Abstract
The antioxidant properties and effect of essential oil of black pepper (Piper guineense) seeds on α-amylase, α-glucosidase (key enzymes linked to type-2 diabetes), and angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) (key enzyme linked to hypertension) were assessed. The essential oil was obtained by hydrodistillation and dried with anhydrous Na2SO4, and the phenolic content, radical [1,1-diphenyl-2 picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) (ABTS) and nitric oxide (NO)] scavenging abilities as well as the ferric reducing antioxidant property (FRAP) and Fe2+-chelating ability of the essential oil were investigated. Furthermore, the effect on α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and ACE enzyme activities was also investigated. The characterization of the constituents was done using GC. The essential oil scavenged DPPH∗, NO∗, and ABTS∗ and chelated Fe2+. α-Pinene, β-pinene, cis-ocimene, myrcene, allo-ocimene, and 1,8-cineole were among the constituents identified by GC. The essential oil inhibited α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and ACE enzyme activities in concentration-dependent manners, though exhibiting a stronger inhibition of α-glucosidase than α-amylase activities. Conclusively, the phenolic content, antioxidant activity, and inhibition of α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and angiotensin-1 converting enzyme activities by the essential oil extract of black pepper could be part of the mechanism by which the essential oil could manage and/or prevent type-2 diabetes and hypertension.
1. Introduction
Essential oils from aromatic spice plants have been shown to be good antioxidants using various antioxidant assay models [1–3] and the antioxidant activities have been linked to the phenolic contents in some of the oils [4, 5]. Furthermore, some medicinal properties of essential oils from aromatic spice plants have been established, especially essential oils from black pepper (Piper guineense) seeds which have been shown to have antimicrobial, antihypertensive, anticonvulsive, and sedative activities [5–7]. Black pepper (Piper guineense) is a spicy plant whose essential oils from the seed and leaves are being extracted and sold in commercial quantities in many countries [8]. Monoterpenes, benzoids, and sesquiterpenes have been identified among the volatile compounds of the black pepper [9].
In recent years, the management of type-2 diabetes and hypertension through natural sources has been done in two major ways: the scavenging of free radicals and inhibition of key enzymes involved in starch digestion (α-amylase and α-glucosidase) and high blood pressure (angiotensin-1 converting enzyme). Diabetes has been associated with an increased generation of free radicals and defective antioxidant defense systems [10, 11]. Furthermore, oxidative stress has been implicated in the diabetogenic process and in the physiological effects of diabetes [12, 13]. Therefore, antioxidant-rich foods have a good dietary intervention in the management of type-2 diabetes.
α-Amylase and α-glucosidase are two key enzymes that are therapeutic targets in the management of diabetes [14]. These two enzymes are involved in the breakdown of starch to glucose, thereby increasing the amount of glucose in the bloodstream. However, the inhibition of α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities delays the absorption of glucose and thereby moderates “postprandial blood glucose elevation” [15, 16]. Similarly, inhibition of angiotensin-1 converting enzyme (ACE) activity is a therapeutic approach to the management of hypertension as ACE converts angiotensin-I to angiotensin-II, which is a potent vasoconstrictor which leads to elevated blood pressure [17].
Essential oils from black pepper have been in use in folklore for the management of diabetes and hypertension. However, there is a dearth of information on the possible mechanism for the use of the essential oils for managing such degenerative conditions. This study, therefore sought to investigate the suitability of essential oils from black pepper seeds as a dietary means for the management of type-2 diabetes and hypertension by investigating the antioxidant properties of the oil and also its effect on α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and angiotensin-1 converting enzyme activities.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
The Ashanti black peper (Piper guineense) was collected from the main market, Akure, south westren Nigeria (7.2500° N, 5.1950° E), over a period of seven days. The black pepper was ground to fine powder. The powder was stored in an air tight plastic container and placed at room temperature until it was used.
