Abstract
The metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a cluster of risk factors including obesity, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, elevated blood pressure and glucose intolerance. The MetS increases the risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD) and type 2 diabetes. Each component of the MetS causes cardiac dysfunction and their combination carries additional risk. The mechanisms underlying cardiac dysfunction in the MetS are complex and might include lipid accumulation, increased fibrosis and stiffness, altered calcium homeostasis, abnormal autophagy, altered substrate utilization, mitochondrial dysfunction and increased oxidative stress. Mitochondrial and extra-mitochondrial sources of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduced antioxidant defense mechanisms characterize the myocardium of humans and animals with the MetS. The mechanisms for increased cardiac oxidative stress in the MetS are not fully understood but include increased fatty acid oxidation, mitochondrial dysfunction and enhanced NADPH oxidase activity. Therapies aimed to reduce oxidative stress and enhance antioxidant defense have been employed to reduce cardiac dysfunction in the MetS in animals. In contrast, large scale clinical trials using antioxidants therapies for the treatment of CVD have been disappointing because of the lack of efficacy and undesired side effects. The focus of this review is to summarize the current knowledge about the mechanisms underlying cardiac dysfunction in the MetS with a special interest in the role of oxidative stress. Finally, we will update the reader on the results obtained with natural antioxidant and mitochondria-targeted antioxidant therapies for the treatment of CVD in the MetS.
Keywords: Cardiac dysfunction, mitochondrial dysfunction, reactive oxygen species, antioxidants, oxidative stress, substrate utilization, metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance
INTRODUCTION
The metabolic syndrome (MetS) represents a cluster of cardiovascular risk factors that includes abdominal obesity, dyslipidimia, hypertension, and impaired glucose tolerance. The MetS increases the risk for type 2 diabetes (T2D) and cardiovascular disease (CVD). Thus, people with the MetS have a five-fold higher risk of T2D and a two to three-fold higher risk of atherosclerotic CVD than those without [1–2]. The etiology of CVD in patients with MetS may involve: coronary atherosclerotic disease, arterial hypertension, left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy, diastolic dysfunction, endothelial dysfunction, coronary micro-vascular disease and autonomic dysfunction. The pathogenesis of CVD in the MetS is multifactorial as it can be caused by one or more factors associated with this condition such as the systemic abnormalities, insulin resistance, diabetes and/or inflammation. One common characteristic of CVD in the MetS and the insulin resistant state is increased oxidative stress in the heart [3–4]. Indeed, patients with the MetS have elevated systemic oxidative damage as a result of overproduction of ROS and decreased antioxidant protection [5–6]. In this review, we will first summarize the contribution of each component of the MetS to cardiac dysfunction and then highlight the underlying mechanisms with a special focus on the contribution of oxidative stress. Finally, we will summarize and discuss past and current studies using antioxidant therapies to treat CVD in the MetS.
CARDIAC DYSFUNCTION IN THE METABOLIC SYNDROME
Each component of the MetS is known to independently affect cardiac structure and function, but their combination under this syndrome seems to carry additional risk [7–8]. Thus, cardiac dysfunction can occur in patients with normal coronary artery disease or other etiologies, suggesting the existence of specific cardiomyopathies such as obesity-related cardiomyopathy, diabetic cardiomyopathy and insulin resistance-related cardiac dysfunction. As summarized in (Fig. 1), common mechanisms responsible for cardiac dysfunction are shared between obesity, diabetes and insulin resistance, however unique mechanisms characterize each component of the MetS.
Fig. 1. Mechanisms for altered cardiac function in the metabolic syndrome.
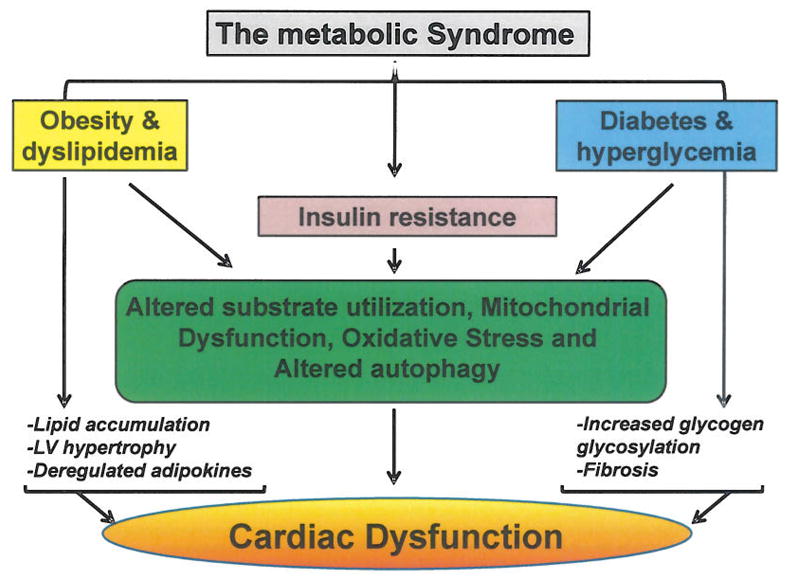
Common and distinct mechanisms responsible for cardiac dysfunction are highlighted for three important components of the metabolic syndrome; Obesity and dyslipidemia, diabetes and hyperglycemia and insulin resistance.
MECHANISMS FOR OBESITY-RELATED CARDIOMYOPATHY
Obesity itself or in association with dyslipidimia promotes hearts failure in humans [9–10]. Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain cardiac dysfunction in obesity including increased hemodynamic load, cardiac hypertrophy, increased lipid accumulation and altered substrate metabolism. For example, an association between myocardial triacylglycerol (TG) content and concentric LV hypertrophy with subtle reduction in systolic function was reported in humans [11]. Similarly, a higher cardiac TG content was observed in heart of obese or T2D patients [12], suggesting the involvement of cardiac lipid accumulation in the pathogenesis of cardiac dysfunction in the MetS (See Review by Kusminski et al. [13]). In addition to the above mentioned mechanisms, it was recently suggested that adipose-derived factors and adipokines such as leptin, adiponectin, resistin and fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4) can directly affect cardiac structure and function. Indeed, elevated circulating leptin levels are predictors of worse outcome in patients with CVD and heart failure [14]. Furthermore, leptin treatment of neonatal ventricular myocytes promotes cardiac hypertrophy through the regulation of actin dynamics [15]. In contrast, leptin treatment of the leptin-deficient (ob/ob) or the leptin receptor-deficient (db/db) mice completely normalized cardiac hypertrophy [16], suggesting rather an antihypertrophic role for leptin. Depressed plasma adiponectin levels correlated inversely with the MetS and T2D and increased the risk of myocardial infarction and heart failure [17–19]. Similar to findings with leptin, adiponectin also has antihypertrophic properties as its reduction in mice promotes the development of LV hypertrophy [20]. Moreover, serum resistin levels are usually high in mouse models of the MetS and in humans with heart failure [21–24]. Resistin affects both the structure and the function of the heart. Indeed, in-vitro and in-vivo studies have suggested a role for resistin in promoting cardiac hypertrophy and reducing contractility [21, 25]. Finally, adipocytes-derived fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4) levels were found to correlate positively with the MetS in a cross-sectional study [26] and this fat-specific factor reduced cardiac function through modulation of intracellular calcium [27–28].
MECHANISMS FOR DIABETIC CARDIOMYOPATHY
Since its first introduction by Rubier et al. [29] forty years ago, the existence of a unique diabetic cardiomyopathy has been confirmed in numerous studies (see reviews by Boudina and Abel [30–31]). Indeed, diabetes increased the risk for heart failure even after adjusting for age, blood pressure, weight, cholesterol and coronary artery disease. Thus, CVD is 2–3 times more common, and survival is worse in subjects with diabetes in comparison with age-matched and sex-matched counterparts [32–34]. According to the molecular theory of diabetic cardiomyopathy, hyperglycemia is the main pathogenetic factor, which causes abnormalities at the cardiac myocyte level, eventually leading to structural and functional abnormalities [35]. Diabetic cardiomyopathy is characterized by an initial diastolic dysfunction that occurs before altered systolic function [36–37]. One proposed mechanism for altered diastolic function in diabetic myocardium is enhanced deposition of glycosylated glycogen, which is known to promote cardiac stiffness via increased fibrosis [38–40]. In parallel, hyperglycemia was shown to directly alter components of calcium homeostasis, leading to diastolic dysfunction (See review by Dobrin and Lebeche [41]). Indeed, the activity and the content of the sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) is decreased in diabetes [42–43] and the hemodynamic dysfunction is prevented by up-regulation of SERCA in a rat model of the MetS [44]. In addition to reducing left ventricular relaxation time, SERCA2a gene transfer therapy reduced oxygen cost for contraction in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes [45], highlighting the importance of calcium in metabolic regulation. The mechanisms by which hyperglycemia affects SERCA activity are through (1) oxidative stress-mediated oxidation of its cysteine thiols which interferes with the ATP binding site, making it unable to hydrolyze ATP [46] and (2) through direct cross-linking of collagen with SERCA, which inhibits its activity. More recently, a role of micro RNAs in cardiac dysfunction caused by diabetes has emerged [47]. Indeed, the expression of miR133, the most abundant micro RNA in the heart, was reduced by diabetes, and hyperglycemia-induced cardiac hypertrophy was prevented by miR133 over-expression in cardiac myocytes in-vitro [48].
