Abstract
Duodenal stenosis usually occurs in isolation and has a variable presentation in infancy due to partial obstruction. An unusual case of congenital double duodenal diaphragms in an infant presenting as failure to thrive has been described and pertinent literature has been reviewed herein. Excision of webs with double Heineke-Mikulicz closure was performed.
KEY WORDS: Duodenal web, duodenal obstruction, double diaphragms
INTRODUCTION
Duodenal stenosis usually occurs in isolation, although it may be occasionally associated with annular pancreas.[1] Here, an unusual case of congenital double duodenal diaphragms presenting in infancy has been described. This case highlights the golden rule of ensuring distal patency per operatively for congenital anomalies.
CASE REPORT
An 11-month-old cachexic baby weighing 4.3kg presented with post-cibal recurrent non-bilious vomiting since day 5 of life. The epigastrium was full with visible peristalsis from left to right. There was no palpable lump. He had visited various hospitals over last 5 months with a suspected diagnosis of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. As ultrasound abdomen was normal; malabsorption was the provisional diagnosis elsewhere before he was referred for further assessment.
A dye study delineated a grossly dilated stomach and duodenum [Figure 1]. At laparotomy, a duodenal web with a hole admitting a 6 Fr infant feeding tube was identified in the second part of the duodenum after kocherization [Figure 2]. A feeding tube, passed after excising the first web, could not be negotiated freely into jejunum. On releasing kinks around ligament of Treitz and checking for distal patency, another web was suspected at duodenojejunal junction that was confirmed on second duodenotomy, with a small hole negotiating a 6 Fr feeding tube.
Figure 1.
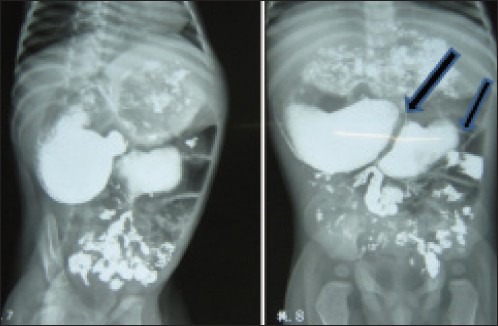
A barium meal follow throughout study, delineating a grossly dilated stomach and duodenum with definite duodenal obstruction (first arrow) and doubtful obstruction at duodenojejunal level (second arrow)
Figure 2.
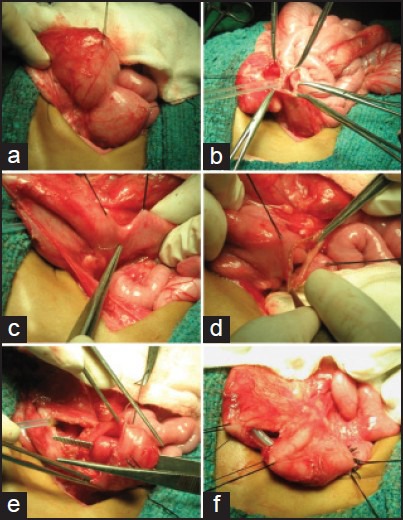
(a) At laparotomy, an area of duodenal stenosis was identified. (b) A duodenotomy confirmed the first duodenal diaphragm with a hole of the size of infant feeding tube (#6). (c) Suspicious area of a second duodenal stenosis identified at the duodenojejunal junction. (d) Second duodenotomy confirming the second duodenal diaphragm. (e) The second duodenal web with #6 Fr hole, through which a forceps prong has been passed. (f) Heineke-Mikulicz closure done at both sites. A trans anastomotic silastic Foley catheter was put through the Malecot catheter put as gastrostomy
Excision of the webs with Heineke-Mikulicz closure was done at both sites, separated at a distance of 8 cm. A transanastomotic silicon Foley's catheter was passed through a gastrostomy. Postoperatively, the child gained 2 kg weight within 2 months. At a follow-up of 24 months, the baby is asymptomatic and has gained adequate weight.
