Abstract
Spilanthes acmella is an important medicinal plant, found in tropical and subtropical countries mainly India and South America. Popularly, it is known as toothache plant which reduces the pain associated with toothaches and can induce saliva secretion. Various extracts and active metabolites from various parts of this plant possess useful pharmacological activities. Literature survey proposed that it has multiple pharmacological actions, which include antifungal, antipyretic, local anaesthetic, bioinsecticide, anticonvulsant, antioxidant, aphrodisiac, analgesic, pancreatic lipase inhibitor, antimicrobial, antinociception, diuretic, vasorelaxant, anti-human immunodeficiency virus, toothache relieve and anti-inflammatory effects. This review is elaborately describing the traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology of this plant. This review would assist researchers to search scientific information in the future.
1. Introduction
The increasing demand on herbal medicines and their acceptance in international market because of potent pharmacological potential and high therapeutic value have been proving to be real blessing to the people. However, efforts are needed to explore, standardise, and validate ayurvedic medicines for their potency, safety, and efficacy in order to bring them to market as main line therapeutics. Spilanthes acmella refers to the important medicinal plant distributed in the tropical and subtropical regions around the world with rich source of therapeutic and medicinal constituents. The main constituents, namely, “spilanthol” and “acmellonate”, are sometimes used to reduce the pain associated with toothaches and can induce saliva secretion [1, 2]. Other important traditional uses of this herb are the following: treatment of rheumatism, as a sialagogue for stammering, tongue paralysis, antipyretic, sore throat, and gum infections [3], and as an antipyretie herb. Spilanthes acmella has been well documented for its uses as spices, as antiseptic, antibacterial, antifungal, and antimalarial, treatment, and as remedy for toothache, flu, cough, rabies diseases, and tuberculosis [2, 4].
2. Traditional Uses
This plant is very popular among the ancient tribal community; special food item is prepared from this plant in religious festival. The poor people offered this plant along with the “Ajeng Dues” in Dobur Uie [5]. In particular, this plant is famous as a folklore remedy for toothache and for throat and gum infections [6]. The flowers are crushed and applied at the site of toothache, particularly in “Irula tribe of Hasanur hills in Erode district of Tamilnadu” where it is known by the local name “Mandal Poo Chedi” [7]. Apart from Tamil Nadu, root paste of the plant is used in throat problems in Chindwara and Betul district of Madhya Pradesh [8]. The plant is also known to be used as panacea (Sumatra), as stimulant, for toothache (Sudan), for stomatitis (Java), and for wound healing (India) [9]. In Cameroon, the plant is used as a snakebite remedy and in the treatment of articular rheumatism [10]. It is supposed to be useful in cases of tuberculosis [4]. In India, S. acemella flower heads are used to treat stammering in children. Leaves and flowers of the plant are also used to treat leucorrhoea in females among people of tribes in Bangladesh [9]. The whole plant paste of Spilanthes acmella is also used as “poisonous sting” in Chittagong hill tracts of Bangladesh where the plant is also known as Jhummosak [11].
3. Phytochemistry
It is necessary to explore the phytochemical constituents of any medicinal plant to establish a relation between pharmacology and chemistry of the plant. Many studies have been carried out for chemical analysis and structural determination of pungent alkamides from Spilanthes acmella. The major pungent constituent reported in this plant S. acemella is “spilanthol,” which is an isobutylamide and is well known for its insecticidal properties [12, 13]. The flower head and root part of the plant have been reported to be the rich source of active principles. Triterpenoids have also been found in the plant [14]. Spilanthol is chemically N-isobutylamide which is bitter in taste and could stimulate salivation. The molecular formula of spilanthol was determined as (2E,6Z,8E)-N-isobutylamide-2,6,8-decatrienamide [15]. Spilanthol has a strong pungent taste; it may produce local astringency and anaesthetic effects. Spilanthes acmella contains secondary metabolites which are summarised in Table 1. Spilanthol can be concentrated in the ethanol extract, which has once been found to contain 9.04% of total N-alkylamides yet 88.84% spilanthol [16].
Table 1.
Chemical structures of secondary metabolites of Spilanthes acmella.
