inside-out membrane patches. Calcium inhibited r-eag channel activity with a mean IC50 of 67 nM. Activation of muscarinic receptors, generating calcium oscillations in the transfected cells, induced a synchronous inhibition of r-eag mediated outward currents. This shows that calcium can mediate r-eag current inhibition following muscarinic receptor activation. The data indicate that r-eag channels are calcium-inhibitable voltage-activated potassium channels.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beech D. J., Bernheim L., Mathie A., Hille B. Intracellular Ca2+ buffers disrupt muscarinic suppression of Ca2+ current and M current in rat sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):652–656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemann A., Pardo L. A., Stühmer W., Pongs O. Ether-à-go-go encodes a voltage-gated channel permeable to K+ and Ca2+ and modulated by cAMP. Nature. 1993 Sep 30;365(6445):445–448. doi: 10.1038/365445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi E. J., Wong S. T., Hinds T. R., Storm D. R. Calcium and muscarinic agonist stimulation of type I adenylylcyclase in whole cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12440–12442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias M., Wei A. A., Salkoff L. Shaker, Shal, Shab, and Shaw express independent K+ current systems. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):763–773. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90279-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi T., Kohda K., Miyawaki A., Mikoshiba K. Intracellular channels. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1994 Jun;4(3):294–303. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(94)90089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang X. Y., Morielli A. D., Peralta E. G. Tyrosine kinase-dependent suppression of a potassium channel by the G protein-coupled m1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1145–1156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90324-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Potassium channels and their evolving gates. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):119–122. doi: 10.1038/371119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood A., Simmons M. A., Mather R. J., Lisman J. Muscarinic suppression of the M-current is mediated by a rise in internal Ca2+ concentration. Neuron. 1991 Jun;6(6):1009–1014. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90240-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig J., Terlau H., Wunder F., Brüggemann A., Pardo L. A., Marquardt A., Stühmer W., Pongs O. Functional expression of a rat homologue of the voltage gated either á go-go potassium channel reveals differences in selectivity and activation kinetics between the Drosophila channel and its mammalian counterpart. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 3;13(19):4451–4458. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06767.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J. The control of neuronal Ca2+ homeostasis. Prog Neurobiol. 1991;37(3):255–285. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(91)90028-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae J., Cooper K., Gates P., Watsky M. Low access resistance perforated patch recordings using amphotericin B. J Neurosci Methods. 1991 Mar;37(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(91)90017-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanguinetti M. C., Jiang C., Curran M. E., Keating M. T. A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired cardiac arrhythmia: HERG encodes the IKr potassium channel. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90340-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selyanko A. A., Brown D. A. Intracellular calcium directly inhibits potassium M channels in excised membrane patches from rat sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1996 Jan;16(1):151–162. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terlau H., Ludwig J., Steffan R., Pongs O., Stühmer W., Heinemann S. H. Extracellular Mg2+ regulates activation of rat eag potassium channel. Pflugers Arch. 1996 Jun;432(2):301–312. doi: 10.1007/s004240050137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trouslard J., Marsh S. J., Brown D. A. Calcium entry through nicotinic receptor channels and calcium channels in cultured rat superior cervical ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1993 Aug;468:53–71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudeau M. C., Warmke J. W., Ganetzky B., Robertson G. A. HERG, a human inward rectifier in the voltage-gated potassium channel family. Science. 1995 Jul 7;269(5220):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.7604285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2396–2404. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmke J. W., Ganetzky B. A family of potassium channel genes related to eag in Drosophila and mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3438–3442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmke J., Drysdale R., Ganetzky B. A distinct potassium channel polypeptide encoded by the Drosophila eag locus. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1560–1562. doi: 10.1126/science.1840699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins C. S., Mathie A. A non-inactivating K+ current sensitive to muscarinic receptor activation in rat cultured cerebellar granule neurons. J Physiol. 1996 Mar 1;491(Pt 2):401–412. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. P., O'Malley D. M., Adams P. R. Regulation of M current by intracellular calcium in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion neurons. J Neurosci. 1994 Jun;14(6):3487–3499. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-06-03487.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]