MECHANISMS FOR INSULIN RESISTANCE-RELATED CARDIAC DYSFUNCTION
The MetS and insulin resistance are associated with abnormal LV diastolic function and structure independently of age, gender, blood pressure and fasting plasma glucose [49]. Furthermore, insulin resistance predicts the incidence of heart failure independently of other established risk factors, including diabetes and obesity [50]. Moreover, the contribution of insulin resistance to cardiac dysfunction without the systemic abnormalities associated with the MetS has recently been studied using a mouse model of cardiac insulin resistance obtained by deletion of insulin receptors specifically in cardiomyocytes (CIRKO mice) [51]. Whereas at baseline, these mice exhibit mild alterations of cardiac performance, their response to pressure overload [52], isoproterenol treatment [53] or myocardial infarction [54] is altered, suggesting that insulin resistance increased the susceptibility for the development of cardiac dysfunction independently of obesity or diabetes. The mechanisms involved in insulin resistance-mediated cardiac dysfunction include altered substrate metabolism, persistent expression of the fetal beta-myosin heavy chain isoform, reduced angiogenesis and mitochondrial dysfunction.
COMMON MECHANISMS BETWEEN OBESITY, DIABETES AND INSULIN RESISTANCE
1- Altered Cardiac Substrate Metabolism
The mammalian heart possesses the capacity of oxidizing any available substrate to maintain a steady level of ATP required for contraction. Although, oxidation of fatty acids (FA) is predominant in the adult heart, the use of glucose, lactate and ketones can be enhanced in certain pathological condition (See review by Duncan JG [55]. This flexibility in substrate use is important for normal cardiac function and its alteration by the MetS contribute to cardiac dysfunction. Thus, obesity, diabetes and/or insulin resistance independently or in combination affect this flexibility due to alteration in substrate availability or to impairment in transcriptional regulation of oxidation pathways. For example, obesity in mice enhances cardiac FA oxidation and reduces glucose oxidation independently of diabetes [56]. The mechanisms for obesity-related alteration in cardiac substrate utilization are not completely understood but involve enhanced FA and reduced glucose availability and leptin resistance [57]. Similarly, type 1 and type 2 diabetes enhanced FA oxidation and uptake whereas glucose utilization was reduced [58–60]. The mechanisms for increased cardiac FA uptake and oxidation in the MetS include impaired glucose transport, enhanced long-chain FA uptake through relocation of the FA transporter CD36 in the sarcolema [61] and increased mitochondrial CPT-1 activity [62]. Whereas, altered cardiac substrate metabolism is evident in the MetS, there was no correlation between impaired substrate use and LV diastolic dysfunction in type 2 diabetic patients, thus excluding a causal role in the development of cardiac dysfunction during the MetS [60]. Finally, insulin resistance without confounding systemic abnormalities was shown to reduce both glucose and FA oxidation in the heart possibly via a reduction in the expression of genes involved in FA oxidation and by impairing mitochondrial oxidative capacity [51, 63].
2- Altered Cardiac Mitochondrial Function and Biogenesis
Mitochondrial dysfunction plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of cardiac dysfunction in the MetS. Indeed, each component of the MetS is known to independently modulate mitochondrial function, proteome and biogenesis. Whereas most studies examining changes in mitochondrial function in the MetS in humans have been performed in skeletal muscle, the results cannot be extrapolated to the heart due to its higher mitochondrial oxidative capacity and content. Thus, most of what we currently know about mitochondrial function in the heart comes from animal models of the MetS with the exception of few indirect studies looking at cardiac oxygen consumption, phosphocreatine (Pcr)/ATP ratios or atrium mitochondrial oxygen consumption in obese or T2D patients. These studies associated mitochondrial uncoupling and/or dysfunction with increased cardiac oxygen cost for contraction in obese individuals [64], decreased high energy phosphate metabolism in the diabetic heart [65–66] and reduced mitochondrial maximal capacity to oxidize FA and glutamate in T2D patients [67]. In contrast to human studies, mitochondrial dysfunction in the heart of genetically obese db/db mice was first reported in the 80s by Kuo et al. [68] and then confirmed by a recent study [69]. Furthermore, impaired mitochondrial function and biogenesis was identified in other mouse models of obesity and insulin resistance such as the leptin-deficient ob/ob mice [70] and UCP-DTA mice [71]. The mechanisms for impaired cardiac mitochondrial function and biogenesis in the MetS and the insulin resistant state have been extensively reviewed [3, 72–74] and include enhanced FA-induced mitochondrial uncoupling [69], increased mitochondrial oxidative stress [67, 75–76], impaired mitochondrial calcium handling [77–78], enhanced mitochondrial DNA damage [79], altered mitochondrial proteome [80–84] and deregulation of mitochondrial biogenesis [72–73, 85].
3- Impaired Cardiac Autophagy
Although autophagy, which is a physiologic process by which a cell clean damaged proteins and organelles, has been known since the 60s, its role in CVD has been recently introduced. Thus, defect in autophagy causes cardiac dysfunction and heart failure particularly under increased cellular stress such as ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) [86]. Furthermore, autophagy plays a central role in cardiac dysfunction during aging and its modulation might represent a promising way to treat cardiac senescence [87–89]. Similarly, long-term caloric restriction enhances autophagy and preserves cardiac function in otherwise healthy mice [90]. Although autophagy has been implicated in various pathologies of the heart, it is until recently that the pathophysiologic role of autophagy in the MetS has been introduced [91–92]. Thus, autophagy is reduced in the hearts of OVE26 mice, a mouse model of severe type 1 diabetes that develop diabetic cardiomyopathy, an effect that was exacerbated by the inhibition of AMPK and alleviated by metformin treatment [93]. More recently, autophagy was found to be deregulated in the heart of high fat-fed mice (a mouse model of the MetS), rendering them more susceptible to I/R injury [94]. The mechanisms underlying the deregulation of autophagy and whether it can be targeted to treat cardiac dysfunction in the MetS require more work.
4- Increased Cardiac Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress (OS) is defined as an excess formation or insufficient removal of highly reactive molecules such as reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) [95]. Many aspects of the relationship between OS and endothelial dysfunction in the MetS and diabetes have been previously reviewed [96–97], this review will focus on the role of OS in cardiac dysfunction in the MetS. Increased systemic OS, as evidenced by reduced serum vitamin C and α-tocopherol concentrations and decreased superoxide dismutase activity, has been previously documented in patient with the MetS [5–6, 98]. Furthermore, a positive correlation between systemic OS and the development of insulin resistance and diabetes was found in the Framingham Offspring Study [99]. Thus, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) emission was found to be higher in right atrial appendages obtained from patients with T2D undergoing non-emergent coronary artery bypass graft surgery [67]. In contrast to the fewer human studies, many studies have confirmed the existence of OS in the myocardium of animal models with one or more components of the MetS. Thus, succinate-supported H2O2 production as well as lipid and protein oxidation markers were increased in the heart of db/db mice [69]. Furthermore, insulin resistance enhanced cardiac ROS generation independently of hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia and hyperinsulinemia in mice [63], and superoxide production was elevated in the myocardium of high fat-fed spontaneously hypertensive (SHR) rats [100]. Furthermore reduced GSH/GSSG ratio was shown in ob/ob hearts [101] and decreased cardiac expression of manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD), glutathione peroxidase I (GPxI) was observed in high fat-fed and obese Zucker rats [102–103]. Although an association between elevated OS and cardiac dysfunction in the MetS has been established, a causal role for OS in the development of myocardial dysfunction has not been proven yet but one could emphasize that ROS-mediated damage to proteins, DNA and RNA may exacerbate cardiac dysfunction. Furthermore, OS is involved in the pathogenesis of apoptosis as it can directly activate pro-apoptotic signaling pathways such as JNK, p38 and ASK-1 [104–105]. In addition, increased mitochondrial ROS can lead to cytochrome c release and the initiation of apoptosis [106]. The induction of apoptosis by OS plays an important role in cardiac remodeling and fibrosis.
THE SOURCES AND THE MOLECULAR MECHANISMS OF INCREASED OXIDATIVE STRESS IN THE METS
1- Mitochondrial Sources
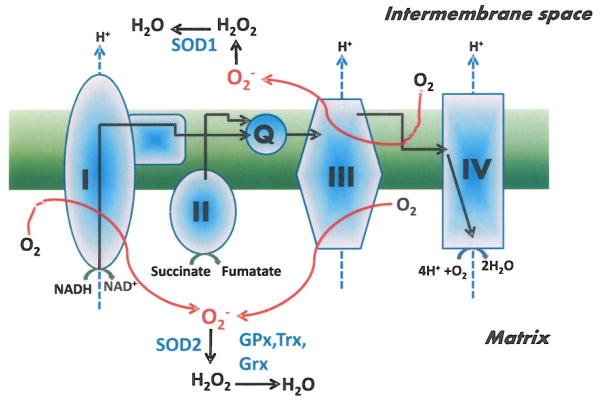
Mitochondrial function is particularly important in the heart since it provides over 90% of myocardial ATP [107]. In the process of normal respiration, 0.4 to 4% of oxygen consumed by mitochondria is incompletely reduced and form ROS [108]. As illustrated in (Fig. 2), ROS are generated at several sites of the electron transport chain (ETC), where electrons leak to O2 to generate superoxide [109]. A significant amount of superoxide is produced at the level of complex I and III of the ETC. Complex I produces superoxide in the matrix [110] whereas its production by complex III happens both in the matrix and in the inter-membrane space [111]. In addition to complex I and III, other less important sources of mitochondrial superoxide have been documented and include pyruvate dehydrogenase, 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase, the electron transferring flavoprotein ubiquinone oxidoreductase (ETF-QOR) (receiving electrons from the β-oxidation) and the glyceraol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase [112–113]. Because of the susceptibility of mitochondrial membranes and DNA to oxidative damage, detoxifying systems are in place to reduce superoxide accumulation. This detoxification is achieved by the conversion of superoxide to H2O2 by MnSOD [114–115] and peroxide reduction by GPx1 and GPx4, thioredoxin reductases (Trx2), glutaredoxin (Grx2) and peroredoxins (Prdx3 and Prdx5), which are all expressed in the mitochondria [116].