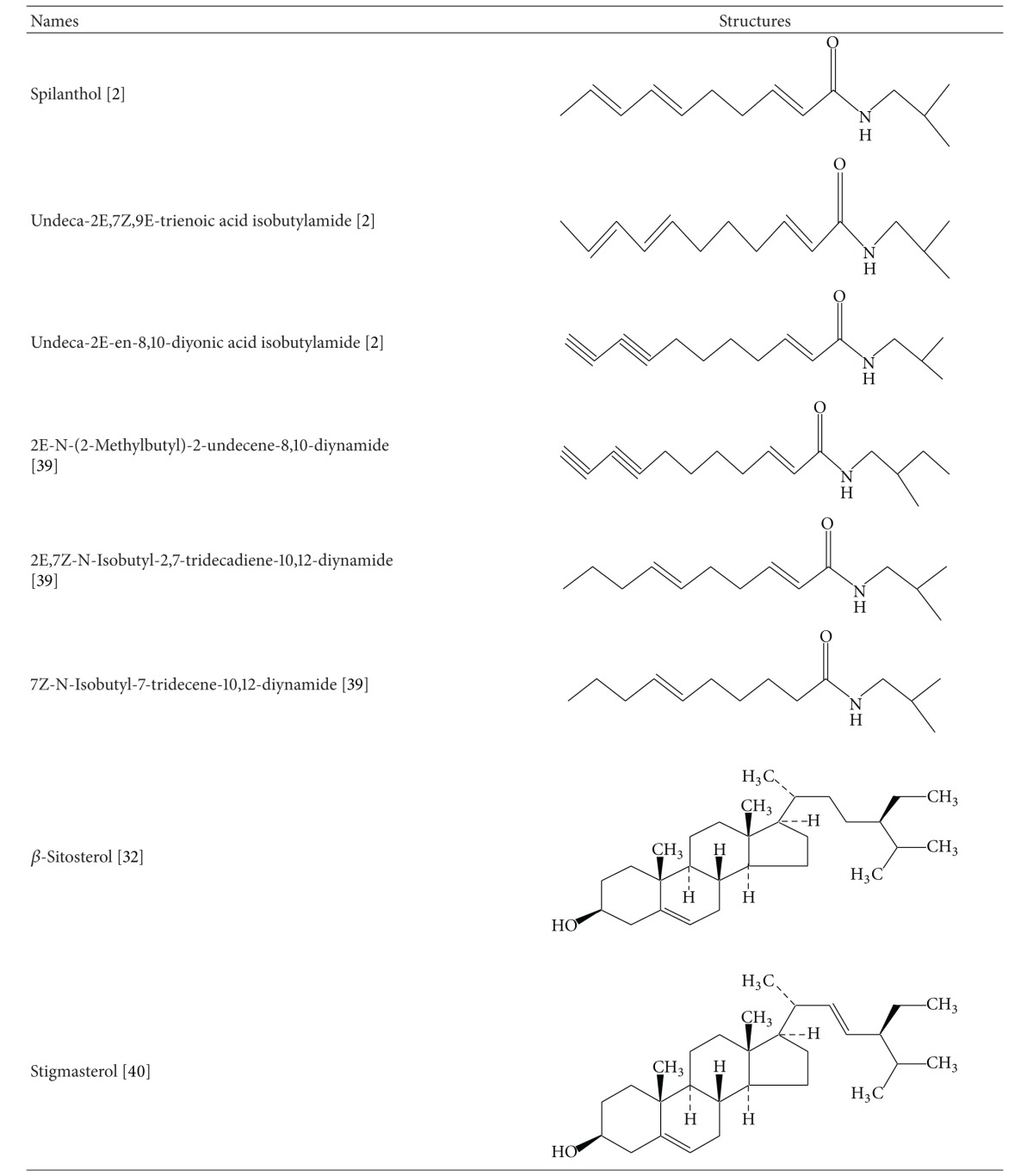
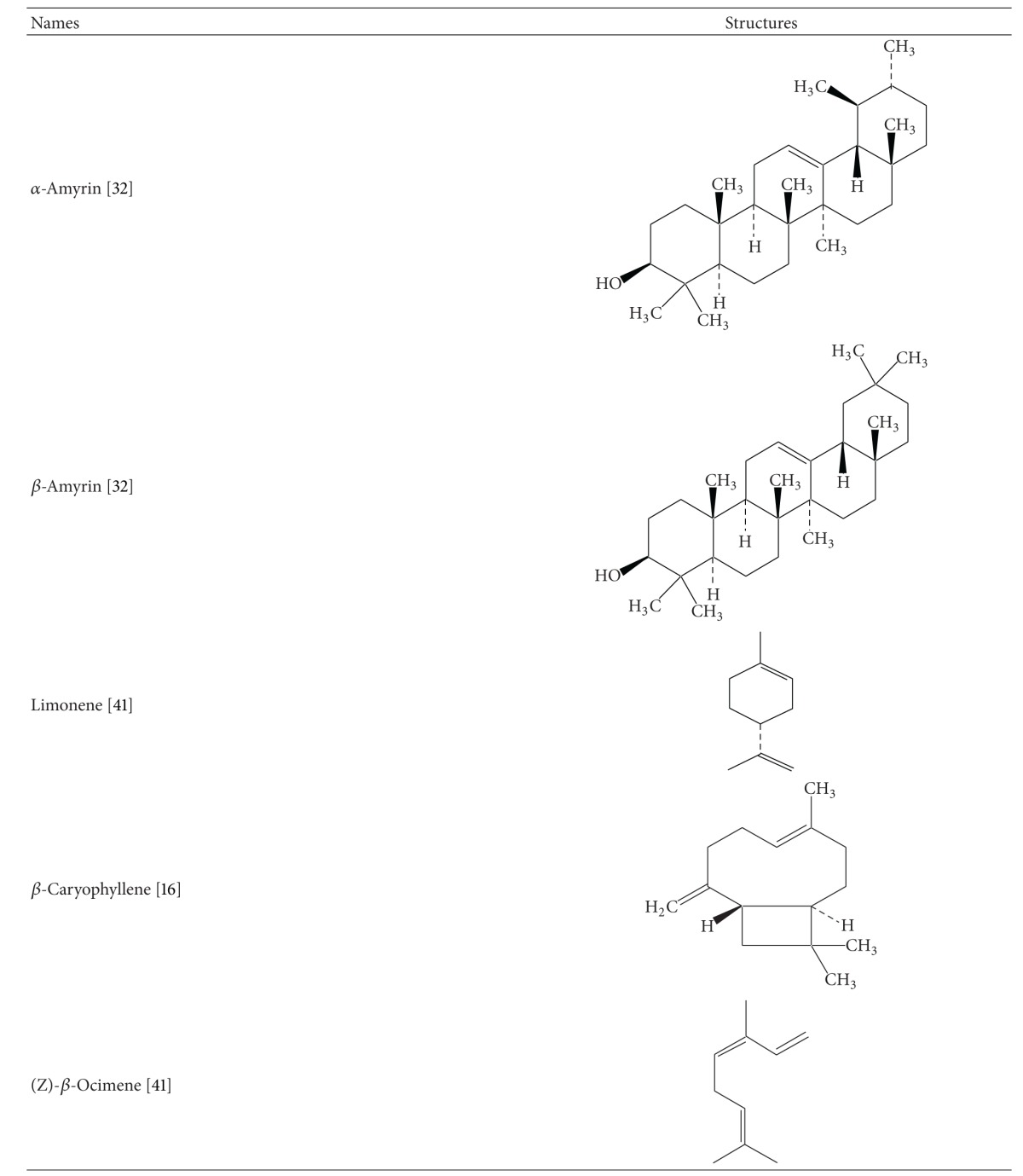
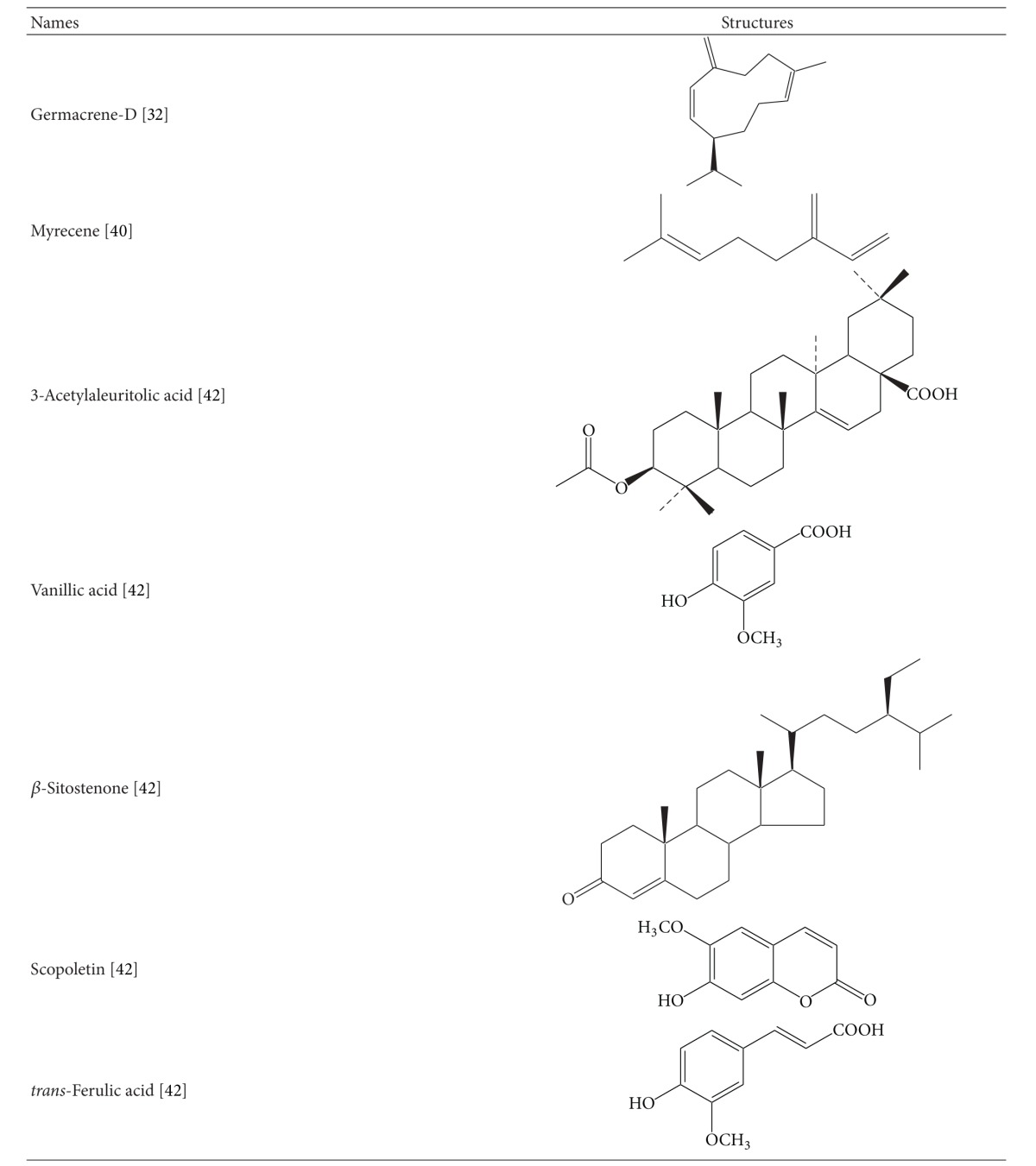

|
4. Pharmacology
Spilanthes acmella has multiple pharmacological actions which are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2.
Summary of pharmacological actions of Spilanthes acmella.
| SL. no. | Pharmacological activity | Parts of plant used | Experimental models | Animals used | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Local anaesthetic | Whole plant | Intracutaneous wheal in guinea pigs and plexus anaesthesia in frog | Guinea pig, frog | [19] |
| 2 | Antipyretic activity | Whole plant | Yeast induced pyrexia | Albino rats | [19] |
| 3 | Anti-inflammatory activity | Whole plant, leaves | Carrageenan induced paw oedema | Albino rats | [22, 31] |
| 4 | Analgesic activity | Whole plant | Tail flick method, acetic acid induced abdominal constriction |
Albino rats | [22] |
| 5 | Antifungal activity | Flowers | — | — | [23] |