2.2. Essential Oil Isolation
100 g of the ground Ashanti black peper was subjected to hydrodistillation for 3 h in an all glass Clevenger-type apparatus according to the method recommended by the European Pharmacopoeia [18]. The extracted oil sample was dried over anhydrous sodium sulphate and stored in sealed vials at 4°C for further analysis.
2.3. Reagents
All chemicals used in this study were of analytical grade and glass-distilled water was used.
2.4. Determination of Total Phenol Content
The total phenol content was determined according to the method of Singleton et al. [19]. Briefly, appropriate dilutions of the extract were oxidized with 2.5 mL 10% Folin-Ciocalteau's reagent (v/v) and neutralized by 2.0 mL of 7.5% sodium carbonate. The reaction mixture was incubated for 40 minute at 45°C and the absorbance was measured at 765 nm in the spectrophotometer. The total phenol content was subsequently calculated as gallic acid equivalent.
2.5. GC Analysis
The analytical GC was carried out by Hewlett Packard 5890 Gas Chromatograph (Hewlett-Packard Corp., Palo Alto, CA) equipped with flame ionization detectors (FID) with DB-5 column (30 m length, 0.25 mm column id., 0.25 μm film thickness). The following conditions were applied: injection temperature: 290°C, injection volume: 1.0 μL, injection mode: split (1 : 50), temperature program: 50°C for 4 min, rising at 3°C/min to 240°C, then rising at 15°C/min to 300°C, held at 300°C for 3 min, FID (290°C): H2, flow: 50 mL/min, and air flow: 400 mL/min.
2.6. 1,1-Diphenyl-2 Picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Radical Scavenging Ability
The free radical scavenging ability of the oil against DPPH (1,1-diphenyl–2 picrylhydrazyl) free radical was evaluated as described by Gyamfi et al. [20]. Briefly, appropriate dilution of the extract (1 mL) was mixed with 1 mL, 0.4 mM methanolic solution containing DPPH radicals; the mixture was left in the dark for 30 min and the absorbance was taken at 516 nm. The DPPH free radical scavenging ability was subsequently calculated.
2.7. Fenton Reaction (Degradation of Deoxyribose)
The method of Halliwell and Gutteridge [21] was used to determine the ability of the extract to prevent Fe2+/H2O2 induced decomposition of deoxyribose. The extract 0–100 μL was added to a reaction mixture containing 120 μL of 20 mM deoxyribose, 400 μL of 0.1 m phosphate buffer, and 40 μL of 500 μm of FeSO4, and the volume was made up to 800 μL with distilled water. The reaction mixture was incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes and the reaction was then stopped by the addition of 0.5 mL of 28% trichloro acetic acid. This was followed by addition of 0.4 mL of 0.6% thiobarbituric acid solution. The tubes were subsequently incubated in boiling water for 20 minutes. The absorbance was measured at 532 nm in a spectrophotometer.
2.8. 2,2′-Azino-bis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) (ABTS) Radical Scavenging Ability
The ABTS* scavenging ability of the essential oil was determined according to the method described by Re et al. [22]. The ABTS* was generated by the reaction of an (7 mmol/L) ABTS aqueous solution with K2S2O8 (2.45 mmol/L, final concentration) in the dark for 16 h and adjusting the Abs734 nm to 0.700 with ethanol. Samples of 0.2 mL of the extract were added to 2.0 mL ABTS* solution and the absorbance was measured at 734 nm after 15 mins. The trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity was subsequently calculated.
2.9. Nitric Oxide Radical Scavenging Assay
The scavenging effect of the extract on nitric oxide (NO•) radical was measured according to the method of Mercocci et al. [23]. Samples of 100–400 μL of the oil extract were added in the test tubes to 1 mL of Sodium nitroprusside solution (25 mM) and tubes incubated at 37°C for 2 hours. An aliquot (0.5 mL) of the incubation was removed and diluted with 0.3 mL Griess reagent (1% sulphanilamide in 5% H3PO4 and 0.1% naphthlethylenediaminedihy drochloride). The absorbance of the chromophore formed was immediately read at 570 nm against distilled water as blank with catechin (50 μg) used as standard. Results were expressed as percentage radical scavenging activity (RSA).