Fig. 2. Major sites for mitochondrial superoxide (O2−) generation and its detoxification.
Black arrows indicate electron flow, blue hatched arrows indicate proton flow and red arrows indicate superoxide production. SOD1 and SOD2: superoxide dismutase 1 and 2; GPx: glutathione peroxidase; Trx: thioredoxin and Grx: glutaredoxin. (The color version of the figure is available in the electronic copy of the article).
Mitochondrial-generated H2O2 was documented in the hearts of genetically obese and diabetic db/db mice and in CIRKO mice lacking insulin receptors in cardiac cells [63, 69]. One common finding between these mice is enhanced FA oxidation, which can promote ROS formation. Indeed, a study by St-Pierre et al. [111] demonstrated that mitochondrial H2O2 production in the heart is enhanced when mitochondria are respiring on the FA substrate palmitoylcarnitine compared to other substrate such as glutamate or pyruvate. This is possibly due to enhanced superoxide generation from the ETF-QOR, as a result of accelerated electrons flux through the β-oxidation. This is further confirmed by the association of enhanced activity of enzymes involved in β-oxidation with mitochondrial generation of H2O2 in db/db and CIRKO mice [63, 69], whereas no changes in β-oxidation enzymes activity and no mitochondrial H2O2 generation was detected in ob/ob hearts despite increased FA oxidation [69]. Another possible mechanism for increased mitochondrial ROS is inhibition of the ETC, which can trigger superoxide generation through the reverse electron transfer [111]. This inhibition can be caused in part by glucose or hyperglycemia-mediated O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine glycosylation (O-GlcNAcylation) of mitochondrial complex I, which can lead to ROS generation especially in the presence of excess reducing equivalents [81]. Furthermore, hyperglycemia increased H2O2 formation in neonatal cardiomyocyte cell line that was dependent on mitochondrial fission [117]. Whether increased mitochondrial ROS formation is indeed responsible for cardiac dysfunction in animals with the MetS is possible but has not been fully investigated (see antioxidant therapy section bellow).
2- Extra-mitochondrial Sources
While mitochondria are considered the major source of cell-damaging ROS in the heart, there are other cellular sources. The three predominant extra-mitochondrial systems that produce ROS mammalian cells are NADPH oxidase (NOX), xanthine oxidase (a form of xanthine oxidoreductase) and uncoupled nitric oxide [118]. Thus, the activity of NOX is enhanced in the hearts of obese Zucker rats, leptin-deficient ob/ob mice and high fat-fed rats [103, 119–121]. Interestingly, and confirming the involvement of NOX in ROS generation, NOX inhibition abolished superoxide production in the hearts of these animals [103]. In addition to NOX, xanthine oxidoreductase activity was shown to be elevated in ob/ob hearts whereas nitric oxide synthase level was decreased [122]. All these studies highlight a role for NOX and xanthine oxidoreductase as potential extra-mitochondrial source of ROS but the consequences of inhibiting these enzymes on cardiac function in the MetS have not been extensively investigated. Thus, inhibition of NOX alleviated contractile defects in ob/ob mice, in high fat-fed mice subjected to myocardial infarction and in mice with experimental diabetes [120, 123–124]. One additional cardiac ROS-generating system that is relevant in the MetS is the rennin-angiotensin system (RAS). Indeed, RAS is up-regulated by various components of the MetS such as glucose, circulating lipids, obesity and blood pressure [125], and its activation promotes ROS generation by NADPH oxidase and mitochondria [126].
ANTIOXIDANT THERAPIES AND CARDIAC DYSFUNCTION IN THE METS
I- Non Mitochondria-targeted Antioxidants
Systemic therapeutics for the treatment of CVD in the context of the MetS need to address one or several underlying conditions, including metabolic abnormalities (dyslipidemia and hyperglycemia), hypertension, arterosclerosis, and sleep apnea. There has been a substantial interest in using natural antioxidant compounds for the treatment of CVD such as vitamins, flavonoids and polyphenols. More recently, synthetic antioxidants with selective mitochondrial targeting property have been discovered and used to treat abnormalities associated with the MetS (See Table 1).
Table 1.
Human and animals studies using non mitochondria-targeted or mitochondria-targeted antioxidants for the treatment of cardiovascular disease in the metabolic syndrome Table 1. Human and animals studies using non mitochondria-targeted or mitochondria-targeted antioxidants for the treatment of cardiovascular disease in the metabolic syndrome
| Class of Antioxidants | Name of Antioxidants | Mode of Action | Effect | Animal/In Vitro Studies | Human Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-mitochondria-targeted antioxidants | |||||
| Vitamins | Vitamin C (L-ascorbic acid) | Suppression of adrenergic activity | Reduction of blood pressure | Reduction of blood pressure in non-MetS patients [169] | |
| Vitamin E | No effect | CHAOS trial [128] | |||
| Natural compounds | CoenzymeQ10 | Vitamin-like lipid-soluble component of mitochondrial electron transport chain | Slight reduction of LV mass and systolic blood pressure | Female db/db mice [152] | |
| Reduction of diastolic dysfunction | Children with cardiomyopathy [153] | ||||
| No effect on hypertension | Patients with the MetS [154–155] | ||||
| Resveratrol | Increases expression of SIRT1 [138]. Increases GLUT1, IRS1 expression, AMPK and mTOR phosphorylation, reduces RBP4 and PPAR gamma expression [135]. | Prevention of LV hypertrophy, diastolic dysfunction, interstitial fibrosis | HFHS-fed C57B16 mice [134]. | ||
| Improvement of blood pressure, and cardiac function | Yorkshire miniswine [135]. | ||||
| Moderate reduction of blood pressure | Obese humans [138] | ||||
| Anthocyanin | Nonspecific/Unknown | Reduces oxidative stress | In vitro [141] | ||
| No reduction of blood pressure | Dyslipedemic patients [142] | ||||
| Curcumin | p300 blocker | Regulation of cardiac hypertrophy | Rat neonatal cardiomyocytes cultured in high-glucose medium and rats with STZ-induced diabetes [170] | ||
| Melatonin | Scavenges HO−, O2−, and NO) capable of crossing cell membranes and the blood–brain barrier [171–175] | Reduction of infarct size after IR diet and whole-body metabolic abnormalities | Wistar rats on a high-calorie diet | ||
| Allopurinol | Xantine oxidase inhibitor | ||||
| N-acetylcysteine | Reduction of oxidative stress but compromised cardioprotection | Rats [176]. | |||
| Synthetic compounds | Edaravone (3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazolin-5-one) | Non-specific ROS scavenger | Significant improvement of clinical outcomes | Patients with AMI given during, given during stenting of stenotic arteries [177–178] | |
| Derivatives of natural products | SkQBerb, SkQ-Palm | Mitochondria-targeted derivatives of natural products | Potent ROS-scavenging | Isolated mitochondria and human cells [165] | |
| S17834 | Synthetic analog of resveratrol | ||||
| Mitochondria targeted antioxidants | |||||
| Mn (III) tetrakis 4-benzoic acid porphyrin (MnTBAP) | Improvement of glucose tolerance | Ob/ob mice [148] | |||
| Prevention of cardiac hypertrophy | UCP-DTA mice (unpublished data) | ||||
| MitoTempo and MitoQuinone | Improvement of mitochondrial function and coronary collateral growth after ischemia injury | Zucher obese fatty rats [160] | |||
| Mitochondria-targeted synthetic antioxidant peptide | SS-31 | Targeting to inner mitochondrial membrane | Prevention of cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury | HF-fed rats [179]. | |
| Prevention of mitochondrial depolarization | Immortalized cell lines [180] | ||||
| Bendavia | Analog of SS-31 | Moderate reduction of infarct size and improved cardiomyocyte survival | Sheep, rabbit, and guinea pig models of ischemia/reperfusion injury [162] | ||
| Scavenging of H2O2 | Immortalized cell lines [163] | ||||
List of non- standard abbreviations and acronyms
CPT-1: Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1
FA: Fatty acid
AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase
OS: Oxidative stress
GSH: Reduced glutathione
GSSG: Oxidized glutathione
ETC: Electron transport chain
NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-oxidase
SIRT-1: Sirtuin 1
LDL: Low density lipoprotein
JNK: Jun N-terminal kinase
ASK-1: apoptosis signal-regulated kinase 1
Vitamins
Vitamin E supplementation in Chinese women for 4 month improved plasma cholesterol levels and markers of oxidative stress [127]. However, unlike smaller trials, investigation of vitamins administration to larger cohorts of patients did not show positive results. A randomized trial using Vitamin E daily did not have significant effects on cardiovascular outcomes in patients enrolled in the Cambridge Heart Antioxidant Study (CHAOS) [128]. A combination of vitamins C and E did not affect metabolic parameters (body weights, hemoglobin Alc, low density lipoprotein or triglycerides) of patients with the MetS or T2D [129]. Furthermore, co-administration of α-lipoic acid and vitamin E to patients with the MetS, failed to improve their metabolic profile [130]. Overall, vitamin supplementation does not appear sufficient to improve preexisting metabolic or cardiovascular complications in humans as reviewed elsewhere [131–132].
