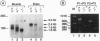Abstract
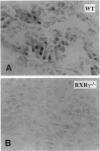
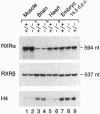
The RXR gamma (RXR, retinoid X receptor) gene was disrupted in the mouse. Homozygous mutant mice developed normally and were indistinguishable from their RXR gamma +/- or wild-type littermates with respect to growth, fertility, viability, and apparent behavior in the animal facility. Moreover, RXR alpha -/-/RXR gamma -/- and RXR beta -/-/RXR gamma -/- mutant phenotypes were indistinguishable from those of RXR alpha -/- and RXR beta -/- mutants, respectively. Strikingly, RXR alpha +/-/RXR beta -/-/RXR gamma -/- triple mutants were viable. Thus, it appears that RXR gamma does not exert any essential function that cannot be performed by RXR alpha or RXR beta, and one copy of RXR alpha is sufficient to perform most of the functions of the RXRs.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adra C. N., Boer P. H., McBurney M. W. Cloning and expression of the mouse pgk-1 gene and the nucleotide sequence of its promoter. Gene. 1987;60(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouillet P., Oulad-Abdelghani M., Vicaire S., Garnier J. M., Schuhbaur B., Dollé P., Chambon P. Efficient cloning of cDNAs of retinoic acid-responsive genes in P19 embryonal carcinoma cells and characterization of a novel mouse gene, Stra1 (mouse LERK-2/Eplg2). Dev Biol. 1995 Aug;170(2):420–433. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.1226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J., Young W. S., 3rd, Weinberger C. Differential expression of alpha and beta thyroid hormone receptor genes in rat brain and pituitary. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7250–7254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. Altering the genome by homologous recombination. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2660260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambon P. The retinoid signaling pathway: molecular and genetic analyses. Semin Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;5(2):115–125. doi: 10.1006/scel.1994.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Fraulob V., Kastner P., Chambon P. Developmental expression of murine retinoid X receptor (RXR) genes. Mech Dev. 1994 Feb;45(2):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(94)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V. Retinoic acid receptors and cellular retinoid binding proteins: complex interplay in retinoid signaling. Endocr Rev. 1994 Feb;15(1):61–79. doi: 10.1210/edrv-15-1-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronemeyer H., Laudet V. Transcription factors 3: nuclear receptors. Protein Profile. 1995;2(11):1173–1308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes M. R., Malloy P. J., Kieback D. G., Kesterson R. A., Pike J. W., Feldman D., O'Malley B. W. Point mutations in the human vitamin D receptor gene associated with hypocalcemic rickets. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1702–1705. doi: 10.1126/science.2849209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastner P., Grondona J. M., Mark M., Gansmuller A., LeMeur M., Decimo D., Vonesch J. L., Dollé P., Chambon P. Genetic analysis of RXR alpha developmental function: convergence of RXR and RAR signaling pathways in heart and eye morphogenesis. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):987–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastner P., Mark M., Chambon P. Nonsteroid nuclear receptors: what are genetic studies telling us about their role in real life? Cell. 1995 Dec 15;83(6):859–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90202-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastner P., Mark M., Leid M., Gansmuller A., Chin W., Grondona J. M., Décimo D., Krezel W., Dierich A., Chambon P. Abnormal spermatogenesis in RXR beta mutant mice. Genes Dev. 1996 Jan 1;10(1):80–92. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Chambon P. Multiplicity generates diversity in the retinoic acid signalling pathways. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90014-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Q., Linney E. The mouse retinoid-X receptor-gamma gene: genomic organization and evidence for functional isoforms. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 May;7(5):651–658. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.5.8391126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohnes D., Mark M., Mendelsohn C., Dollé P., Dierich A., Gorry P., Gansmuller A., Chambon P. Function of the retinoic acid receptors (RARs) during development (I). Craniofacial and skeletal abnormalities in RAR double mutants. Development. 1994 Oct;120(10):2723–2748. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.10.2723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lufkin T., Dierich A., LeMeur M., Mark M., Chambon P. Disruption of the Hox-1.6 homeobox gene results in defects in a region corresponding to its rostral domain of expression. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1105–1119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90034-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo J., Sucov H. M., Bader J. A., Evans R. M., Giguère V. Compound mutants for retinoic acid receptor (RAR) beta and RAR alpha 1 reveal developmental functions for multiple RAR beta isoforms. Mech Dev. 1996 Mar;55(1):33–44. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(95)00488-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Borgmeyer U., Heyman R. A., Zhou J. Y., Ong E. S., Oro A. E., Kakizuka A., Evans R. M. Characterization of three RXR genes that mediate the action of 9-cis retinoic acid. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):329–344. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell. 1995 Dec 15;83(6):841–850. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C., Lohnes D., Décimo D., Lufkin T., LeMeur M., Chambon P., Mark M. Function of the retinoic acid receptors (RARs) during development (II). Multiple abnormalities at various stages of organogenesis in RAR double mutants. Development. 1994 Oct;120(10):2749–2771. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.10.2749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata T., Kanno Y., Ozato K., Taketo M. The mouse Rxrb gene encoding RXR beta: genomic organization and two mRNA isoforms generated by alternative splicing of transcripts initiated from CpG island promoters. Gene. 1994 May 16;142(2):183–189. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90259-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe A., Eager N. S., Brickell P. M. A member of the RXR nuclear receptor family is expressed in neural-crest-derived cells of the developing chick peripheral nervous system. Development. 1991 Mar;111(3):771–778. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.3.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucov H. M., Dyson E., Gumeringer C. L., Price J., Chien K. R., Evans R. M. RXR alpha mutant mice establish a genetic basis for vitamin A signaling in heart morphogenesis. Genes Dev. 1994 May 1;8(9):1007–1018. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.9.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara A., Yen P. M., Qi Y., Lechan R. M., Chin W. W. Isoform-specific retinoid-X receptor (RXR) antibodies detect differential expression of RXR proteins in the pituitary gland. Endocrinology. 1995 Apr;136(4):1766–1774. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.4.7895689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tontonoz P., Hu E., Spiegelman B. M. Regulation of adipocyte gene expression and differentiation by peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995 Oct;5(5):571–576. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(95)80025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]