| 6 | Diuretic activity | Flowers (cold water extract), whole plant | Induction of dieresis using cold water extract | Albino rats | [24, 25] |
| 7 | Vasorelaxant activity | Flowers | Partially endothelium induced nitric oxide and PGI2 | Albino rats | [30, 31] |
| 8 | Antioxidant activity | Leaves & whole plant | DPPH Assay, TBARs and SOD method | Invitro, no animal | [30, 31] |
| 9 | Pancreatic lipase inhibition | Flowers | — | Invitro, no animal | [29] |
| 10 | Antimalarial & larvicidal activity | Spilanthol extracted from whole plant | — | Eggs & pupae of vector | [37] |
| 11 | Aphrodisiac activity | Whole plant | — | Male rats | [1] |
| 12 | Antinociceptive activity | Whole plant | Acetic acid induced writhing | Mice | [31] |
| 13 | Immunomodulatory activity | Whole plant | — | Rats | [36] |
| 14 | Bioinsecticidal | Whole plant, leaves | — | — | [2, 12, 32] |
| 15 | Convulsant | Whole plant | Electroencephalogram (EEG) analysis | Albino rat | [25] |
4.1. Local Anaesthetic Activity [17]
The local anaesthetic activity of Spilanthes acmella has been carried out using two different animal models: (i) intracutaneous wheal in guinea pigs using nupercaine as standard (suitable for determining degree of anaesthesia) and (ii) plexus anaesthesia in frog using cocaine as standard (used for determining onset of anaesthesia). The mean onset of local anaesthetic action was very potent which could be attributed to the presence of alkylamides.
4.2. Antipyretic Effects [18]
Chakraborty et al. (2010) studied the antipyretic activity of Spilanthes acmella which was carried out by yeast induced method as yeast is commonly used for the induction of pyrexia. The dose varies accordingly in various studies. Various workers used different concentrations and different doses of yeast. The antipyretic activity of Spilanthes acmella demonstrated in the study is attributed to the presence of flavonoids which are predominant inhibitors of either cyclo-oxygenase or lipo-oxygenase [19].
