Abstract
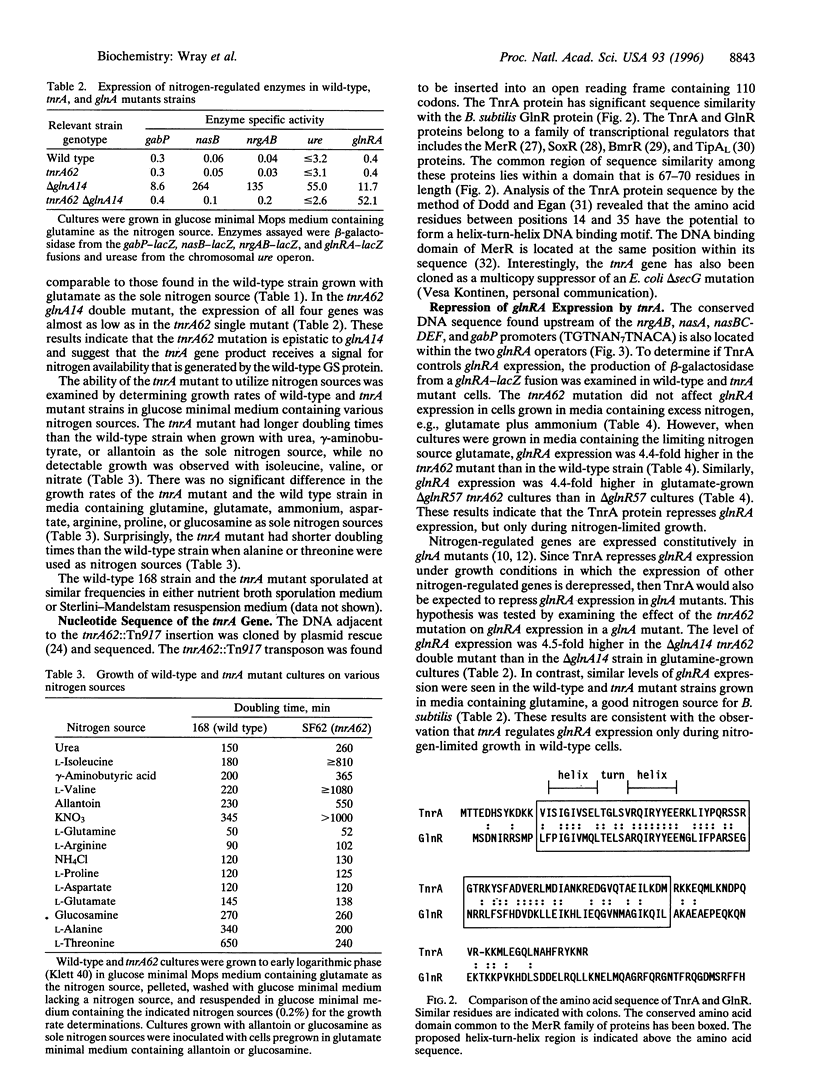
Expression of the Bacillus subtilis nrgAB operon is derepressed during nitrogen-limited growth. We have identified a gene, tnrA, that is required for the activation of nrgAB expression under these growth conditions. Analysis of the DNA sequence of the tnrA gene revealed that it encodes a protein with sequence similarity to GlnR, the repressor of the B. subtilis glutamine synthetase operon. The tnrA mutant has a pleiotropic phenotype. Compared with wild-type cells, the tnrA mutant is impaired in its ability to utilize allantoin, gamma-aminobutyrate, isoleucine, nitrate, urea, and valine as nitrogen sources. During nitrogen-limited growth, transcription of the nrgAB, nasB, gabP, and ure genes is significantly reduced in the tnrA mutant compared with the levels seen in wild-type cells. In contrast, the level of glnRA expression is 4-fold higher in the, tnrA mutant than in wild-type cells during nitrogen restriction. The phenotype of the tnrA mutant indicates that a global nitrogen regulatory system is present in B. subtilis and that this system is distinct from the Ntr regulatory system found in enteric bacteria.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed M., Borsch C. M., Taylor S. S., Vázquez-Laslop N., Neyfakh A. A. A protein that activates expression of a multidrug efflux transporter upon binding the transporter substrates. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 11;269(45):28506–28513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amábile-Cuevas C. F., Demple B. Molecular characterization of the soxRS genes of Escherichia coli: two genes control a superoxide stress regulon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4479–4484. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. R., Fisher S. H. Identification of genes and gene products whose expression is activated during nitrogen-limited growth in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):23–27. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.23-27.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. R., Wray L. V., Jr, Fisher S. H. Regulation of histidine and proline degradation enzymes by amino acid availability in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4758–4765. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4758-4765.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumberg S., Harwood C. R. Carbon and nitrogen repression of arginine catabolic enzymes in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):189–196. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.189-196.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender R. A. The role of the NAC protein in the nitrogen regulation of Klebsiella aerogenes. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2575–2580. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. W., Sonenshein A. L. Autogenous regulation of the Bacillus subtilis glnRA operon. J Bacteriol. 1996 Apr;178(8):2450–2454. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.8.2450-2454.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes I. W., Mandelstam J. Sporulation of Bacillus subtilis in continuous culture. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):529–535. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.529-535.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. R., Hoch J. A., Aronson A. I. Alteration of the Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase results in overproduction of the enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1977 Sep;131(3):981–987. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.3.981-987.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd I. B., Egan J. B. Improved detection of helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motifs in protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5019–5026. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Débarbouillé M., Martin-Verstraete I., Kunst F., Rapoport G. The Bacillus subtilis sigL gene encodes an equivalent of sigma 54 from gram-negative bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9092–9096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J., Vogt C. H. Isolation and characterization of mutations in the gene encoding an endogenous Bacillus subtilis beta-galactosidase and its regulator. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):488–490. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.488-490.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. H., Rosenkrantz M. S., Sonenshein A. L. Glutamine synthetase gene of Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. H., Sonenshein A. L. Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase mutants pleiotropically altered in glucose catabolite repression. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):612–621. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.612-621.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutowski J. C., Schreier H. J. Interaction of the Bacillus subtilis glnRA repressor with operator and promoter sequences in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):671–681. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.671-681.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. J., Caso J. L., Thompson C. J. Autogenous transcriptional activation of a thiostrepton-induced gene in Streptomyces lividans. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3183–3191. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra T. K., Brown N. L., Fritzinger D. C., Pridmore R. D., Barnes W. M., Haberstroh L., Silver S. Mercuric ion-resistance operons of plasmid R100 and transposon Tn501: the beginning of the operon including the regulatory region and the first two structural genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5975–5979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M. M., Yang F., Hardin P., Zuber P. Nitrogen regulation of nasA and the nasB operon, which encode genes required for nitrate assimilation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1995 Feb;177(3):573–579. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.3.573-579.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano Y., Kimura K. Purification and characterization of a repressor for the Bacillus cereus glnRA operon. J Biochem. 1991 Feb;109(2):223–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):704–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier H. J., Brown S. W., Hirschi K. D., Nomellini J. F., Sonenshein A. L. Regulation of Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase gene expression by the product of the glnR gene. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 5;210(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier H. J., Fisher S. H., Sonenshein A. L. Regulation of expression from the glnA promoter of Bacillus subtilis requires the glnA gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3375–3379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier H. J., Rostkowski C. A. Bacillus subtilis glnR mutants defective in regulation. Gene. 1995 Aug 8;161(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00238-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewchuk L. M., Helmann J. D., Ross W., Park S. J., Summers A. O., Walsh C. T. Transcriptional switching by the MerR protein: activation and repression mutants implicate distinct DNA and mercury(II) binding domains. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 7;28(5):2340–2344. doi: 10.1021/bi00431a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenshein A. L., Cami B., Brevet J., Cote R. Isolation and characterization of rifampin-resistant and streptolydigin-resistant mutants of Bacillus subtilis with altered sporulation properties. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):253–265. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.253-265.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch M. A., Aronson A. I., Brown S. W., Schreier H. J., Sonenhein A. L. Sequence of the Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase gene region. Gene. 1988 Nov 30;71(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D. X., Setlow P. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of the Bacillus subtilis ans operon, which codes for L-asparaginase and L-aspartase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3831–3845. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3831-3845.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega-Palas M. A., Flores E., Herrero A. NtcA, a global nitrogen regulator from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus that belongs to the Crp family of bacterial regulators. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jul;6(13):1853–1859. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray L. V., Jr, Atkinson M. R., Fisher S. H. The nitrogen-regulated Bacillus subtilis nrgAB operon encodes a membrane protein and a protein highly similar to the Escherichia coli glnB-encoded PII protein. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jan;176(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.1.108-114.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