Flavonoids and Polyphenols
In contrast to vitamins, flavonoids and polyphenols supplementation has proven to be efficacious in reducing the metabolic abnormalities as well as cardiac dysfunction in patients or animals with the MetS. Thus, resveratrol, which is an antioxidant found in red wine and grape skin/seed, has protective cardiovascular properties [133]. Resveratrol and S17834 (a synthetic flavonoid derivative) prevented LV hypertrophy, diastolic dysfunction, and interstitial fibrosis and reduced levels of oxidative modifications and hyper-insulinemia in high fat high sucrose-fed C57B16 mice [134]. Similarly, resveratrol improved LDL, plasma glucose and insulin, blood pressure, and cardiac function, in Yorkshire mini swine fed a high cholesterol diet [135]. Furthermore, resveratrol supplementation in rats fed 65% sucrose, improved glucose tolerance, plasma insulin and triglyceride levels and enhanced hepatic catalase and superoxide dismutase enzyme activities [136]. In humans, moderate wine consumption may lower the incidence of the MetS and the associated cardiovascular complications, a finding that has been recently reviewed (See review by Liu et al. [137]). A recent study in obese humans showed that 30 days of resveratrol supplementation increased metabolic rate, moderately lowered blood pressure, and reduced plasma insulin, glucose and triglyceride levels. This was paralleled by an increase in skeletal muscle mitochondrial function as a result of enhanced AMPK activity and SIRT1 expression [138]. These beneficial effects of resveratrol are believed to be mediated by AMPK as mice deficient in this metabolic sensor are resistant to the beneficial metabolic effect of resveratrol in high fat-fed mice [139]. Overall, human and animal studies hold a great promise for resveratrol use to treat cardiovascular complications in the MetS [140].
Similar to resveratrol, anthocyanin was shown to reduce oxidative stress in-vitro [141] and LDL cholesterol but not blood pressure or other metabolic parameters in dyslipidemic patients [142]. Finally, quercetin reduced systolic blood pressure and plasma oxidized LDL concentration in overweight subjects with high-cardiovascular disease risk [143] reduced blood pressure and improved cardiac function in Wistar rats fed high carbohydrate high fat diet [144]. Other natural supplements such as genistein, triterpenoid, naringenin and curcumin have shown some in-vitro activity against the MetS but in-vivo studies are required to confirm their benefits on CVD [145].
II- Mitochondria-Targeted Antioxidants
Since mitochondria is considered a substantial source of ROS in the heart of humans and animals with the MetS and mitochondrial dysfunction is believed to participate in the development of CVD under this condition, antioxidant therapies should focus on novel class of compounds with high mitochondrial affinity as the new way to treat CVD in the MetS, a topic that has been recently reviewed by Subramanian et al [146]. Among mitochondria-targeted compounds that have been used in animal studies are superoxide dismutase (SOD) mimetics, CoenzymeQ10 and its analogues and mitochondria-targeted small peptides.
SOD Mimetics
Pharmacological mimetics of antioxidant enzymes, including MnSOD, were shown to be effective in reducing ROS and restoring mitochondrial function [147]. Treatment of ob/ob mice with the SOD mimetic and peroxynitrite scavenger MnTBAP, improved glucose tolerance but cardiac function was not assessed in this study [148]. Furthermore, treatment of L6 myotubes with MnTBAP was able to restore insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation after palmitate treatment and in high fat feeding in mice [149]. Whether MnTBAP treatment improves cardiac dysfunction in the MetS is yet to be determined in future studies (See Table 1).
CoenzymeQ10 and its Analogs
CoenzymeQ10 is a vitamin-like lipid-soluble component of the mitochondrial ETC. Studies in cells showed that exogenous administration of CoenzymeQ10 leads to its mitochondrial localization in contrast to vitamin E, as its distribution in cells correlates directly with lipid distribution [150]. A recent study demonstrated that the use of CoenzymeQ10 supplementation reduced superoxide generation and ameliorated diastolic dysfunction in db/db mice [151]. Furthermore, CoenzymeQ10 treatment, in female db/db mice, slightly lowered LV mass, systolic blood pressure, and lipid peroxidation [152]. Similarly, addition of CoenzymeQ10 to regular medications, reduced diastolic dysfunction in children with cardiomyopathy [153]. However, supplementation with CoenzymeQ10 was not sufficient to reduce hypertension in patients with the MetS [154–155].
MitoQ, a triphenylphosphonium-conjugated derivative of Co-enzymeQ, is a mitochondria-targeted antioxidant that efficiently reduces oxidative stress [156] but has no adverse effects on wild-type mice [156–157]. When supplemented in drinking water, MitoQ decreased cardiac dysfunction in rats subjected to I/R [158]. Similarly, MitoQ decreased adiposity, hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia in high fat-fed ApoE−/− and ATM+/−/ApoE−/− mouse models of the MetS [159]. So far, human studies using this compound have been performed only in the context of Parkinson’s disease and chronic hepatitis C [157]. Finally, administration of MitoTempol (another mitochondria-targeted antioxidant) and MitoQ in drinking water improved mitochondrial function and coronary collateral growth after I/R in Zucher obese fatty rats [160].
Mitochondria-targeted Peptides
A mitochondria-targeted synthetic antioxidant peptide SS-31 protected against cardiac I/R injury when given ex-vivo and ameliorated hypertensive cardiomyopathy and myocardial oxidative stress induced by Angiotensin-II [161]. In sheep, rabbit, and guinea pig models of I/R, SS-31 analogs moderately reduced infarct size and improved cardiomyocyte survival [162]. Administration of another SS-31 analog at the onset of reperfusion reduced infarct size in diabetes [163–164]. Whereas the use of these small mitochondria-targeted peptides is protective against I/R, their use for the treatment of cardiac dysfunction in the MetS needs further investigations.
Other Semi-natural Products
SkQBerb and SkQPalm (derivatives of natural products) are novel mitochondria-targeted antioxidants that showed potent ROS-scavenging properties in isolated mitochondria and in human cells [165]. Their use in the context of CVD and the MetS has not yet been explored.
Ill- Gene Transfer Therapy
Despite disappointing results of various oral antioxidant treatment trials, promising findings have been reported using gene delivery of enzymes to improve NO bioavailability and decrease oxidative stress in animal models for cardiovascular diseases. Increased MnSOD expression in diabetic cardiomyocytes led to improved contractility [166]. Furthermore, over-expression of cardiac specific metallothionein (a heavy metal scavenger) in mice reduced ROS levels and improved cardiac and mitochondrial function after long-term high-fat feeding [167]. Finally, enhanced MnSOD or catalase expression normalized contractility in mouse models of type 1 and type 2 diabetes [166, 168]. Whereas these results suggest a protective role of anti-oxidants gene delivery, more work is needed to investigate the signaling pathways involved.
CONCLUSION
Because of the increasing obesity and T2D rates worldwide, there is an urgent need to develop new therapeutic strategies to prevent the CVD associated with these conditions. Therapeutic strategies aimed to reducing systemic abnormalities associated with these conditions such as reducing circulating glucose, cholesterol and triglyceride levels, were unable to reverse cardiovascular complications (ACCORD study) or were abandoned due to failure to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. These disappointing results indicate that targeted therapies are indeed required to reduce or prevent the development of CVD in the MetS. The use of antioxidant as a therapy for the treatment of CVD in the MetS is to be considered however, care in their use in hearts exhibiting oxidative stress might be useful. Furthermore, caution has to be taken when the rates of FA oxidation are high, because the use of antioxidants in this case might eliminate the beneficial effect of ROS on facilitating FA-induced mitochondrial uncoupling, a process that is required to reduce further ROS generation. Finally, and based on animal studies, antioxidant therapies have proven to be effective only as treatments but not as prevention strategies potentially because of negative effects associated with excessive antioxidant scavenging in non-stressed hearts.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants 09SDG2220218 from the American Heart Association and P30-HL-101310 from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to Sihem Boudina and Grant T32DK091317 from NIH/NIDDK to Olesya Ilkun. O.I. researched literature and wrote part of the manuscript. S.B. researched the literature, wrote part of the manuscript and constructed and edited the manuscript.
Footnotes
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflicts of interest.