2.10. Determination of Reducing Property
The reducing property of the essential oil was determined by assessing the ability of the extract to reduce FeCl3 solution as described by Oyaizu [24]. 2.5 mL aliquot was mixed with 2.5 mL 200 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.6) and 2.5 mL 1% potassium ferricyanide. The mixture was incubated at 50°C for 20 min and then 2.5 mL of 10% trichloroacetic acid was added. This mixture was centrifuged at 650 g for 10 min. 5 mL of the supernatant was mixed with an equal volume of water and 1 mL of 0.1% ferric chloride. The absorbance was measured at 700 nm. The ferric reducing antioxidant property was subsequently calculated.
2.11. Fe2+ Chelation Assay
The Fe2+ chelating ability of the essential oil was determined using a modified method of Minotti and Aust [25] with a slight modification by Puntel et al. [26]. Freshly prepared 500 μM FeSO4 (150 μL) was added to a reaction mixture containing 168 μL of 0.1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 218 μL saline, and the extracts (0–25 μL). The reaction mixture was incubated for 5 min, before the addition of 13 μL of 0.25% 1, 10-phenanthroline (w/v). The absorbance was subsequently measured at 510 nm in a spectrophotometer. The Fe (II) chelating ability was subsequently calculated.
2.12. α-Amylase Inhibition Assay
The essential oil (500 μL) and 500 μL of 0.02 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.9 with 0.006 M NaCl) containing hog pancreatic α-amylase (EC 3.2.1.1) (0.5 mg/mL) were incubated at 25°C for 10 minutes. Then, 500 μL of 1% starch solution in 0.02 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.9 with 0.006 M NaCl) was added to each tube. The reaction mixtures were incubated at 25°C for 10 minutes and stopped with 1.0 mL of dinitrosalicylic acid colour reagent. Thereafter, the mixture was incubated in a boiling water bath for 5 minutes and cooled to room temperature. The reaction mixture was then diluted by adding 10 mL of distilled water, and absorbance was measured at 540 nm [27].
2.13. α-Glucosidase Inhibition Assay
The essential oil (50 μL) and 100 μL of α-glucosidase solution (1.0 U/mL) in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 6.9) were incubated at 25°C for 10 min. Then, 50 μL of 5 mM p-nitrophenyl-α-D-glucopyranoside solution in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 6.9) was added. The mixtures were incubated at 25°C for 5 min, before reading the absorbance at 405 nm in the spectrophotometer. The α-glucosidase inhibitory activity was expressed as percentage inhibition [28].
2.14. Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibition Assay
The essential oil extract (50 μL) and ACE solution (50 μL, 4 mU) were incubated at 37°C for 15 min. The enzymatic reaction was initiated by adding 150 μL of 8.33 mM of the substrate Bz-Gly-His-Leu in 125 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.3) to the mixture. After incubation for 30 min at 37°C, the reaction was arrested by adding 250 μL of 1 M HCl. The Gly-His bond was then cleaved and the Bz-Gly produced by the reaction was extracted with 1.5 mL ethyl acetate. Thereafter the mixture was centrifuged to separate the ethyl acetate layer; then 1 mL of the ethyl acetate layer was transferred to a clean test tube and evaporated. The residue was redissolved in distilled water and its absorbance was measured at 228 nm. The ACE inhibitory activity was expressed as percentage inhibition [29].
2.15. Data Analysis
The results of three replicates were pooled and expressed as mean ± standard deviation (S.D.). Student's t-test, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), and least significance difference (LSD) were carried out [30]. Significance was accepted at P ≤ 0.05. EC50 was determined using linear regression analysis.