4.3. Anti-Inflammatory/Analgesic Activity [20]
The anti-inflammatory activity of Spilanthes acmella has been carried out by the researchers using carrageenan induced hind paw oedema. Carrageenan is a standard phlogistic agent to study anti-inflammatory activity. The extract was found to produce considerable dose-dependent inhibition of paw oedema which was less than the standard drug. They also demonstrated the analgesic activity of Spilanthes acmella using acetic acid induced abdominal constriction and tail flick method. The former procedure is often used to evaluate the activity of peripherally acting analgesics while the later indicates the involvement of central nervous system. The aqueous extract produced better results as compared to tail flick method which meant that the plant can be explored as peripherally acting analgesic. The activity was attributed to the presence of flavonoids which are potent inhibitors of prostaglandins at later stages of acute inflammation.
4.4. Antifungal Activity [21]
The effect of different concentrations of Spilanthes acmella flower head extract against four different fungi: Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus parasiticus, Fusarium oxysporum, and Fusarium moniliformi, was evaluated by Rani and Murty (2006). All the concentrations of the test solution inhibited the fungal species with varying degree of sensitivity. The maximum zone of inhibition was found to be for highest concentration and increased proportionally with the dose. Among the test organisms, high inhibition zones were observed in F. oxysporium and F. moniliformis followed by A. niger and A. paraiticus.
4.5. Diuretic Effect
The diuretic potential of Spilanthes acmella whole plant as well as freshflowers has been extracted using cold water extract method and shows that the highest dose of flowers tested possesses strong diuretic activity when given orally in a single dose [22, 23]. The diuresis induced by the Spilanthes acmella flowers was found to be strong with intensity similar to that of furosemide and accompanied by marked increases in both urinary Na+ and K+ levels. Researchers proposed that since the urine was slightly acidified, this suggests that it is acting as a loop diuretic. Phytochemically, Spilanthes acmella flowers are shown to contain N-isobutylamides [2], alkaloids [24], and amino acids [24, 25]. Therefore, Spilanthes acmella flowers may be useful as a nontoxic natural therapeutic agent in the treatment of such conditions by traditional practitioners. The onset of the diuretic action of the aqueous extract was extremely rapid, and it also had a fairly long duration of action. This is an appealing diuretic profile as it would curtail the frequency of administration.
4.6. Pancreatic Lipase Inhibition
Ethanolic extracts of the flowers of Spilanthes acmella are demonstrated to inhibit pancreatic lipase activity (40% at 2 mg/mL concentration in vitro) [26]. The activity was compared with Aframomum meleguetta (90% inhibition) and proved to be inferior, whereas 0.75 mg/mL extract inhibited more pancreatic lipase than Spilanthes.
4.7. Vasorelaxant (Effect on Blood Flow) and Antioxidant Activity [27, 28]
The plant extracts elicited vasorelaxations via partially endothelium induced nitric oxide and prostaglandin-I2 in a dose-dependent manner. However, the researchers suggested that other underlying mechanisms may participate. Significantly, the ethyl acetate extract exhibited immediate vasorelaxation in nanogram levels and is the most potent antioxidant in the diphenylpicryl hydrazine assay. The chloroform extract displays the highest vasorelaxation with the highest antioxidant concentration. Antioxidant potential of leaves of Spilanthes acmella was also studied recently by the researchers and they found that the potent antioxidant activity in the crude ethanol extract of the leaves of the plant was attributed to the presence of tannins, flavonoids and phenolic compounds.
4.8. Antimalarial and Larvicidal Effects
Spilanthol is more effective even at low doses against eggs and pupae. In pupae, it seems to work on nervous system as evident by abnormal movement like jerks, spinning and uncoordinated muscular activity. This suggested that the drug disturbed the nerve conduction somewhere. The mortality of pupae in short span of time upon exposure to the drug also indicated that spilanthol greatly disturbs the ongoing processes of histolysis and histogenesis. Many researchers also reported spilanthol as a potent larvicidal agent [13].
4.9. Aphrodisiac Action (Interaction with Testosterone and Sexuality) [1]
Aphrodisiac effect of the plant extract has been studied in male rats by Sharma et al., 2011. They stated that mount latency, intromission latency, ejaculation frequency, and postejaculatory interval were increased in a dose-dependent manner after oral administration of extract. Although exact quantification of these improvements was not given, estimation derived from graphs suggested that after 28 days of 150 mg/kg dose, the improvements were reduced in mount latency, intromission latency, and post ejaculatory latency. These benefits were more significant 28 days after supplementation relative to 14 days, suggesting a build-up effect. The plant proved to be superior to Viagra in all aspects studied except proerectile properties.