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net
References
- 1.Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation. 2005;112(17):2735–52. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.169404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Grundy SM. Metabolic syndrome: a multiplex cardiovascular risk factor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Feb;92(2):399–404. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-0513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bugger H, Abel ED. Molecular mechanisms for myocardial mitochondrial dysfunction in the metabolic syndrome. Clin Sci (Lond) 2008;114(3):195–210. doi: 10.1042/CS20070166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nicolson GL. Metabolic syndrome and mitochondrial function: molecular replacement and antioxidant supplements to prevent membrane peroxidation and restore mitochondrial function. J Cell Biochem. 2007;100(6):1352–69. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Palmieri VO, Grattagliano I, Portincasa P, Palasciano G. Systemic oxidative alterations are associated with visceral adiposity and liver steatosis in patients with metabolic syndrome. J Nutr. 2006;136(12):3022–6. doi: 10.1093/jn/136.12.3022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Armutcu F, Ataymen M, Atmaca H, Gurel A. Oxidative stress markers, C-reactive protein and heat shock protein 70 levels in subjects with metabolic syndrome. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2008;46(6):785–90. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2008.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Voulgari C, Moyssakis I, Papazafiropoulou A, et al. The impact of metabolic syndrome on left ventricular myocardial performance. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2010;26(2):121–7. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chinali M, de Simone G, Roman MJ, et al. Cardiac markers of pre-clinical disease in adolescents with the metabolic syndrome: the strong heart study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52(11):932–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.04.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.He J, Ogden LG, Bazzano LA, Vupputuri S, Loria C, Whelton PK. Risk factors for congestive heart failure in US men and women: NHANES I epidemiologic follow-up study. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161(7):996–1002. doi: 10.1001/archinte.161.7.996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kenchaiah S, Evans JC, Levy D, et al. Obesity and the risk of heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(5):305–13. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa020245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins RL, Metzger GJ, et al. Myocardial triglycerides and systolic function in humans: in vivo evaluation by localized proton spectroscopy and cardiac imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2003;49(3):417–23. doi: 10.1002/mrm.10372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sharma S, Adrogue JV, Golfman L, et al. Intramyocardial lipid accumulation in the failing human heart resembles the lipotoxic rat heart. FASEB J. 2004;18(14):1692–700. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-2263com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kusminski CM, Shetty S, Orci L, Unger RH, Scherer PE. Diabetes and apoptosis: lipotoxicity. Apoptosis. 2009;14(12):1484–95. doi: 10.1007/s10495-009-0352-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Karmazyn M, Purdham DM, Rajapurohitam V, Zeidan A. Leptin as a cardiac hypertrophic factor: a potential target for therapeutics. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2007;17(6):206–11. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2007.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zeidan A, Javadov S, Karmazyn M. Essential role of Rho/ROCK-dependent processes and actin dynamics in mediating leptin-induced hypertrophy in rat neonatal ventricular myocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 2006;72(1):101–11. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.06.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Barouch LA, Berkowitz DE, Harrison RW, O’Donnell CP, Hare JM. Disruption of leptin signaling contributes to cardiac hypertrophy independently of body weight in mice. Circulation. 2003;108(6):754–9. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000083716.82622.FD. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mohan V, Deepa R, Pradeepa R, et al. Association of low adiponectin levels with the metabolic syndrome--the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES-4) Metabolism. 2005;54(4):476–81. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2004.10.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pischon T, Girman CJ, Hotamisligil GS, Rifai N, Hu FB, Rimm EB. Plasma adiponectin levels and risk of myocardial infarction in men. JAMA. 2004;291(14):1730–7. doi: 10.1001/jama.291.14.1730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Schulze MB, Shai I, Rimm EB, Li T, Rifai N, Hu FB. Adiponectin and future coronary heart disease events among men with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2005;54(2):534–9. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.2.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Shibata R, Ouchi N, Ito M, et al. Adiponectin-mediated modulation of hypertrophic signals in the heart. Nat Med. 2004;10(12):1384–9. doi: 10.1038/nm1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kim M, Oh JK, Sakata S, et al. Role of resistin in cardiac contractility and hypertrophy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008;45(2):270–80. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2008.05.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Takeishi Y, Niizeki T, Arimoto T, et al. Serum resistin is associated with high risk in patients with congestive heart failure--a novel link between metabolic signals and heart failure. Circ J. 2007;71(4):460–4. doi: 10.1253/circj.71.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhang MH, Na B, Schiller NB, Whooley MA. Association of resistin with heart failure and mortality in patients with stable coronary heart disease: data from the heart and soul study. J Card Fail. 2011;17(1):24–30. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2010.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Frankel DS, Vasan RS, D’Agostino RB, Sr, et al. Resistin, adiponectin, and risk of heart failure the Framingham offspring study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53(9):754–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.07.073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chemaly ER, Hadri L, Zhang S, et al. Long-term in vivo resistin overexpression induces myocardial dysfunction and remodeling in rats. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011;51(2):144–55. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.04.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Xu A, Wang Y, Xu JY, et al. Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein is a plasma biomarker closely associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome. Clin Chem. 2006;52(3):405–13. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2005.062463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lamounier-Zepter V, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Karczewski P, Haase H, Bornstein SR, Morano I. Human adipocytes attenuate cardiomyocyte contraction: characterization of an adipocyte-derived negative inotropic activity. FASEB J. 2006;20(10):1653–9. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-5436com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lamounier-Zepter V, Look C, Alvarez J, et al. Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein suppresses cardiomyocyte contraction: a new link between obesity and heart disease. Circ Res. 2009;105(4):326–34. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.200501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rubler S, Dlugash J, Yuceoglu YZ, Kumral T, Branwood AW, Grishman A. New type of cardiomyopathy associated with diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Am J Cardiol. 1972 Nov 8;30(6):595–602. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(72)90595-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Boudina S, Abel ED. Diabetic cardiomyopathy revisited. Circulation. 2007;115(25):3213–23. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.679597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Boudina S, Abel ED. Diabetic cardiomyopathy, causes and effects. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2010 Mar;11(1):31–9. doi: 10.1007/s11154-010-9131-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Regan TJ, Lyons MM, Ahmed SS, et al. Evidence for cardiomyopathy in familial diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1977;60(4):884–99. doi: 10.1172/JCI108843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ho KK, Pinsky JL, Kannel WB, Levy D. The epidemiology of heart failure: the Framingham Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993;22(4 Suppl A):6A–13A. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(93)90455-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kannel WB, McGee DL. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The Framingham study. JAMA. 1979;241 (19):2035–8. doi: 10.1001/jama.241.19.2035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hayat SA, Patel B, Khattar RS, Malik RA. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment. Clin Sci (Lond) 2004;107(6):539–57. doi: 10.1042/CS20040057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Fang ZY, Prins JB, Marwick TH. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: evidence, mechanisms, and therapeutic implications. Endocr Rev. 2004;25(4):543–67. doi: 10.1210/er.2003-0012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Carugo S, Giannattasio C, Calchera I, et al. Progression of functional and structural cardiac alterations in young normotensive uncomplicated patients with type I diabetes mellitus. J Hypertens. 2001;19(9):1675–80. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200109000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Falcao-Pires I, Hamdani N, Borbely A, et al. Diabetes mellitus worsens diastolic left ventricular dysfunction in aortic stenosis through altered myocardial structure and cardiomyocyte stiffness. Circulation. 2011;124(10):1151–9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.025270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Avendano GF, Agarwal RK, Bashey RI, et al. Effects of glucose intolerance on myocardial function and collagen-linked glycation. Diabetes. 1999;48(7):1443–7. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.48.7.1443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ma H, Li SY, Xu P, et al. Advanced glycation endproduct (AGE) accumulation and AGE receptor (RAGE) up-regulation contribute to the onset of diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13(8B):1751–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 41.Dobrin JS, Lebeche D. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: signaling defects and therapeutic approaches. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2010;8(3):373–91. doi: 10.1586/erc.10.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tang WH, Cheng WT, Kravtsov GM, et al. Cardiac contractile dysfunction during acute hyperglycemia due to impairment of SERCA by polyol pathway-mediated oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010;299(3):C643–53. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00137.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Connelly KA, Kelly DJ, Zhang Y, et al. Functional, structural and molecular aspects of diastolic heart failure in the diabetic (mRen-2)27 rat. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;76(2):280–91. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2007.06.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Miklos Z, Kemecsei P, Biro T, et al. Early cardiac dysfunction is rescued by upregulation of SERCA2a pump activity in a rat model of metabolic syndrome. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2012;205(3):381–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2012.02420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sakata S, Lebeche D, Sakata Y, et al. Mechanical and metabolic rescue in a type II diabetes model of cardiomyopathy by targeted gene transfer. Mol Ther. 2006;13(5):987–96. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2006.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Xu KY, Zweier JL, Becker LC. Hydroxyl radical inhibits sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase function by direct attack on the ATP binding site. Circ Res. 1997;80(1):76–81. doi: 10.1161/01.res.80.1.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kantharidis P, Wang B, Carew RM, Lan HY. Diabetes complications: the microRNA perspective. Diabetes. 