3. Results
The total phenolic content reported as gallic acid equivalent, ABTS* scavenging ability reported as trolox equivalent, and ferric reducing antioxidant property reported as ascorbic acid equivalent as presented in Table 1 were 4.41 mg/100 g, 2.25 mmol./g, and 11.12 mg/100 g, respectively. The GC analysis as presented in Table 2 revealed the presence of α-pinene (13.63%), β-pinene (41.24%), cis-ocimene (3.63%), myrcene (4.37%), allo-ocimene (3.43%), pinene-2-ol (2.79%), α-thujene (2.98%), gamma terpinene (5.68%), and 1,8-cineole (17.22%). As shown in Figures 1, 2, and 3 and Table 3, the essential oil scavenged DPPH* and NO* and chelated Fe2+ in concentration-dependent manners, with EC50 values of 414.59 mL/L, 161.92 mL/L, and 130.21 mL/L, respectively. The effects of the essential oil on α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and angiotensin-I converting enzyme activities are presented in Figures 4, 5, and 6. The EC50 values as presented in Table 3 are 86.06 mL/L (α-amylase), 68.29 mL/L (α-glucosidase), and 28.99 mL/L (ACE).
Table 1.
The total phenolic content reported as gallic acid equivalent, trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity and ferric reducing antioxidant property reported as ascorbic acid equivalent of essential oils from black pepper.
| Parameter (unit) | Value |
|---|---|
| Total phenol (gallic acid equivalent) (mg/100 g) | 4.41 ± 0.34 |
| Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (mmol/g) | 2.25 ± 0.32 |
| Ferric reducing antioxidant property (ascorbic acid equivalent) (mg/100 g) | 11.12 ± 0.83 |
Values represent means ± standard deviation of triplicate readings.
Table 2.
Chemical composition of essential oils from black pepper.
| Composant | RT | % |
|---|---|---|
| Camphene | 4.738 | 0.26 |
| Limonene | 7.715 | 0.34 |
| α-Pinene | 9.428 | 13.63 |
| β-Pinene | 10.955 | 41.24 |
| Benzyl alcohol | 11.502 | 0.62 |
| Cis-ocimene | 12.526 | 3.63 |
| Myrcene | 13.042 | 4.37 |
| Allo-ocimene | 13.147 | 3.43 |
| Pinene-2-ol | 13.790 | 2.79 |
| α-Thujene | 14.176 | 2.98 |
| Gamma terpinene | 14.902 | 5.68 |
| Neral | 15.337 | 0.54 |
| Geranial | 15.405 | 0.43 |
| Isoartemisia | 16.364 | 0.26 |
| 1,8-Cineole | 16.569 | 17.22 |
| Linalool | 17.665 | 0.87 |
| Borneol | 17.801 | 0.52 |
| Terpinen-4-ol | 18.544 | 0.29 |
| α-Terpineol | 18.710 | 0.28 |
| Thymyl methyl ether | 19.662 |
0.34 |
| α-Copane | 25.091 | 0.22 |
RT: retention time.
Figure 1.

DPPH radical scavenging ability of essential oils from black pepper. Values represent means ± standard deviation of triplicate readings.
Figure 2.
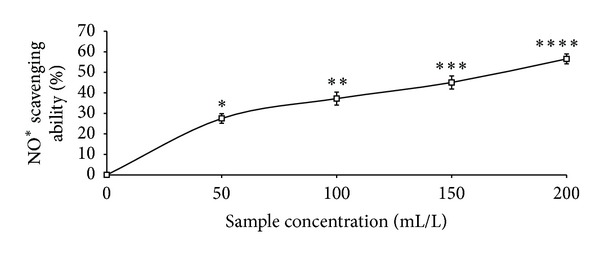
NO radical scavenging ability of essential oils from black pepper. Values represent means ± standard deviation of triplicate readings.
Figure 3.

Fe2+chelating ability of essential oils from black pepper. Values represent means ± standard deviation of triplicate readings.
Table 3.