4.10. Antinociceptive Activity [29, 30]
Antinociceptive activity of the crude ethanol extract of S. acemella using acetic acid induced writhing model in mice is available elsewhere in literature. The animals of test groups received test substance at the dose of 250 and 500 mg/kg body weight. Positive control group was administered Diclofenac sodium (standard drug) at the dose of 25 mg/kg body weight, and vehicle control group was treated with 1% Tween 80 in water at the dose of 10 mL/kg body weight. Test samples, standard drug, and control vehicle were administered orally 30 min before intraperitoneal administration of 0.7% acetic acid. After an interval of 15 min, the mice were observed to be writhing (constriction of abdomen, turning of trunk, and extension of hind legs) for 5 min. Crude ethanol extract of S. acemella leaves was found to possess significant antinociceptive activity.
4.11. Immunomodulatory Activity [31]
Hexane and chloroform extracts of Spilanthes acmella were found to suppress nitric oxide production in stimulated macrophages at 80 mcg/mL by 72% and 85%, respectively. Isolated spilanthol demonstrated dose-dependent prevention of macrophage activation with 60% and 20% production of nitric oxide at 90 and 360 μM concentrations, respectively. These inhibitory properties were accompanied by less nitric oxide synthetase and cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA and protein content, less cytokine production from macrophages, and less nF-kB activation in the nucleus.
4.12. Bioinsecticide and Convulsant Activity
The genus Spilanthes consists of 42 known species and several insecticidal compounds which have been reported in Spilanthes mauritiana, S. alba, S. ocymifolia, S. oleracea, and Spilanthes acmella [2, 12, 32]. Hexanic extract of Spilanthes acmella plant in rats was reported to induce full tonic-clonic convulsions accompanied by typical electrographic seizures in the electroencephalogram [25].
5. Toxicology
5.1. Evaluated on Zebrafish
It was found that plant contained a high yield of phytotestosterone [33]. Testosterone has an influence on growth rate and feed utilization in low dose-dependent variation in sheep and cattle [34]. Because the zebrafish embryo test is a highly sensitive toxicity test of chemical substances on animals, the result can be used as basic data for the toxicity test in higher animals and environmental contamination regulation. A study shows that Spilanthes acmella Murr. does not have any lethal effect on zebrafish embryo at 20% v/v, which was the highest concentration of the study, while significantly the lowest observable sublethal effect concentration was 10%. According to this study, crude extract of Spilanthes acmella Linn. Murr. can be used in animal feed at 0.01% v/v and 1% v/v, respectively, without any lethal, sublethal, and malformation effect [35].
5.2. Insecticidal Toxicity of Spilanthol
Extract of Spilanthol from the flower heads of Spilanthes acmella was found to be active against P. xylostella [36]. The extracts from Spilanthes acmella were most toxic against different mosquito species (i.e., Anopheles, Culex, and Aedes). The insecticidal property was attributed to spilanthol and alkamides. Besides, nonvolatile sesquiterpenoids and saponins were also reported [14, 32]. Ethanol extract of flower heads of Spilanthes acmella has shown a potent ovicidal, insecticidal, and pupacidal activity at dose of 7.5 ppm concentration with 100% of Anopheles, Culex, and Aedes mosquito [37]. The hexane extract of dried flower buds of Spilanthes acmella (3 N-isobutylamides: spilanthol, undeca-2E,7Z,9E-trienoic acid isobutylamide and undeca-2E-en-8,10-diynoic acid isobutylamide) was found active against Aedes aegypti larvae. Ethanolic extracts of Spilanthes acmella (whole plants) were screened against early 4th instar larvae of Culex quinquefasciatus [38]. Spilanthol was shown to be toxic against adults of P. americana. It is one of the most potent compound when compared with conventional insecticides such as carbaryl, lindane, and bioresmethrin with a potency found to be 1.3, 3.8, and 2.6 times, respectively [36].
6. Summary and Conclusion
Spilanthes acmella is a well known plant in Indian traditional system of medicine with multiple pharmacological action and minor side effects. In this review, we concluded ethnobotany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology in a descriptive manner. The summary of phytochemicals and pharmacological actions is tabulated in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. Extracts and phytoconstituents isolated from this plant have shown to produce different pharmacological response, which includes anticonvulsant, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, vasodilation, diuretic, and antimalarial effects. The most traditional use of this plant is to reduce toothache all over India as well as South America. Other traditional uses of Spilanthes acmella are as stomachic, stimulant, and antidiarrhoeal and is used rarely against tuberculosis. Many researchers proposed that whole plant has local anaesthetic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, aphrodisiac, antinociception, immunomodulator, and insecticidal effect. On the other hand, flower part has shown to produce diuretic, vasorelaxation, antifungal and pancreatic lipase inhibition properties. Its multiple traditional use and pharmacological responses allow us to write a review of Spilanthes acmella. This review will give all the scientific information in a concise manner to the scientific community.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Acknowledgments
Suchita Dubey wishes to express thanks to the University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India, for providing UGC Postgraduate Scholarship and Dr. Sudipta Saha (Corresponding Author) also wishes to express special thanks to the University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India, for providing UGC Start-Up-Grant for newly recruited faculty.