2011;60(7):1832–7. doi: 10.2337/db11-0082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Feng B, Chen S, George B, Feng Q, Chakrabarti S. miR133a regulates cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2010;26(1):40–9. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hwang YC, Jee JH, Kang M, Rhee EJ, Sung J, Lee MK. Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance are associated with abnormal left ventricular diastolic function and structure independent of blood pressure and fasting plasma glucose level. Int J Cardiol. 2011 Mar 9; doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2011.02.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ingelsson E, Sundstrom J, Arnlov J, Zethelius B, Lind L. Insulin resistance and risk of congestive heart failure. JAMA. 2005;294(3):334–41. doi: 10.1001/jama.294.3.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Belke DD, Betuing S, Tuttle MJ, et al. Insulin signaling coordinately regulates cardiac size, metabolism, and contractile protein isoform expression. J Clin Invest. 2002;109(5):629–39. doi: 10.1172/JCI13946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hu P, Zhang D, Swenson L, Chakrabarti G, Abel ED, Litwin SE. Minimally invasive aortic banding in mice: effects of altered cardiomyocyte insulin signaling during pressure overload. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003;285(3):H1261–9. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00108.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.McQueen AP, Zhang D, Hu P, et al. Contractile dysfunction in hypertrophied hearts with deficient insulin receptor signaling: possible role of reduced capillary density. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2005;39(6):882–92. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2005.07.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sena S, Hu P, Zhang D, et al. Impaired insulin signaling accelerates cardiac mitochondrial dysfunction after myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2009;46(6):910–8. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.02.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Duncan JG. Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-alpha (PPARalpha) and PPAR gamma coactivator-1 alpha (PGC-1 alpha) regulation of cardiac metabolism in diabetes. Pediatr Cardiol. 2011;32(3):323–8. doi: 10.1007/s00246-011-9889-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Buchanan J, Mazumder PK, Hu P, et al. Reduced cardiac efficiency and altered substrate metabolism precedes the onset of hyperglycemia and contractile dysfunction in two mouse models of insulin resistance and obesity. Endocrinology. 2005;146(12):5341–9. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-0938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Sloan C, Tuinei J, Nemetz K, et al. Central leptin signaling is required to normalize myocardial fatty acid oxidation rates in caloric-restricted ob/ob mice. 2011;60(5):1424–34. doi: 10.2337/db10-1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Peterson LR, Herrero P, McGill J, et al. Fatty acids and insulin modulate myocardial substrate metabolism in humans with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2008;57(1):32–40. doi: 10.2337/db07-1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.How OJ, Aasum E, Severson DL, Chan WY, Essop MF, Larsen TS. Increased myocardial oxygen consumption reduces cardiac efficiency in diabetic mice. Diabetes. 2006;55(2):466–73. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.55.02.06.db05-1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Rijzewijk LJ, van der Meer RW, Lamb HJ, et al. Altered myocardial substrate metabolism and decreased diastolic function in nonischemic human diabetic cardiomyopathy: studies with cardiac positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(16):1524–32. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.04.074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Ouwens DM, Diamant M, Fodor M, et al. Cardiac contractile dysfunction in insulin-resistant rats fed a high-fat diet is associated with elevated CD36-mediated fatty acid uptake and esterification. Diabetologia. 2007;50(9):1938–48. doi: 10.1007/s00125-007-0735-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Menard SL, Croteau E, Sarrhini O, et al. Abnormal in vivo myocardial energy substrate uptake in diet-induced type 2 diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010;298(5):E1049–57. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00560.2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Boudina S, Bugger H, Sena S, et al. Contribution of impaired myocardial insulin signaling to mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in the heart. Circulation. 2009;119(9):1272–83. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.792101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Peterson LR, Herrero P, Schechtman KB, et al. Effect of obesity and insulin resistance on myocardial substrate metabolism and efficiency in young women. Circulation. 2004;109(18):2191–6. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000127959.28627.F8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Neubauer S, Horn M, Cramer M, et al. Myocardial phosphocreatine-to-ATP ratio is a predictor of mortality in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 1997;96(7):2190–6. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.96.7.2190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Scheuermann-Freestone M, Madsen PL, Manners D, et al. Abnormal cardiac and skeletal muscle energy metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes. Circulation. 2003;107(24):3040–6. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000072789.89096.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Anderson EJ, Kypson AP, Rodriguez E, Anderson CA, Lehr EJ, Neufer PD. Substrate-specific derangements in mitochondrial metabolism and redox balance in the atrium of the type 2 diabetic human heart. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(20):1891–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.07.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Kuo TH, Giacomelli F, Wiener J. Oxidative metabolism of Polytron versus Nagarse mitochondria in hearts of genetically diabetic mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985;806(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(85)90076-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Boudina S, Sena S, Theobald H, et al. Mitochondrial energetics in the heart in obesity-related diabetes: direct evidence for increased uncoupled respiration and activation of uncoupling proteins. Diabetes. 2007;56(10):2457–66. doi: 10.2337/db07-0481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Boudina S, Sena S, O’Neill BT, Tathireddy P, Young ME, Abel ED. Reduced mitochondrial oxidative capacity and increased mitochondrial uncoupling impair myocardial energetics in obesitv. Circulation. 2005;112(17):2686–95. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.554360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Duncan JG, Fong JL, Medeiros DM, Finck BN, Kelly DP. Insulin-resistant heart exhibits a mitochondrial biogenic response driven by the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha/PGC-1 alpha gene regulatory pathway. Circulation. 2007;115(7):909–17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.662296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Nisoli E, Clementi E, Carruba MO, Moncada S. Defective mitochondrial biogenesis: a hallmark of the high cardiovascular risk in the metabolic syndrome? Circ Res. 2007;100(6):795–806. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000259591.97107.6c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Ren J, Pulakat L, Whaley-Connell A, Sowers JR. Mitochondrial biogenesis in the metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. J Mol Med (Berl) 2010;88(10):993–1001. doi: 10.1007/s00109-010-0663-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Szendroedi J, Phielix E, Roden M. The role of mitochondria in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012;8(2):92–103. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2011.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Shen E, Li Y, Shan L, et al. Rac1 is required for cardiomyocyte apoptosis during hyperglycemia. Diabetes. 2009 Oct;58(10):2386–95. doi: 10.2337/db08-0617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Nakamura H, Matoba S, Iwai-Kanai E, et al. p53 promotes cardiac dysfunction in diabetic mellitus caused by excessive mitochondrial respiration-mediated reactive oxygen species generation and lipid accumulation. Circ Heart Fail. 2012;5(1):106–15. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.111.961565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Hansford RG, Zorov D. Role of mitochondrial calcium transport in the control of substrate oxidation. Mol Cell Biochem. 1998;184(1–2):359–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Oliveira PJ, Seica R, Coxito PM, et al. Enhanced permeability transition explains the reduced calcium uptake in cardiac mitochondria from streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. FEBS Lett. 2003;554(3):511–4. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)01233-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Medikayala S, Piteo B, Zhao X, Edwards JG. Chronically elevated glucose compromises myocardial mitochondrial DNA integrity by alteration of mitochondrial topoisomerase function. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011;300(2):C338–48. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00248.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Bugger H, Chen D, Riehle C, et al. Tissue-specific remodeling of the mitochondrial proteome in type 1 diabetic akita mice. Diabetes. 2009;58(9):1986–97. doi: 10.2337/db09-0259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Hu Y, Suarez J, Fricovsky E, et al. Increased enzymatic O-GlcNAcylation of mitochondrial proteins impairs mitochondrial function in cardiac myocytes exposed to high glucose. J Biol Chem. 2009 Jan 2;284(1):547–55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808518200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Dabkowski ER, Baseler WA, Williamson CL, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in the type 2 diabetic heart is associated with alterations in spatially distinct mitochondrial proteomes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010;299(2):H529–40. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00267.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Essop MF, Chan WA, Hattingh S. Proteomic analysis of mitochondrial proteins in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2011;22(4):175–8. doi: 10.5830/CVJA-2010-058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Baseler WA, Dabkowski ER, Williamson CL, et al. Proteomic alterations of distinct mitochondrial subpopulations in the type 1 diabetic heart: contribution of protein import dysfunction. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011;300(2):R186–200. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00423.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Makino A, Suarez J, Gawlowski T, et al. Regulation of mitochondrial morphology and function by O-GlcNAcylation in neonatal cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011;300(6):R1296–302. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00437.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Nakai A, Yamaguchi O, Takeda T, et al. The role of autophagy in cardiomyocytes in the basal state and in response to hemodynamic stress. Nat Med. 2007;13(5):619–24. doi: 10.1038/nm1574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Terman A, Brunk UT. Autophagy in cardiac myocyte homeostasis, aging, and pathology. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;68(3):355–65. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.08.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Hua Y, Zhang Y, Ceylan-Isik AF, Wold LE, Nunn JM, Ren J. Chronic Akt activation accentuates aging-induced cardiac hypertrophy and myocardial contractile dysfunction: role of autophagy. Basic Res Cardiol. 2011;106(6):1173–91. doi: 10.1007/s00395-011-0222-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Nair S, Ren J. Autophagy and cardiovascular aging: Lesson learned from rapamycin. Cell Cycle. 2012;11(11):2092–9. doi: 10.4161/cc.20317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Han X, Turdi S, Hu N, Guo R, Zhang Y, Ren J. Influence of long-term caloric restriction on myocardial and cardiomyocyte contractile function and autophagy in mice. J Nutr Biochem. 2012 Mar 21; doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.11.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Giricz Z, Mentzer RM, Jr, Gottlieb RA. Autophagy, Myocardial Protection and the Metabolic Syndrome. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2012 Apr 2; doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e318256ce10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Sciarretta S, Volpe M, Sadoshima J. Is reactivation of autophagy a possible therapeutic solution for obesity and metabolic syndrome? Autophagy. 