EC50 of DPPH and NO radical scavenging abilities, Fe2+ chelating ability, and inhibition of α-amylase, α-glucosidase and angiotensin-1 converting enzyme activities by black pepper essential oil extracts.
| Parameter | Value (mL/L) |
|---|---|
| DPPH* | 414.59 ± 11.32 |
| NO* | 161.92 ± 14.26 |
| Fe2+ chelation | 130.21 ± 18.49 |
| α-Amylase | 86.06 ± 4.51 |
| α-Glucosidase | 68.29 ± 4.48 |
| Angiotensin-1 converting enzyme | 28.99 ± 2.68 |
Values represent means ± standard deviation of triplicate readings.
Figure 4.
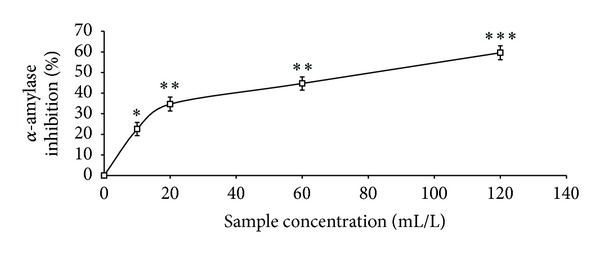
α-Amylase inhibitory activity of essential oils from black pepper. Values represent means ± standard deviation of triplicate readings.
Figure 5.
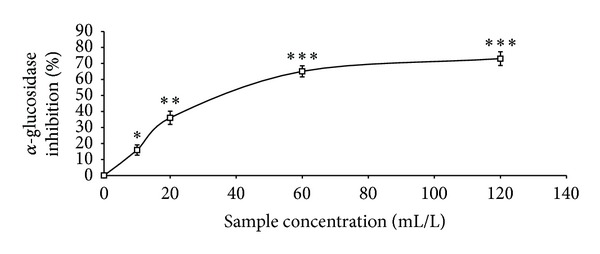
α-Glucosidase inhibitory activity of essential oils from black pepper. Values represent means ± standard deviation of triplicate readings.
Figure 6.
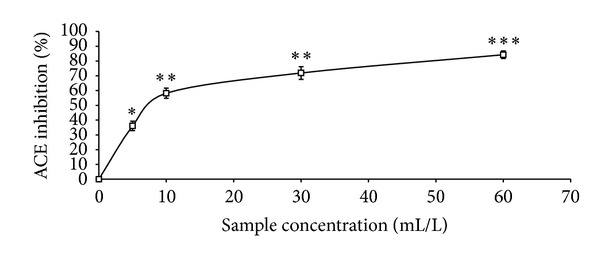
Angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity of essential oils from black pepper. Values represent means ± standard deviation of triplicate readings.
4. Discussion
The link between free radical formation and the development and complications of diabetes has been well-established [31–33]. Furthermore, radical scavengers such as phenolics have been shown to be effective in preventing diabetes in animal models [31]. The radical scavenging abilities of the essential oil and its ferric reducing antioxidant property (FRAP) agree with previous findings by Politeo et al. [1]. Essential oils from Thymus species were also found by Amiri [5] to scavenge the radical. It is noteworthy, however, that the antiradical properties of the essential oils could be attributed to the presence of phenolic monoterpenes [34]. However, the individual and synergistic bioactivities of other compounds with strong antioxidant properties which were identified in the essential oil using GC would also have contributed to the observed antioxidant effects. The ferric reducing ability of the black pepper essential oil could be linked to the α-pinene and 1,8-cineole content, which have been shown to have reductive potentials [35]. Furthermore, the presence of functional groups such as “–OH”, “–O–”, and “–C = O–”, which are present in the volatile compounds of the oil in a favourable structure-function configuration, could contribute to the Fe2+ chelating ability [36, 37].
A modern therapeutic approach to the management of diabetes and its related complications is the inhibition of starch metabolizing enzymes such as α-amylase and α-glucosidase [38] as this will slow down the catabolism of starch into glucose and ultimately moderate the blood glucose level [39]. As presented in this study, black pepper essential oil extracts showed a concentration-dependent inhibition of α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities. Furthermore, the EC50 values revealed that the oil showed a stronger inhibition of α-glucosidase activity than α-amylase activity and this is therapeutically important in preventing some of the side effects associated with the use of synthetic α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitors [40]. Similarly, the inhibition of Angiotensin-1 converting enzyme (ACE) activity is a modern therapeutic approach in the management of hypertension which is one of the complications associated with type-2 diabetes [16]. The essential oil inhibited ACE activity in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner and therefore could have the ability to moderate the conversion of angiotensin-I to angiotensin-II which is a vasoconstrictor that has been implicated in the development of hypertension [41].