DISCUSSION
The incidence of duodenal atresia is 1 in 5,000-10,000 cases.[2] Most cases are congenital and idiopathic, although rarely there have been two reports of cases in siblings, which suggest to a familial predisposition.[3,4]
Duodenal stenosis comprises upto 10% cases of duodenal obstruction. The most common site is between the first and second part of duodenum. Symptoms vary from recurrent episodes of vomiting, aspiration, or failure to thrive in the early childhood to gastroesophageal reflux, peptic ulceration, or duodenal obstruction proximal to stenosis by a bezoar in the adulthood.
Only anecdotal cases of double duodenal atresia or stenosis have been reported; double duodenal atresia being more commonly reported including an antenatal case.[1,5,6,7] While double duodenal atresia may present in newborn period, double duodenal webs usually present later, either in infancy or even in adulthood.[8,9,10] Obstruction at the duodenojejunal junction is extremely rare with only one case of a diaphragm web at this sitereported.[11]
The case described presented in an infant weighing 4.3 kg, much below the 5th percentile (7.5 kg) for age. A diagnosis of duodenal stenosis was made on physical examination and confirmed by barium study. During operation, the second web could only be localized after a strong desire to ensure good distal patency. The duodenum distal to the web was also distended, while the jejunum was narrow. Though successful, endoscopic treatment of a double duodenal web in an infant has recently been described, the authors feel that the kinks at the duodenojejunal junction in the case described could not have been released endoscopically.[10]
Double duodenal atresia has been reported to present with neonatal intestinal obstruction, perforation,and presence of a duodenal cyst after the first duodenal obstruction has been treated.[5,7] Double duodenal webs have been reported to be associated with peptic ulceration.[9]
CONCLUSION
The diagnosis of congenital double duodenal diaphragms is one of suspicion and careful examination during operation, ensuring adequate distal patency. The second duodenal diaphragm, present at a rare site of duodenojejunal junction,could only be demonstrated after release of the kinks at the ligament of Treitz. This case emphasizes the fact that the operative finding of one anomaly does not preclude the presence of a second anomaly, and,therefore, a thorough search for another may prove fruitful.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Papandreou E, Baltogiannis N, Cigliano B, Savanelli A, Settimi A, Keramidas D. Annular pancreas combined with distal stenosis. A report of four cases and review of the literature. Pediatr Med Chir. 2004;26:256–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kimura K, Loening-Baucke V. Bilious vomiting in the newborn: Rapid diagnosis of intestinal obstruction. Am Fam Physician. 2000;61:2791–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Berant M, Kahana D. Familial duodenal atresia. Arch Dis Child. 1970;45:281–2. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.240.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Poki HO, Holland AJ, Pitkin J. Double bubble, double trouble. Pediatr Surg Int. 2005;21:428–31. doi: 10.1007/s00383-005-1448-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Stringer MD, Brereton RJ, Drake DP, Wright VM. Double duodenal atresia/stenosis: A report of four cases. J Pediatr Surg. 1992;27:576–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(92)90450-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hung JH, Shen SH, Chin TW, Hung CY. Prenatal diagnosis of double duodenal atresia by ultrasound and magnetic resonance image. Prenat Diagn. 2007;27:381–3. doi: 10.1002/pd.1658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Keys C, Makkar N, Clarnette T, Muthucumaru M, Cheng W. Double duodenal atresia with perforation: A case report. J Pediatr Surg. 2011;46:e25–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2011.02.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Reiner RG, Alp MH, O’Brien JA, Jones GH. Double duodenal diaphragm: Report of a case. Aust N Z J Surg. 1978;48:310–3. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1978.tb05237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Park SY, Jung JH, Lee JH, Jo JD. A case of double duodenal web associated with peptic ulcer. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1997;40:1319–24. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Barabino A, Gandullia P, Arrigo S, Vignola S, Mattioli G, Grattarola C. Successful endoscopic treatment of a double duodenal web in an infant. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73:401–3. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2010.06.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ganguly S, Chowdhury MM, Ganguly S, Chowdhury J, Mishra PK. Congenital Duodenal Diaphragms in the third part of duodenum. Indian Pediatr. 1995;32:1326–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