References
- 1.Sharma V, Boonen J, Chauhan NS, Thakur M, de Spiegeleer B, Dixit VK. Spilanthes acmella ethanolic flower extract: LC-MS alkylamide profiling and its effects on sexual behavior in male rats. Phytomedicine. 2011;18(13):1161–1169. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2011.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ramsewak RS, Erickson AJ, Nair MG. Bioactive N-isobutylamides from the flower buds of Spilanthes acmella . Phytochemistry. 1999;51(6):729–732. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(99)00101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ley JP, Blings M, Krammer G, Reinders G, Schmidt C-O, Bertram H-J. Isolation and synthesis of acmellonate, a new unsaturated long chain 2-ketol ester from Spilanthes acmella . Natural Product Research. 2006;20(9):798–804. doi: 10.1080/14786410500246733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Storey C, Salem JI. Lay use of Amazonian plants for the treatment of tuberculosis. Acta Amazonica. 1997;27(3):175–182. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sharma UK, Pegu S. Ethnobotany of religious and supernatural beliefs of the Mising tribes of Assam with special reference to the ’Dobur Uie’. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine. 2011;7(16):1–13. doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-7-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chung K-F, Kono Y, Wang C-M, Peng C-I. Notes on acmella (Asteraceae): helianthaceae in Taiwan. Botanical Studies. 2008;49(1):73–82. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Revathi P, Parimelazhghan T. Traditional knowledge on medicinal plants used by Irula tribe of Hasanur hills, Erode District, Tamil Nadu, India. Ethnobotanical Leaflets. 2010;14:136–160. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Vijendra N, Kumar KP. Traditional knowledge on ethno-medicinal uses prevailing in tribal pockets of Chhindwara and Betul Districts, Madhya Pradesh, India. African Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 2010;4(9):662–670. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hossan MS, Hanif A, Agarwala B, et al. Traditional use of medicinal plants in Bangladesh to treat urinary tract infections and sexually transmitted diseases. Ethnobotany Research and Applications. 2010;8:61–74. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Santesson CG. Several drugs of the Cameroon District and their native uses. Archiv Furdie Botanik A. 1926;20(3):1–34. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Biswas A, Bari MA, Roy M, Bhadra SK. Inherited folk pharmaceutical knowledge of tribal people in the Chittagong hill tracts, Bangladesh. Indian Journal of Traditional Knowledge. 2010;9(1):77–89. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jondiko IJO. A mosquito larvicide in Spilanthes mauritiana . Phytochemistry. 1986;25(10):2289–2290. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kadir HA, Zakaria MB, Kechil AA, Azirun MS. Toxicity and electrophysiological effects of Spilanthes acmella Murr. Pesticide Science. 1989;25(4):329–335. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mukharya DK, Ansari AH. Olean-12-en-3-O-beta-D-galactopyranosyl (1-4)-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranoside: a new triterpenoidal saponin from the roots of Spilanthes acmella(Murr.) Indian Journal of Chemical Biology. 1987:26–86. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yasuda I, Takeya K, Itokawa H. The geometric structure of spilanthol. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 1980;28(7):2251–2253. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Boonen J, Baert B, Burvenich C, Blondeel P, de Saeger S, de Spiegeleer B. LC-MS profiling of N-alkylamides in Spilanthes acmella extract and the transmucosal behaviour of its main bio-active spilanthol. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 2010;53(3):243–249. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2010.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chakraborty A, Devi RKB, Rita S, Singh IT. Local anaesthetic effect of Spilanthes acmella in experimental animal models. Indian Journal of Pharmacology. 2002;34:144–145. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.70106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chakraborty A, Devi BRK, Sanjebam R, Khumbong S, Thokchom IS. Preliminary studies on local anesthetic and antipyretic activities of Spilanthes acmella Murr. in experimental animal models. Indian Journal of Pharmacology. 2010;42(5):277–279. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.70106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Narayana KR, Reddy MS, Chaluvadi MR, Krishna DR. Bioflavonoids classification, pharmacological, biochemical effects and therapeutic potential. Indian Journal of Pharmacology. 2001;33(1):2–16. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chakraborty A, Devi RKB, Rita S, Sharatchandra K, Singh TI. Preliminary studies on antiinflammatory and analgesic activities of Spilanthes acmella in experimental animal models. Indian Journal of Pharmacology. 2004;36(3):148–150. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rani SA, Murty SU. Antifungal potential of flower head extract of Spilanthes acmella Linn. African Journal of Biomedical Research. 2006;9:67–69. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ratnasooriya WD, Pieris KPP, Samaratunga U, Jayakody JRAC. Diuretic activity of Spilanthes acmella flowers in rats. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2004;91(2-3):317–320. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2004.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Moreira VM, Maia JG, de Souza JM, Bortolotto ZA, Cavalheiro EA. Characterization of convulsions induced by a hexanic extract of Spilanthes acmella var. oleracea in rats. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research. 1989;22(1):65–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Peiris KPP, Silva GKJ, Ratnasooriya WD. Analgesic activity of water extract of Spilanthes acmella flowers on rats. Journal of Tropical Medicinal Plants. 2001;2:201–204. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mondal AK, Parui S, Mandal S. Analysis of the free amino acid content in pollen of nine Asteraceae species of known allergenic activity. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine. 1998;5(1):17–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ekanem AP, Wang M, Simon JE, Moreno DA. Antiobesity properties of two African plants (Afromomum meleguetta and Spilanthes acmella) by pancreatic lipase inhibition. Phytotherapy Research. 2007;21(12):1253–1255. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wongsawatkul O, Prachayasittikul S, Isarankura-Na-Ayudhya C, Satayavivad J, Ruchirawat S, Prachayasittikul V. Vasorelaxant and antioxidant activities of Spilanthes acmella Murr. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2008;9(12):2724–2744. doi: 10.3390/ijms9122724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hossain H, Shahid-Ud-Daula AFM, Jahan IA, Nimmi I, Hasan K, Haq MM. Evaluation of antinociceptive and antioxidant potential from the leaves of Spilanthes paniculata growing in Bangladesh. International Journal of Pharmacy and Phytopharmacology Research. 2012;1(4):178–186. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Whittle BA. The use of changes in capillary permeability in mice to distinguish between narcotic & non-narcotic analgesics. British Journal of Pharmacology and Chemotherapy. 1964;22:246–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb02030.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ahmed F, Selim MST, Das AK, Choudhuri MSK. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of Lippia nodiflora Linn. Pharmazie. 2004;59(4):329–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wu L-C, Fan N-C, Lin M-H, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of spilanthol from Spilanthes acmella on murine macrophage by down-regulating LPS-induced inflammatory mediators. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2008;56(7):2341–2349. doi: 10.1021/jf073057e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Krishnaswamy NR, Prasanna S, Seshandri TR, Vedantham TNC. α- and β-Amyrin esters and sitosterol glucoside from Spilanthes acmella . Phytochemistry. 1975;14(7):1666–1667. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Suthikrai W, Jintana R, Sophan S, Usawang S, Hengtakulsin R. The study on testosterone progesterone & oestradiol 17B levels in weeds from pasture. Thailand Journal of Toxicology. 2010;25(2):p. 183. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Casida LE, Andrews FN, Clegg MT, Bogart R, Nalbandov AV. Hormonal Relationship & Applications in the Productions of Meats Milk & Egg. Vol. 28. Washington, DC, USA: National Academy of Science-National Research Council; 1959. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ponpornpisit A, Pirarat N, Suthikrai W, Binwihok A. Toxicity test kameng (Eclipta prostrate linn) & Kradhuawean (Spilanthes acmella linn. Murr.) to early stage of zebrafish (Danio rerio) Thailand Journal of Veterinary Medicine. 2011;41(4):543–547. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sharma A, Kumar V, Rattan RS, Kumar N, Singh B. Insecticidal toxicity of Spilanthol from Spilanthes acmella Murr. against Plutella xylostella . American Journal of Plant Sciences. 2012;3:1568–1572. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Saraf DK, Dixit VK. Spilanthes acmella Murr.: study on its extract spilanthol as larvicidal compound. Asian Journal Experimental Science. 2002;16(1-2):9–19. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Pitasawat B, Choochote W, Kanjanapothi D, Panthong A, Jitpakdi A, Chaithong U. Screening for larvicidal activity of ten carminative plants. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health. 1998;29(3):660–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nakatani N, Nagashima M. Pungent alkamides from Spilanthes acmella L. var. oleracea Clarke. Bioscience Biotechnology Biochemistry. 1992;56(5):759–762. doi: 10.1271/bbb.56.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tiwari HP, Kakkar A. Phytochemical examination of Spilanthus acemella (Murr.) Journal of the Indian Chemical Society. 1990;67(9):784–785. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Baruah RN, Leclercq PA. Characterization of the essential oil from flower heads of Spilanthes acmella . Journal of Essential Oil Research. 1993;5(6):693–695. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Prachayasittikul S, Suphapong S, Worachartcheewan A, Lawung R, Ruchirawat S, Prachayasittikul V. Bioactive metabolites from Spilanthes acmella Murr. Molecules. 2009;14(2):850–867. doi: 10.3390/molecules14020850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