5. Conclusion
The antioxidant activity of essential oil from black pepper as well as its inhibition of α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and angiotensin-1 converting enzyme activities could be part of the mechanism by which the oil manages and/or prevents type-2 diabetes and hypertension. However, further in vivo experiments and clinical trials are recommended.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
References
- 1.Politeo O, Jukić M, Miloš M. Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of essential oils of twelve spice plants. Croatica Chemica Acta. 2006;79(4):545–552. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nakatami N. Antioxidants from spices and herbs. In: Shahidi F, editor. Natural Antioxidants: Chemistry, Health Effects and Applications. Champaign, Ill, USA: AOAC Press; 1997. pp. 64–75. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Puertas-Mejía M, Hillebrand S, Stashenko E, Winterhalter P. In vitro radical scavenging activity of essential oils from Columbian plants and fractions from oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) essential oil. Flavour and Fragrance Journal. 2002;17(5):380–384. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kulisic T, Radonic A, Katalinic V, Milos M. Use of different methods for testing antioxidative activity of oregano essential oil. Food Chemistry. 2004;85(4):633–640. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Amiri H. Essential oils composition and antioxidant properties of three thymus species. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2012;2012:8 pages. doi: 10.1155/2012/728065.728065 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Neuwinger HD, editor. Stuttgart, Germany: Med-pharm; 2000. African traditional medicine; p. p. 402. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Udoh FV, Lot TJ, Braide VB. Effects of extracts of seed and leaf of piper guineense on skeletal muscle activity in rat and frog. Phytotherapy Research. 1999;13:106–110. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1573(199903)13:2<106::AID-PTR362>3.0.CO;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Douglas M, Heyes J, Smallfield B. Herbs, Spices and Essential Oils Post-Harvest Operations in Developing Countries. United Nations Industrial Development Organization and Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jirovetz L, Leitner E, Buchbauer G. Recent research—developments in agricultural and food chemistry. Research Signpost. 2001;5:p. 143. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Maritim AC, Sanders RA, Watkins JB., III Diabetes, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: a review. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology. 2003;17(1):24–38. doi: 10.1002/jbt.10058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Baynes JW, Thorpe SR. Role of oxidative stress in diabetic complications: a new perspective on an old paradigm. Diabetes. 1999;48(1):1–9. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.48.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.McLennan SV, Heffernan S, Wright L, et al. Changes in hepatic glutathione metabolism in diabetes. Diabetes. 1991;40(3):344–348. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.3.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lipinski B. Pathophysiology of oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus. Journal of Diabetes and Its Complications. 2001;15(4):203–210. doi: 10.1016/s1056-8727(01)00143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Krentz AJ, Bailey CJ. Oral antidiabetic agents: current role in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs. 2005;65(3):385–411. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200565030-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bischoff H. Pharmacology of α-glucosidase inhibition. The European Journal of Clinical Investigation. 1994;24(3):3–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kwon Y-II, Vattem DA, Shetty K. Evaluation of clonal herbs of Lamiaceae species for management of diabetes and hypertension. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2006;15(1):107–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Erdos EG, Skidgel RA. The angiotensin I-converting enzyme. Laboratory Investigation. 1987;56(4):345–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Council of Europe. European Pharmacopoeia. 3rd edition. Strasbourg, France: Council of Europe; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Singleton VL, Orthofer R, Lamuela-Raventós RM. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of folin-ciocalteu reagent. Methods in Enzymology. 1999;299:152–178. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gyamfi MA, Yonamine M, Aniya Y. Free-radical scavenging action of medicinal herbs from Ghana: Thonningia sanguinea on experimentally-induced liver injuries. General Pharmacology. 1999;32(6):661–667. doi: 10.1016/s0306-3623(98)00238-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC. Formation of a thiobarbituric-acid-reactive substance from deoxyribose in the presence of iron salts: the role of superoxide and hydroxyl radicals. FEBS Letters. 