2012;8(8) doi: 10.4161/auto.20670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Xie Z, Lau K, Eby B, et al. Improvement of cardiac functions by chronic metformin treatment is associated with enhanced cardiac autophagy in diabetic OVE26 mice. Diabetes. 2011;60(6):1770–8. doi: 10.2337/db10-0351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Sciarretta S, Zhai P, Shao D, et al. Rheb is a critical regulator of autophagy during myocardial ischemia: pathophysiological implications in obesity and metabolic syndrome. Circulation. 2012;125(9):1134–46. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.078212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Halliwell B. Biochemistry of oxidative stress. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007;35(Pt 5):1147–50. doi: 10.1042/BST0351147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Huang PL. eNOS, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2009;20(6):295–302. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2009.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.de Haan JB, Cooper ME. Targeted antioxidant therapies in hyperglycemia-mediated endothelial dysfunction. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 2011;3:709–29. doi: 10.2741/s182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Ford ES, Mokdad AH, Giles WH, Brown DW. The metabolic syndrome and antioxidant concentrations: findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes. 2003;52(9):2346–52. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.52.9.2346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Meigs JB, Larson MG, Fox CS, Keaney JF, Jr, Vasan RS, Benjamin EJ. Association of oxidative stress, insulin resistance, and diabetes risk phenotypes: the Framingham Offspring Study. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(10):2529–35. doi: 10.2337/dc07-0817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Cao J, Sodhi K, Puri N, Monu SR, Rezzani R, Abraham NG. High fat diet enhances cardiac abnormalities in SHR rats: Protective role of heme oxygenase-adiponectin axis. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2011;3(1):37. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-3-37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Saraiva RM, Minhas KM, Zheng M, Pitz E, Treuer A, Gonzalez D, et al. Reduced neuronal nitric oxide synthase expression contributes to cardiac oxidative stress and nitroso-redox imbalance in ob/ob mice. Nitric Oxide. 2007;16(3):331–8. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2006.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Ballal K, Wilson CR, Harmancey R, Taegtmeyer H. Obesogenic high fat western diet induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in rat heart. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010;344(1–2):221–30. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0546-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Serpillon S, Floyd BC, Gupte RS, et al. Superoxide production by NAD(P)H oxidase and mitochondria is increased in genetically obese and hyperglycemic rat heart and aorta before the development of cardiac dysfunction. The role of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-derived NADPH. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009;297(1):H153–62. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01142.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Matsuzawa A, Ichijo H. Stress-responsive protein kinases in redox-regulated apoptosis signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005;7(3–4):472–81. doi: 10.1089/ars.2005.7.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Erickson JR, Joiner ML, Guan X, et al. A dynamic pathway for calcium-independent activation of CaMKII by methionine oxidation. Cell. 2008;133(3):462–74. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Maejima Y, Kuroda J, Matsushima S, Ago T, Sadoshima J. Regulation of myocardial growth and death by NADPH oxidase. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011;50(3):408–16. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.12.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Ventura-Clapier R, Garnier A, Veksler V. Energy metabolism in heart failure. J Physiol. 2004;555(Pt 1):1–13. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.055095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Golden TR, Hinerfeld DA, Melov S. Oxidative stress and aging: beyond correlation. Aging Cell. 2002;1(2):117–23. doi: 10.1046/j.1474-9728.2002.00015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Boveris A. Determination of the production of superoxide radicals and hydrogen peroxide in mitochondria. Methods Enzymol. 1984;105:429–35. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Han D, Antunes F, Canali R, Rettori D, Cadenas E. Voltage-dependent anion channels control the release of the superoxide anion from mitochondria to cytosol. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(8):5557–63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M210269200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.St-Pierre J, Buckingham JA, Roebuck SJ, Brand MD. Topology of superoxide production from different sites in the mitochondrial electron transport chain. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(47):44784–90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207217200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Starkov AA, Fiskum G, Chinopoulos C, et al. Mitochondrial alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex generates reactive oxygen species. J Neurosci. 2004;24(36):7779–88. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1899-04.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Brand MD. The sites and topology of mitochondrial superoxide production. Exp Gerontol. 2010;45(7–8):466–72. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2010.01.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.McCord JM, Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein) J Biol Chem. 1969;244(22):6049–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Barra D, Schinina ME, Simmaco M, et al. The primary structure of human liver manganese superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem. 1984;259(20):12595–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Patenaude A, Ven Murthy MR, Mirault ME. Mitochondrial thioredoxin system: effects of TrxR2 overexpression on redox balance, cell growth, and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(26):27302–14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M402496200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Yu T, Robotham JL, Yoon Y. Increased production of reactive oxygen species in hyperglycemic conditions requires dynamic change of mitochondrial morphology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(8):2653–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0511154103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Dikalov S. Cross talk between mitochondria and NADPH oxidases. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011;51(7):1289–301. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.06.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Rosen P, Osmers A. Oxidative stress in young Zucker rats with impaired glucose tolerance is diminished by acarbose. Horm Metab Res. 2006;38(9):575–86. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-950397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Li SY, Yang X, Ceylan-Isik AF, Du M, Sreejayan N, Ren J. Cardiac contractile dysfunction in Lep/Lep obesity is accompanied by NADPH oxidase activation, oxidative modification of sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase and myosin heavy chain isozyme switch. Diabetologia. 2006;49(6):1434–46. doi: 10.1007/s00125-006-0229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Feillet-Coudray C, Sutra T, Fouret G, et al. Oxidative stress in rats fed a high-fat high-sucrose diet and preventive effect of polyphenols: Involvement of mitochondrial and NAD(P)H oxidase systems. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009;46(5):624–32. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.11.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Letavic MA, Keith JM, Ly KS, et al. Novel naphthyridines are histamine H3 antagonists and serotonin reuptake transporter inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007;17(9):2566–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Matsushima S, Kinugawa S, Yokota T, et al. Increased myocardial NAD(P)H oxidase-derived superoxide causes the exacerbation of postinfarct heart failure in type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009;297(1):H409–16. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01332.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Roe ND, Thomas DP, Ren J. Inhibition of NADPH oxidase alleviates experimental diabetes-induced myocardial contractile dysfunction. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011;13(5):465–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2011.01369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Putnam K, Shoemaker R, Yiannikouris F, Cassis LA. The renin-angiotensin system: a target of and contributor to dyslipidemias, altered glucose homeostasis, and hypertension of the metabolic syndrome. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012;302(6):H1219–30. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00796.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Zhang GX, Lu XM, Kimura S, Nishiyama A. Role of mitochondria in angiotensin II-induced reactive oxygen species and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;76(2):204–12. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2007.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Wang Q, Sun Y, Ma A, Li Y, Han X, Liang H. Effects of vitamin E on plasma lipid status and oxidative stress in Chinese women with metabolic syndrome. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2010;80(3):178–87. doi: 10.1024/0300-9831/a000015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Stephens NG, Parsons A, Schofield PM, Kelly F, Cheeseman K, Mitchinson MJ. Randomised controlled trial of vitamin E in patients with coronary disease: Cambridge Heart Antioxidant Study (CHAOS) Lancet. 1996;347(9004):781–6. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)90866-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Lavie CJ, Milani JN. Do antioxidant vitamins ameliorate the beneficial effects of exercise training on insulin sensitivity? J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 2011;31(4):211–6. doi: 10.1097/HCR.0b013e318211e3d8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Manning PJ, Sutherland WH, Williams SM, et al. The effect of lipoic acid and vitamin E therapies in individuals with the metabolic syndrome. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2012 Mar 6; doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2011.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Debreceni B, Debreceni L. Why Do Homocysteine-Lowering B Vitamin and Antioxidant E Vitamin Supplementations Appear To Be Ineffective in the Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases? Cardiovascular Therapeutics. 2011 doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5922.2011.00266.x. no-no. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Avignon A, Hokayem M, Bisbal C, Lambert K. Dietary antioxidants: Do they have a role to play in the ongoing fight against abnormal glucose metabolism? Nutrition. 2012;28(7–8):715–21. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2012.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Wang H, Yang YJ, Qian HY, Zhang Q, Xu H, Li JJ. Resveratrol in cardiovascular disease: what is known from current research? Heart Fail Rev. 2012;17(3):437–48. doi: 10.1007/s10741-011-9260-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Qin F, Siwik DA, Luptak I, et al. The Polyphenols Resveratrol and S17834 Prevent the Structural and Functional Sequelae of Diet-Induced Metabolic Heart Disease in Mice / Clinical Perspective. Circulation. 2012;125(14):1757–64. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.067801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Robich MP, Osipov RM, Chu LM, et al. Resveratrol modifies risk factors for coronary artery disease in swine with metabolic syndrome and myocardial ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011;664(1–3):45–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.04.059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Bagul PK, Middela H, Matapally S, et al. Attenuation of insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome and hepatic oxidative stress by resveratrol in fructose-fed rats. Pharmacol Res. 2012 May 22; doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2012.05.003. (0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Liu L, Wang Y, Lam KS, Xu A. Moderate wine consumption in the prevention of metabolic syndrome and its related medical complications. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2008 Jun;8(2):89–98. doi: 10.2174/187153008784534385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Timmers S, Konings E, Bilet L, et al. Calorie Restriction-like Effects of 30 Days of Resveratrol Supplementation on Energy Metabolism and Metabolic Profile in Obese Humans. Cell Metabolism. 2011;14(5):612–22. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.10.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Um JH, Park SJ, Kang H, Yang S, Foretz M, McBurney MW, et al. AMP-activated protein kinase-deficient mice are resistant to the metabolic effects of resveratrol. Diabetes. 2010;59(3):554–63. doi: 10.2337/db09-0482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Penumathsa SV, Maulik N. Resveratrol: a promising agent in promoting cardioprotection against coronary heart disease. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009;87(4):275–86. doi: 10.1139/Y09-013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Guo H, Ling W, Wang Q, Liu C, Hu Y, Xia M. Cyanidin 3-glucoside protects 3T3-L1 adipocytes against H2O2- or TNF-alpha-induced insulin resistance by inhibiting c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008;75(6):1393–401. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Qin Y, Xia M, Ma J, et al. Anthocyanin supplementation improves serum LDL- and HDL-cholesterol concentrations associated with the inhibition of cholesteryl ester transfer protein in dyslipidemic subjects. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2009;90(3):485–92. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2009.27814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Egert S, Bosy-Westphal A, Seiberl J, et al. Quercetin reduces systolic blood pressure and plasma oxidised low-density lipoprotein concentrations in overweight subjects with a high-cardiovascular disease risk phenotype: a double-blinded, placebo-controlled cross-over study. The British journal of nutrition. 2009;102(7):1065–74. doi: 10.1017/S0007114509359127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Panchal SK, Poudyal H, Brown L. Quercetin Ameliorates Cardiovascular, Hepatic, and Metabolic Changes in Diet-Induced Metabolic Syndrome in Rats. J Nutrition. 2012;142(6):1026–32. doi: 10.3945/jn.111.157263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Xia X, Weng J. Targeting metabolic syndrome: candidate natural agents. J Diabetes. 2010;2(4):243–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-0407.2010.00090.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Subramanian S, Kalyanaraman B, Migrino RQ. Mitochondrially targeted antioxidants for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov. 2010;5(1):54–65. doi: 10.2174/157489010790192601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Ramos-Marquez ME, Siller-Lopez F. Current antioxidant molecular therapies for oxidative stress-related ailments. Current gene therapy. 2008;8(4):256–63. doi: 10.2174/156652308785160665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Houstis N, Rosen ED, Lander ES. Reactive oxygen species have a causal role in multiple forms of insulin resistance. Nature. 2006;440(7086):944–8. doi: 10.1038/nature04634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Hoehn KL, Salmon AB, Hohnen-Behrens C, et al. Insulin resistance is a cellular antioxidant defense mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(42):17787–92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0902380106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Saito Y, Fukuhara A, Nishio K, et al. Characterization of cellular uptake and distribution of coenzyme Q10 and vitamin E in PC12 cells. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry. 2009;20(5):350–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2008.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Huynh K, Kiriazis H, Du XJ, et al. Coenzyme Q10 attenuates diastolic dysfunction, cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and cardiac fibrosis in the db/db mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2012;55(5):1544–53. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2495-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Huynh K, Kiriazis H, Du XJ, et al. Coenzyme Q< sub> 10< /sub> attenuates diastolic dysfunction, cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and cardiac fibrosis in the < i> db/db mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2012;55(5):1544–53. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2495-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Kocharian A, Shabanian R, Rafiei-Khorgami M, Kiani A, Heidari-Bateni G. Coenzyme Q10 improves diastolic function in children with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Cardiology in the Young. 2009;19(05):501–6. doi: 10.1017/S1047951109990795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Young JM, Florkowski CM, Molyneux SL, et al. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study of Coenzyme Q10 Therapy in Hypertensive Patients With the Metabolic Syndrome. Am J Hypertens. 2012;25(2):261–70. doi: 10.1038/ajh.2011.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Bjelakovic G, Nikolova D, Gluud LL, Simonetti RG, Gluud C. Antioxidant supplements for prevention of mortality in healthy participants and patients with various diseases. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;(2):CD007176. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Rodriguez-Cuenca S, Cochemé HM, Logan A, et al. Consequences of long-term oral administration of the mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ to wild-type mice. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2010;48(1):161–72. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.10.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Smith RA, Murphy MP. Mitochondria-targeted antioxidants as therapies. Discov Med. 2011;11(57):106–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Adlam VJ, Harrison JC, Porteous CM, et al. Targeting an antioxidant to mitochondria decreases cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury. FASEB J. 2005;19(9):1088–95. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-3718com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Mercer JR, Yu E, Figg N, et al. The mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ decreases features of the metabolic syndrome in ATM+/−/ApoE−/− mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012;52(5):841–9. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.11.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Pung YF, Rocic P, Murphy MP, et al. Resolution of Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress Rescues Coronary Collateral Growth in Zucker Obese Fatty Rats. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2012;32(2):325–34. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.241802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Dai D-F, Chen T, Szeto H, et al. Mitochondrial Targeted Antioxidant Peptide Ameliorates Hypertensive Cardiomyopathy. J Am College Cardiol. 2011;58(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.12.044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Kloner RA, Hale SL, Dai W, et al. Reduction of Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury With Bendavia, a Mitochondria-Targeting Cytoprotective Peptide. J Am Heart Association. 2012;1(3) doi: 10.1161/JAHA.112.001644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Chen M, Liu B, Gao Q, Zhuo Y, Ge J. Mitochondria-Targeted Peptide MTP-131 Alleviates Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Damage in Human Trabecular Meshwork Cells. Investigative Ophthalmol Visual Sci. 2011;52(10):7027–37. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-7524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Sloan RC, Moukdar F, Frasier CR, et al. Mitochondrial permeability transition in the diabetic heart: Contributions of thiol redox state and mitochondrial calcium to augmented reperfusion injury. J Mol Cellular Cardiol. 2012;52(5):1009–18. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Lyamzaev K, Pustovidko A, Simonyan R, et al. Novel Mitochondria-Targeted Antioxidants: Plastoquinone Conjugated with Cationic Plant Alkaloids Berberine and Palmatine. Pharm Res. 2011;28(11):2883–95. doi: 10.1007/s11095-011-0504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Shen X, Zheng S, Metreveli NS, Epstein PN. Protection of cardiac mitochondria by overexpression of MnSOD reduces diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes. 2006;55(3):798–805. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.55.03.06.db05-1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Dong F, Li Q, Sreejayan N, Nunn JM, Ren J. Metallothionein Prevents High-Fat Diet–Induced Cardiac Contractile Dysfunction. Diabetes 2007 September. 2007;56(9):2201–12. doi: 10.2337/db06-1596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Ye G, Metreveli NS, Donthi RV, et al. Catalase protects cardiomyocyte function in models of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2004;53(5):1336–43. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.5.1336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Bruno RM, Daghini E, Ghiadoni L, et al. Effect of acute administration of vitamin C on muscle sympathetic activity, cardiac sympathovagal balance, and baroreflex sensitivity in hypertensive patients. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012 Jun 13; doi: 10.3945/ajcn.112.035022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Feng B, Chen S, Chiu J, George B, Chakrabarti S. Regulation of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in diabetes at the transcriptional level. American journal of physiology Endocrinology and metabolism. 2008;294(6):E1119–26. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00029.2008. [Research Support, Non-U. S Gov’t] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Hardeland R. Antioxidative protection by melatonin: multiplicity of mechanisms from radical detoxification to radical avoidance. Endocrine. 2005;27(2):119–30. doi: 10.1385/endo:27:2:119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Hardeland R, Pandi-Perumal SR. Melatonin, a potent agent in antioxidative defense: actions as a natural food constituent, gastrointestinal factor, drug and prodrug. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2005;2:22. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-2-22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Reiter RJ, Manchester LC, Tan DX. Neurotoxins: free radical mechanisms and melatonin protection. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2010;8(3):194–210. doi: 10.2174/157015910792246236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Poeggeler B, Saarela S, Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Chen LD, Manchester LC, et al. Melatonin--a highly potent endogenous radical scavenger and electron donor: new aspects of the oxidation chemistry, of this indole accessed in vitro. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994;738:419–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb21831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Nduhirabandi F, du Toit EF, Lochner A. Melatonin and the metabolic syndrome: a tool for effective therapy in obesity-associated abnormalities? Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2012;205(2):209–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2012.02410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Kolar F, Jezkova J, Balkova P, et al. Role of oxidative stress in PKC-delta upregulation and cardioprotection induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;292(1):H224–30. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00689.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Tsujita K, Shimomura H, Kawano H, et al. Effects of edaravone on reperfusion injury in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 2004;94(4):481–4. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2004.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Kikuchi K, Uchikado H, Miyagi N, et al. Beyond neurological disease: new targets for edaravone (Review) International journal of molecular medicine. 2011;28(6):899–906. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2011.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Anderson EJ, Lustig ME, Boyle KE, et al. Mitochondrial H2O2 emission and cellular redox state link excess fat intake to insulin resistance in both rodents and humans. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(3):573–81. doi: 10.1172/JCI37048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Zhao K, Zhao G-M, Wu D, et al. Cell-permeable Peptide Antioxidants Targeted to Inner Mitochondrial Membrane inhibit Mitochondrial Swelling, Oxidative Cell Death, and Reperfusion Injury. J Biological Chem. 2004;279(33):34682–90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M402999200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]