Abstract
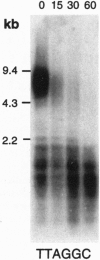
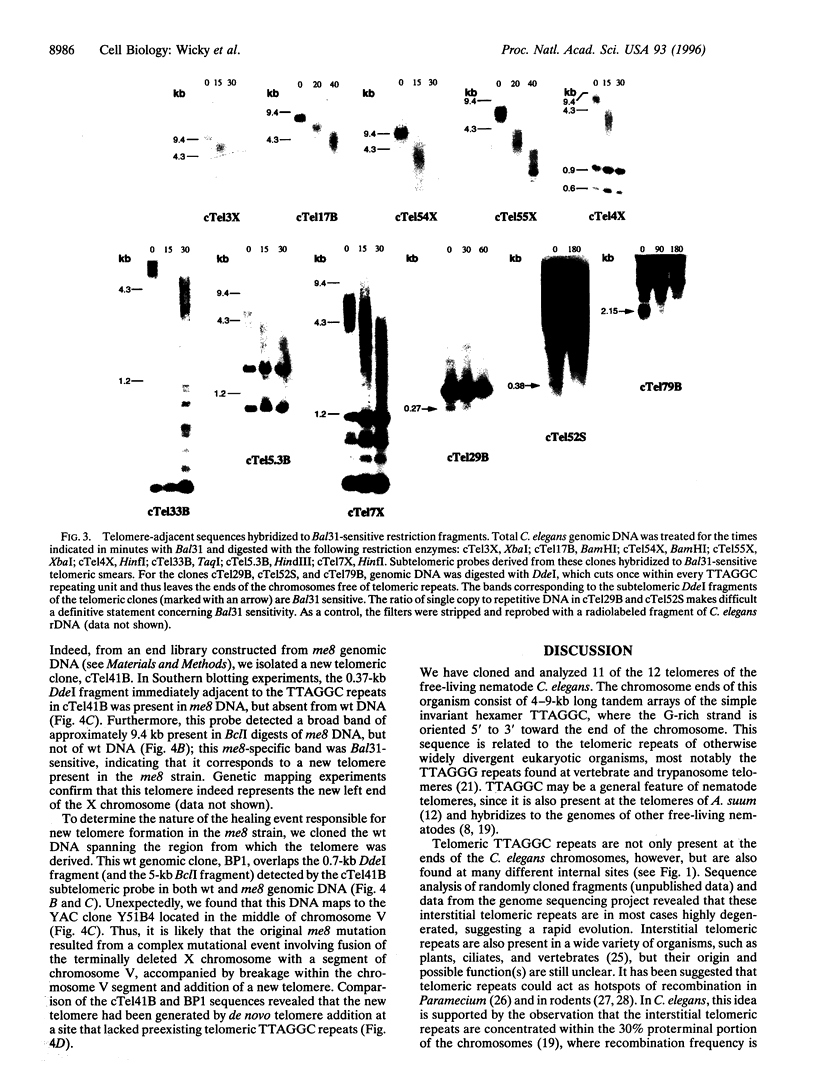
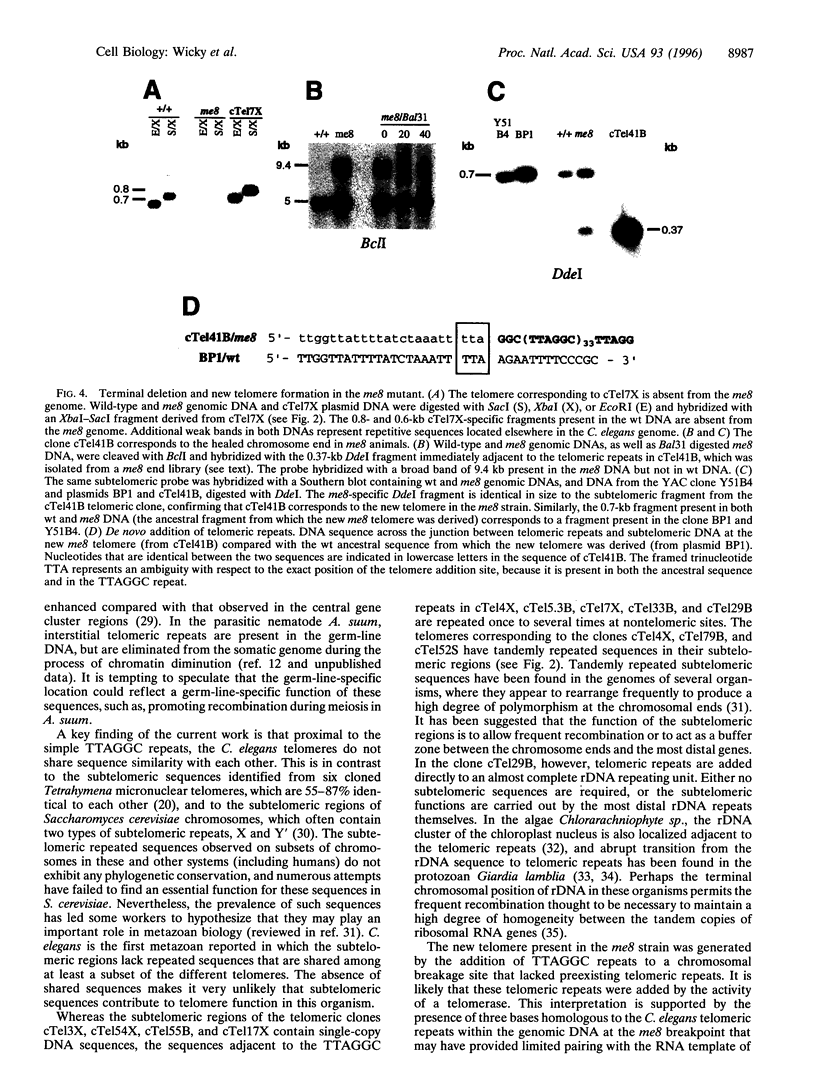
Telomeres are specialized structures located at the ends of linear eukaryotic chromosomes that ensure their complete replication and protect them from fusion and degradation. We report here the characterization of the telomeres of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. We show that the chromosomes terminate in 4-9 kb of tandem repeats of the sequence TTAGGC. Furthermore, we have isolated clones corresponding to 11 of the 12 C. elegans telomeres. Their subtelomeric sequences are all different from each other, demonstrating that the terminal TTAGGC repeats are sufficient for general chromosomal capping functions. Finally, we demonstrate that the me8 meiotic mutant, which is defective in X chromosome crossing over and segregation, bears a terminal deficiency, that was healed by the addition of telomeric repeats, presumably by the activity of a telomerase enzyme. The 11 cloned telomeres represent an important advance for the completion of the physical map and for the determination of the entire sequence of the C. elegans genome.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam R. D., Nash T. E., Wellems T. E. Telomeric location of Giardia rDNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3326–3330. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albertson D. G. Localization of the ribosomal genes in Caenorhabditis elegans chromosomes by in situ hybridization using biotin-labeled probes. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1227–1234. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley T., Cacheiro N. L., Russell L. B., Ward D. C. Molecular characterization of a pericentric inversion in mouse chromosome 8 implicates telomeres as promoters of meiotic recombination. Chromosoma. 1993 Jan;102(2):112–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00356028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley T., Ward D. C. A "hot spot" of recombination coincides with an interstitial telomeric sequence in the Armenian hamster. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1993;62(2-3):169–171. doi: 10.1159/000133464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes T. M., Kohara Y., Coulson A., Hekimi S. Meiotic recombination, noncoding DNA and genomic organization in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1995 Sep;141(1):159–179. doi: 10.1093/genetics/141.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Mason J. M. Genetics and molecular biology of telomeres. Adv Genet. 1992;30:185–249. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Mason J. M. Telomeric repeat sequences. Chromosoma. 1994 Jun;103(3):154–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00368007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Telomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:113–129. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cangiano G., La Volpe A. Repetitive DNA sequences located in the terminal portion of the Caenorhabditis elegans chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1133–1139. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Kozono Y., Lutterbach B., Shownkeen R., Sulston J., Waterston R. YACs and the C. elegans genome. Bioessays. 1991 Aug;13(8):413–417. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Sulston J., Brenner S., Karn J. Toward a physical map of the genome of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7821–7825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Waterston R., Kiff J., Sulston J., Kohara Y. Genome linking with yeast artificial chromosomes. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):184–186. doi: 10.1038/335184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus D. H., Emmons S. W. A transposon-related palindromic repetitive sequence from C. elegans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1871–1877. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. E., Sulston J. E., Coulson A. R. The rDNA of C. elegans: sequence and structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2345–2364. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson P., McFadden G. I. The chlorarachniophyte: a cell with two different nuclei and two different telomeres. Chromosoma. 1995 May;103(9):635–641. doi: 10.1007/BF00357690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. A telomeric sequence in the RNA of Tetrahymena telomerase required for telomere repeat synthesis. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):331–337. doi: 10.1038/337331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. The telomere terminal transferase of Tetrahymena is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme with two kinds of primer specificity. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90576-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heery D. M., Gannon F., Powell R. A simple method for subcloning DNA fragments from gel slices. Trends Genet. 1990 Jun;6(6):173–173. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katinka M. D., Bourgain F. M. Interstitial telomeres are hotspots for illegitimate recombination with DNA molecules injected into the macronucleus of Paramecium primaurelia. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):725–732. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk K. E., Blackburn E. H. An unusual sequence arrangement in the telomeres of the germ-line micronucleus in Tetrahymena thermophila. Genes Dev. 1995 Jan 1;9(1):59–71. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Blancq S. M., Kase R. S., Van der Ploeg L. H. Analysis of a Giardia lamblia rRNA encoding telomere with [TAGGG]n as the telomere repeat. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5790–5790. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis E. J., Naumova E. S., Lee A., Naumov G., Haber J. E. The chromosome end in yeast: its mosaic nature and influence on recombinational dynamics. Genetics. 1994 Mar;136(3):789–802. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.3.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin G. B. Recognition of a chromosome truncation site associated with alpha-thalassaemia by human telomerase. Nature. 1991 Oct 3;353(6343):454–456. doi: 10.1038/353454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Bernard V., Tobler H. Chromatin diminution in nematodes. Bioessays. 1996 Feb;18(2):133–138. doi: 10.1002/bies.950180209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Wicky C., Spicher A., Tobler H. New telomere formation after developmentally regulated chromosomal breakage during the process of chromatin diminution in Ascaris lumbricoides. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):815–822. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90076-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petes T. D. Unequal meiotic recombination within tandem arrays of yeast ribosomal DNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):765–774. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prowse K. R., Avilion A. A., Greider C. W. Identification of a nonprocessive telomerase activity from mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1493–1497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shippen-Lentz D., Blackburn E. H. Telomere terminal transferase activity from Euplotes crassus adds large numbers of TTTTGGGG repeats onto telomeric primers. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2761–2764. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J., Du Z., Thomas K., Wilson R., Hillier L., Staden R., Halloran N., Green P., Thierry-Mieg J., Qiu L. The C. elegans genome sequencing project: a beginning. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):37–41. doi: 10.1038/356037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobler H., Etter A., Müller F. Chromatin diminution in nematode development. Trends Genet. 1992 Dec;8(12):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90326-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeneuve A. M. A cis-acting locus that promotes crossing over between X chromosomes in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1994 Mar;136(3):887–902. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterston R., Sulston J. The genome of Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Nov 21;92(24):10836–10840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.24.10836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicky C., Rose A. M. The role of chromosome ends during meiosis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Bioessays. 1996 Jun;18(6):447–452. doi: 10.1002/bies.950180606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie A. O., Lamb J., Harris P. C., Finney R. D., Higgs D. R. A truncated human chromosome 16 associated with alpha thalassaemia is stabilized by addition of telomeric repeat (TTAGGG)n. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):868–871. doi: 10.1038/346868a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R., Ainscough R., Anderson K., Baynes C., Berks M., Bonfield J., Burton J., Connell M., Copsey T., Cooper J. 2.2 Mb of contiguous nucleotide sequence from chromosome III of C. elegans. Nature. 1994 Mar 3;368(6466):32–38. doi: 10.1038/368032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G. L., Blackburn E. H. Developmentally programmed healing of chromosomes by telomerase in Tetrahymena. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):823–832. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90077-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Prescott D. M. Telomere terminal transferase activity in the hypotrichous ciliate Oxytricha nova and a model for replication of the ends of linear DNA molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):6953–6972. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A. Structure and function of telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:579–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetka M., Rose A. The genetics of meiosis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Trends Genet. 1995 Jan;11(1):27–31. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)88983-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]