1981;128(2):347–352. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80114-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A, Pannala A, Yang M, Rice-Evans C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 1999;26(9-10):1231–1237. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(98)00315-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Marcocci L, Maguire JJ, Droy-Lefaix MT, Packer L. The nitric oxide-scavenging properties of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 1994;201(2):748–755. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Oyaizu M. Studies on products of browning reaction: antioxidative activity of products of browning reaction prepared from glucosamine. Japanese Journal of Nutrition. 1986;44:307–315. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Minotti G, Aust SD. An investigation into the mechanism of citrate-Fe2+-dependent lipid peroxidation. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 1987;3(6):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(87)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Puntel RL, Nogueira CW, Rocha JBT. Krebs cycle intermediates modulate thiobarbituric acid reactive species (TBARS) production in rat brain in vitro. Neurochemical Research. 2005;30(2):225–235. doi: 10.1007/s11064-004-2445-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Worthington Biochemical Corporation. Worthington Enzyme and Related Biochemicals. Freehold, NJ, USA: Worthington Biochemical Corporation; 1978. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Apostolidis E, Kwon YI, Shetty K. Inhibitory potential of herb, fruit, and fungal-enriched cheese against key enzymes linked to type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies. 2007;8(1):46–54. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cushman DW, Cheung HS. Spectrophotometric assay and properties of the angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung. Biochemical Pharmacology. 1971;20(7):1637–1648. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(71)90292-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zar JH. Biostatistical Analysis. Bergen, NJ, USA: Prentice-Hall; 1984. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Oberley LW. Free radicals and diabetes. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 1988;5(2):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(88)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wolff SP. Diabetes mellitus and free radicals. Free radicals, transition metals and oxidative stress in the aetiology of diabetes mellitus and complications. The British Medical Bulletin. 1993;49(3):642–652. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Baynes JW. Role of oxidative stress in development of complications in diabetes. Diabetes. 1991;40(4):405–412. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.4.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mastelić J, Jerković I, Blažević I, et al. Comparative study on the antioxidant and biological activities of carvacrol, thymol, and eugenol derivatives. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2008;56:3989–3996. doi: 10.1021/jf073272v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Aazza S, Lyoussi B, Miguel MG. Antioxidant and antiacetylcholinesterase activities of some commercial essential oils and their major compounds. Molecules. 2011;16(9):7672–7690. doi: 10.3390/molecules16097672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lindsay RC. Food additives. In: Fennema OR, editor. Food Chemistry. New York, NY, USA: Marcel Dekker; 1996. pp. 778–780. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yuan YV, Bone DE, Carrington MF. Antioxidant activity of dulse (Palmaria palmata) extract evaluated in vitro. Food Chemistry. 2005;91(3):485–494. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Shim YJ, Doo HK, Ahn SY, et al. Inhibitory effect of aqueous extract from the gall of Rhus chinensis on alpha-glucosidase activity and postprandial blood glucose. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2003;85(2-3):283–287. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(02)00370-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kwon YI, Apostolidis E, Kim YC, Shetty K. Health benefits of traditional corn, beans, and pumpkin: in vitro studies for hyperglycemia and hypertension management. Journal of Medicinal Food. 2007;10(2):266–275. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2006.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Padmanabha Rao A, Jamil K. Pharmacological evaluation of herbal extracts for their in vitro hypoglycemic activity. International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences. 2011;2(3):15–21. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ahnfelt-Ronne I. Enzyme inhibitors as drugs. In: Krogsgaard-Larsen P, Bundgaard H, editors. A Textbook of Drug Design and Development. Chur, Switzerland: Harvood Academic Publishers; 1991. pp. 302–307. [Google Scholar]


