Abstract
A 59-year-old male with an secundum atrial septal defect status post repair with an Amplatzer occluder in 2001 was admitted with sepsis and MRSA bacteremia. Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE) showed presence of an overlying mobile echogenic structure on the left atrial surface of the device suggestive of a vegetation/infected thrombus. This is only the 3rd case description of late endocarditis involving the Amplatzer ASD closure device in an adult.
Keywords: ASD, Amplatzer, Infective endocarditis
1. Case description
A 59-year-old male with a history of hypertension, type 2 diabetes, Congestive heart failure s/p Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator and a Secundum ASD s/p percutaneous repair with an Amplatzer Atrial Septal Occluder Device (ASO; AGA Medical Corporation, Golden Valley, Minnesota) was admitted with sepsis and positive blood cultures for MRSA. Bacteremia persisted despite IV Vancomycin. With a high suspicion for Infective endocarditis (IE) despite normal Transthoracic echocardiography, a TEE was done. It showed a highly mobile echogenic mass suggestive of vegetation/infected thrombus in the left atrial surface of the device Figs. 1 and 2, Videos 1 and 2. After initiation of IV daptomycin, there was significant clinical improvement leading to discharge with 6 weeks of IV antibiotic.
Fig. 1.
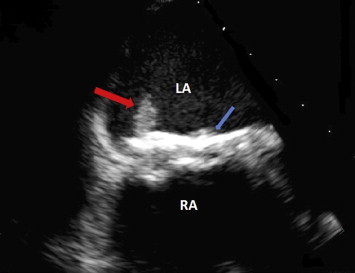
Zoomed 30° transesophageal short axis view of the interatrial septum with Amplatzer device and vegetation. Bold red arrow – Vegetation; Bold blue arrow – Amplatzer septal occluder LA – Left atrium; RA – Right atrium.
Fig. 2.
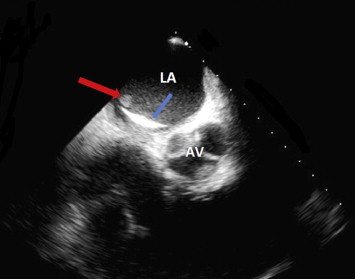
60° Transesophageal short axis view of the interatrial septum with Amplatzer device and vegetation. Bold red arrow – Vegetation; Bold blue arrow – Amplatzer septal occluder LA – Left atrium; RA – Right atrium.
Supplementary video related to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ihj.2013.06.002.
The following are the supplementary video related to this article:
60° Transesophageal short axis view of the interatrial septum showing a highly mobile vegetation on the left atrial side of the Amplatzer device.
Zoomed 60° transesophageal short axis view of the interatrial septum showing a highly mobile vegetation on the left atrial side of the Amplatzer divice.
2. Comments
The Amplatzer septal occluder is one of the most frequently used percutaneous devices for the closure of Secundum ASD.1 Complications of this procedure include device embolization/malposition, arrhythmias, cardiac perforation, thrombus formation and device erosion with infection being the least common.2
Only 2 previous cases of late infection of occluder device have been reported in literature.3–5 A case of IE involving a CardioSEAL device for patent foramen ovale has also been described.6 Device infection can occur in two ways; either through introduction of microbes during the procedure or secondary to seeding of microorganisms at a later time. After device implantation, it is thought that it takes 6 months for complete neoendothelialization. The current guidelines recommend antibiotic prophylaxis for 6 months following device placement.7 The organism isolated in this case is classical for nosocomial infection, likely from infection from an abdominal wound.
In late IE involving ASD closure device medical management with prolonged antibiotic therapy with constant blood culture monitoring might be adequate in the absence of device dehiscence, septal perforation or fistula formation.
Conflicts of interest
All authors have none to declare.
References
- 1.Masura J., Gavora P., Podnar T. Long-term outcome of transcatheter secundum-type atrial septal defect closure using Amplatzer septal occluders. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;45:505–507. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2004.10.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Majunke N., Bialkowski J., Wilson N. Closure of atrial septal defect with the Amplatzer septal occluder in adults. Am J Cardiol. 2009;103:550–554. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.10.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zahr Firas, Katz William E., Toyoda Yoshiya, Anderson William D. 2010. Late Bacterial Endocarditis of an Amplatzer Atrial Septal Defect Occluder Device.http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2009.09.011 Published by Elsevier Inc. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Balasundaram Ram Prakash, Anandaraja S., Juneja Rajnish, Choudhary Shiv Kumar. Infective endocarditis following implantation of amplatzer atrial septal occluder. Indian Heart J. 2005;57:167–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Slesnick Timothy C., Nugent Alan W., Fraser Charles D., Jr., Cannon Bryan C. Incomplete endothelialization and late development of acute bacterial endocarditis after implantation of an amplatzer septal occluder device. Circulation. 2008;117:e326–e327. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.754069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Goldstein Jeffrey A., Beardslee Michael A., Xu Haodong, Sundt Thoralf M., Lasala John M. Infective endocarditis resulting from CardioSEAL closure of a patent foramen ovale. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2002;55:217–220. doi: 10.1002/ccd.2999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.AHA Guideline prevention of Infective Endocarditis Guidelines From the American Heart Association: a Guideline from the American Heart Association Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease Committee, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, and the Council on Clinical Cardiology, Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, and the Quality of Care and Outcomes Research Interdisciplinary Working Group.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
60° Transesophageal short axis view of the interatrial septum showing a highly mobile vegetation on the left atrial side of the Amplatzer device.
Zoomed 60° transesophageal short axis view of the interatrial septum showing a highly mobile vegetation on the left atrial side of the Amplatzer divice.


