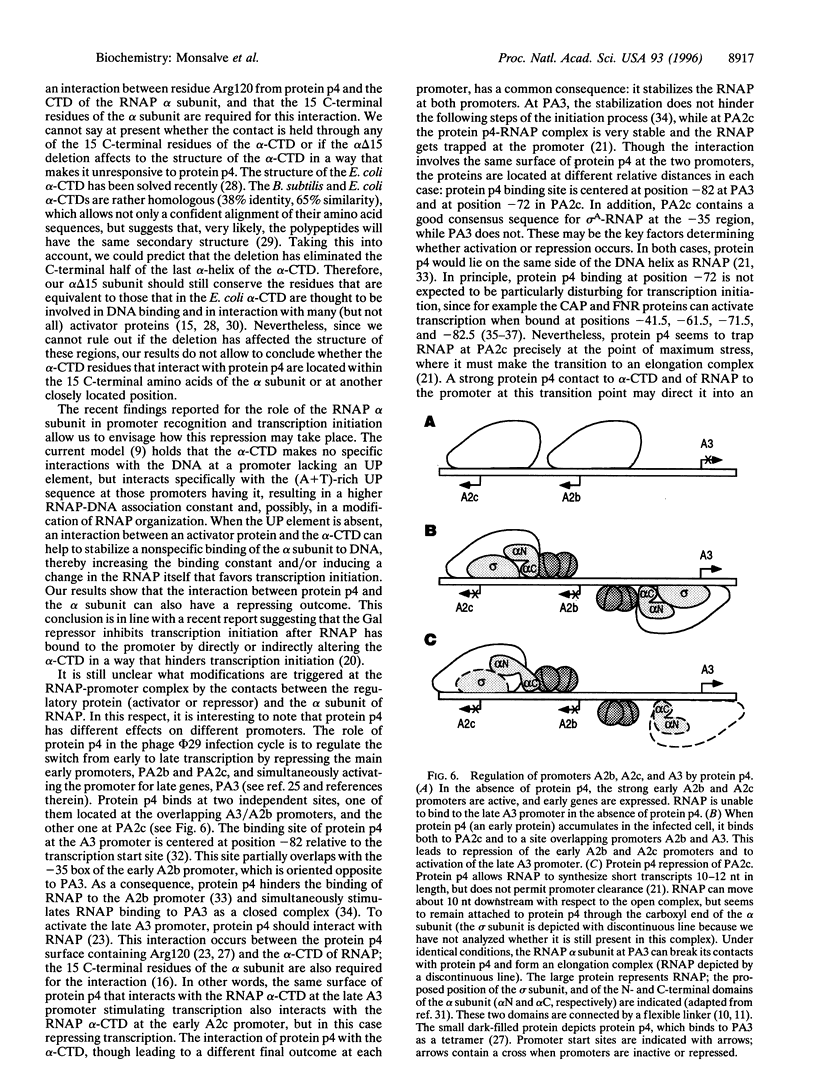
Abstract
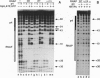
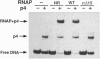
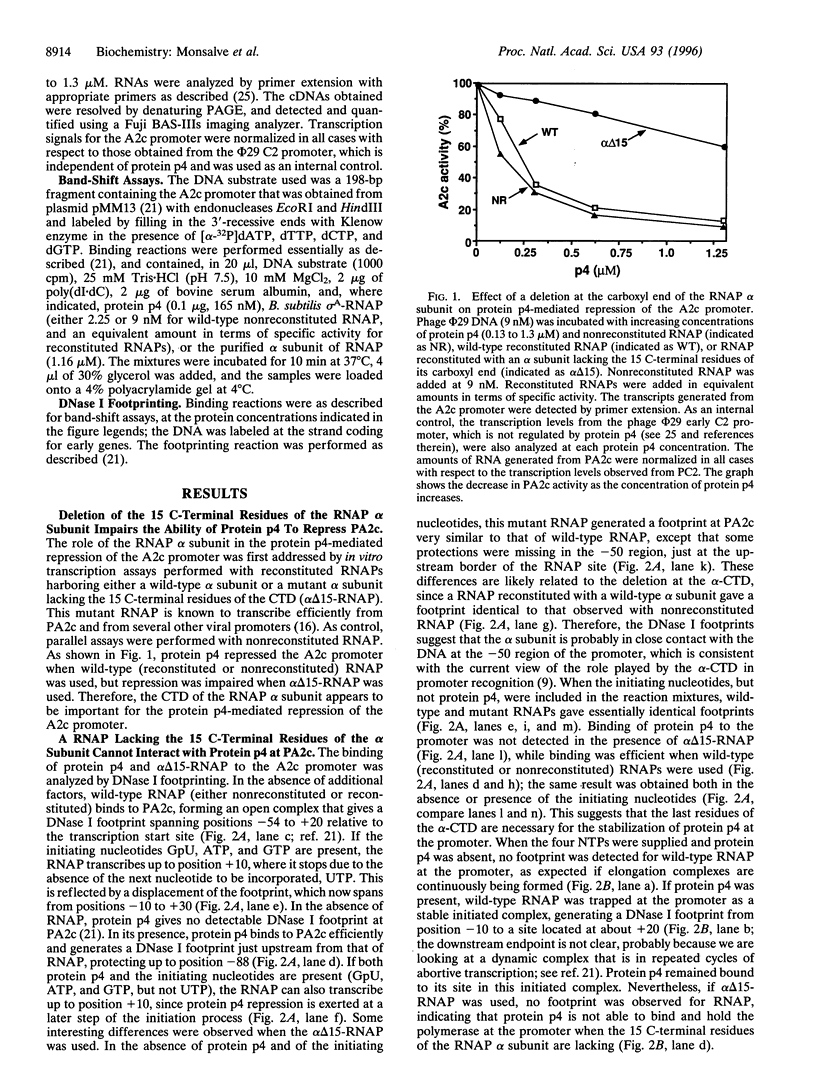
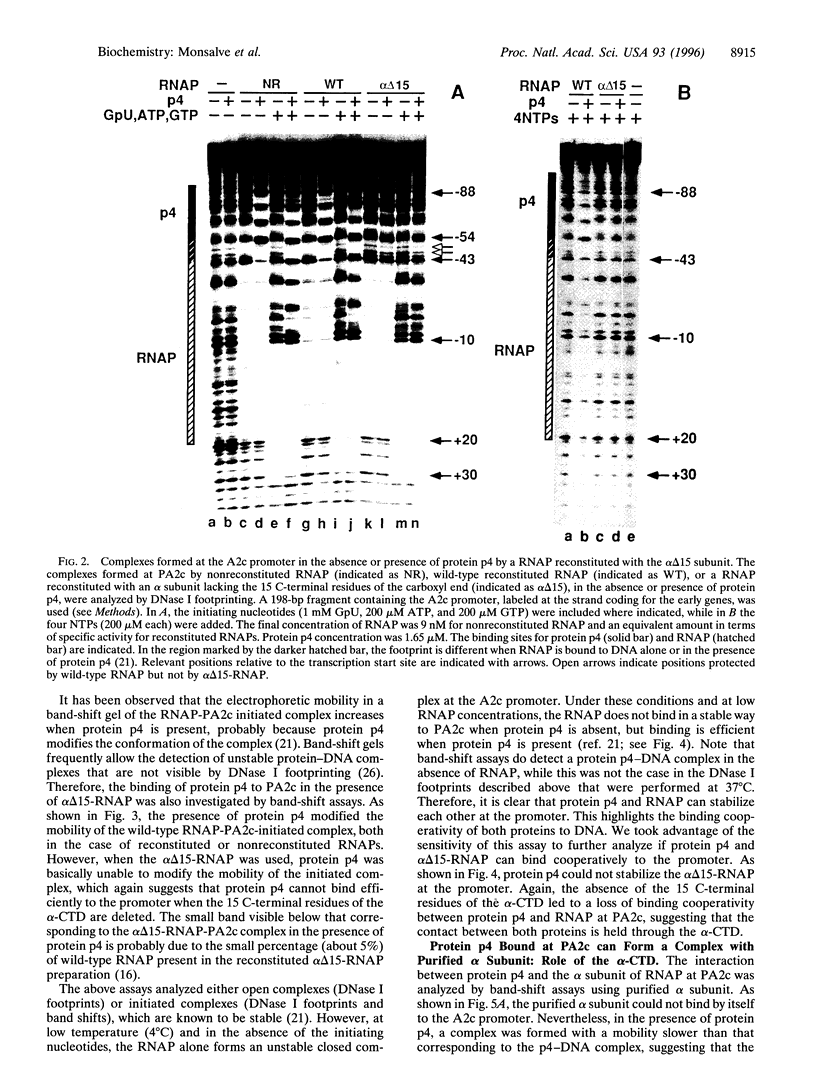
Regulatory protein p4 from Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29 represses the strong viral A2c promoter (PA2c) by preventing promoter clearance; it allows RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter and form an initiated complex, but the elongation step is not reached. Protein p4 binds at PA2c immediately upstream from RNA polymerase; repression involves a contact between both proteins that holds the RNA polymerase at the promoter. This contact is held mainly through p4 residue Arg120, which is also required for activation of the phi 29 late A3 promoter. We have investigated which region of RNA polymerase contacts protein p4 at PA2c. Promoter repression was impaired when a reconstituted RNA polymerase lacking the 15 C-terminal residues of the alpha subunit C-terminal domain was used; this polymerase was otherwise competent for transcription. Binding cooperativity assays indicated that protein p4 cannot interact with this mutant RNA polymerase at PA2c. Protein p4 could form a complex at PA2c with purified wild-type alpha subunit, but not with a deletion mutant lacking the 15 C-terminal residues. Our results indicate that protein p4 represses PA2c by interacting with the C-terminal domain of the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. Therefore, this domain of the alpha subunit can receive regulatory signals not only from transcriptional activators, but from repressors also.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldus J. M., Buckner C. M., Moran C. P., Jr Evidence that the transcriptional activator Spo0A interacts with two sigma factors in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Jul;17(2):281–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.mmi_17020281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthelemy I., Salas M. Characterization of a new prokaryotic transcriptional activator and its DNA recognition site. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jul 20;208(2):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatter E. E., Ross W., Tang H., Gourse R. L., Ebright R. H. Domain organization of RNA polymerase alpha subunit: C-terminal 85 amino acids constitute a domain capable of dimerization and DNA binding. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):889–896. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90682-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang B. Y., Doi R. H. Overproduction, purification, and characterization of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase sigma A factor. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3257–3263. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3257-3263.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy H. E., Park S. W., Aki T., Parrack P., Fujita N., Ishihama A., Adhya S. Repression and activation of transcription by Gal and Lac repressors: involvement of alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. EMBO J. 1995 Sep 15;14(18):4523–4529. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00131.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H., Busby S. The Escherichia coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit: structure and function. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995 Apr;5(2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(95)80008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellinger T., Behnke D., Bujard H., Gralla J. D. Stalling of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in the +6 to +12 region in vivo is associated with tight binding to consensus promoter elements. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jun 17;239(4):455–465. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrick K., Caramori T., Chen Y. F., Galizzi A., Helmann J. D. Promoter architecture in the flagellar regulon of Bacillus subtilis: high-level expression of flagellin by the sigma D RNA polymerase requires an upstream promoter element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2582–2586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaal T., Ross W., Blatter E. E., Tang H., Jia X., Krishnan V. V., Assa-Munt N., Ebright R. H., Gourse R. L. DNA-binding determinants of the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase: novel DNA-binding domain architecture. Genes Dev. 1996 Jan 1;10(1):16–26. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston K., Bell A., Kolb A., Buc H., Busby S. Stringent spacing requirements for transcription activation by CRP. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):733–743. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward R. S., Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Functional specialization within the alpha-subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 5;221(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Identification of a subunit assembly domain in the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 5;218(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A. Protein-protein communication within the transcription apparatus. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(9):2483–2489. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2483-2489.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeon Y. H., Negishi T., Shirakawa M., Yamazaki T., Fujita N., Ishihama A., Kyogoku Y. Solution structure of the activator contact domain of the RNA polymerase alpha subunit. Science. 1995 Dec 1;270(5241):1495–1497. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5241.1495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin R., Sharif K. A., Krakow J. S. Evidence for contact between the cyclic AMP receptor protein and the delta 70 subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 18;270(33):19213–19216. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.33.19213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Functional map of the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Deletion analysis of the amino-terminal assembly domain. J Mol Biol. 1994 Sep 16;242(2):107–115. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuldell N., Hochschild A. Amino acid substitutions in the -35 recognition motif of sigma 70 that result in defects in phage lambda repressor-stimulated transcription. J Bacteriol. 1994 May;176(10):2991–2998. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.10.2991-2998.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Grimes B., Fujita N., Makino K., Malloch R. A., Hayward R. S., Ishihama A. Role of the sigma 70 subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in transcription activation. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jan 14;235(2):405–413. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D., Prentki P., Chandler M. Use of gel retardation to analyze protein-nucleic acid interactions. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Dec;56(4):509–528. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.4.509-528.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., Moyle H., Susskind M. M. Target of the transcriptional activation function of phage lambda cI protein. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):75–77. doi: 10.1126/science.8272867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino K., Amemura M., Kim S. K., Nakata A., Shinagawa H. Role of the sigma 70 subunit of RNA polymerase in transcriptional activation by activator protein PhoB in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):149–160. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mencía M., Monsalve M., Salas M., Rojo F. Transcriptional activator of phage phi 29 late promoter: mapping of residues involved in interaction with RNA polymerase and in DNA bending. Mol Microbiol. 1996 Apr;20(2):273–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1996.tb02616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mencía M., Salas M., Rojo F. Residues of the Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29 transcriptional activator required both to interact with RNA polymerase and to activate transcription. J Mol Biol. 1993 Oct 20;233(4):695–704. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsalve M., Mencia M., Rojo F., Salas M. Activation and repression of transcription at two different phage phi29 promoters are mediated by interaction of the same residues of regulatory protein p4 with RNA polymerase. EMBO J. 1996 Jan 15;15(2):383–391. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsalve M., Mencía M., Rojo F., Salas M. Transcription regulation in Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29: expression of the viral promoters throughout the infection cycle. Virology. 1995 Feb 20;207(1):23–31. doi: 10.1006/viro.1995.1048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negishi T., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Structural map of the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: structural domains identified by proteolytic cleavage. J Mol Biol. 1995 May 12;248(4):723–728. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuez B., Rojo F., Salas M. Phage phi 29 regulatory protein p4 stabilizes the binding of the RNA polymerase to the late promoter in a process involving direct protein-protein contacts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11401–11405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L., Ross W., Appleman J. A., Gaal T., Leirmo S., Schlax P. J., Record M. T., Jr, Gourse R. L. Factor independent activation of rrnB P1. An "extended" promoter with an upstream element that dramatically increases promoter strength. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 4;235(5):1421–1435. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo F., Salas M. A DNA curvature can substitute phage phi 29 regulatory protein p4 when acting as a transcriptional repressor. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3429–3438. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Gosink K. K., Salomon J., Igarashi K., Zou C., Ishihama A., Severinov K., Gourse R. L. A third recognition element in bacterial promoters: DNA binding by the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1407–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.8248780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander C., Schneider R. Database of homology-derived protein structures and the structural meaning of sequence alignment. Proteins. 1991;9(1):56–68. doi: 10.1002/prot.340090107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogo J. M., Inciarte M. R., Corral J., Viñuela E., Salas M. RNA polymerase binding sites and transcription map of the DNA of Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. J Mol Biol. 1979 Feb 5;127(4):411–436. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90230-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang H., Severinov K., Goldfarb A., Fenyo D., Chait B., Ebright R. H. Location, structure, and function of the target of a transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 15;8(24):3058–3067. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.24.3058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushida C., Aiba H. Helical phase dependent action of CRP: effect of the distance between the CRP site and the -35 region on promoter activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6325–6330. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing H. J., Williams S. M., Busby S. J. Spacing requirements for transcription activation by Escherichia coli FNR protein. J Bacteriol. 1995 Dec;177(23):6704–6710. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.23.6704-6710.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yura T., Ishihama A. Genetics of bacterial RNA polymerases. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:59–97. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.000423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y., Pendergrast P. S., Bell A., Williams R., Busby S., Ebright R. H. The functional subunit of a dimeric transcription activator protein depends on promoter architecture. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 3;13(19):4549–4557. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06776.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]