Abstract
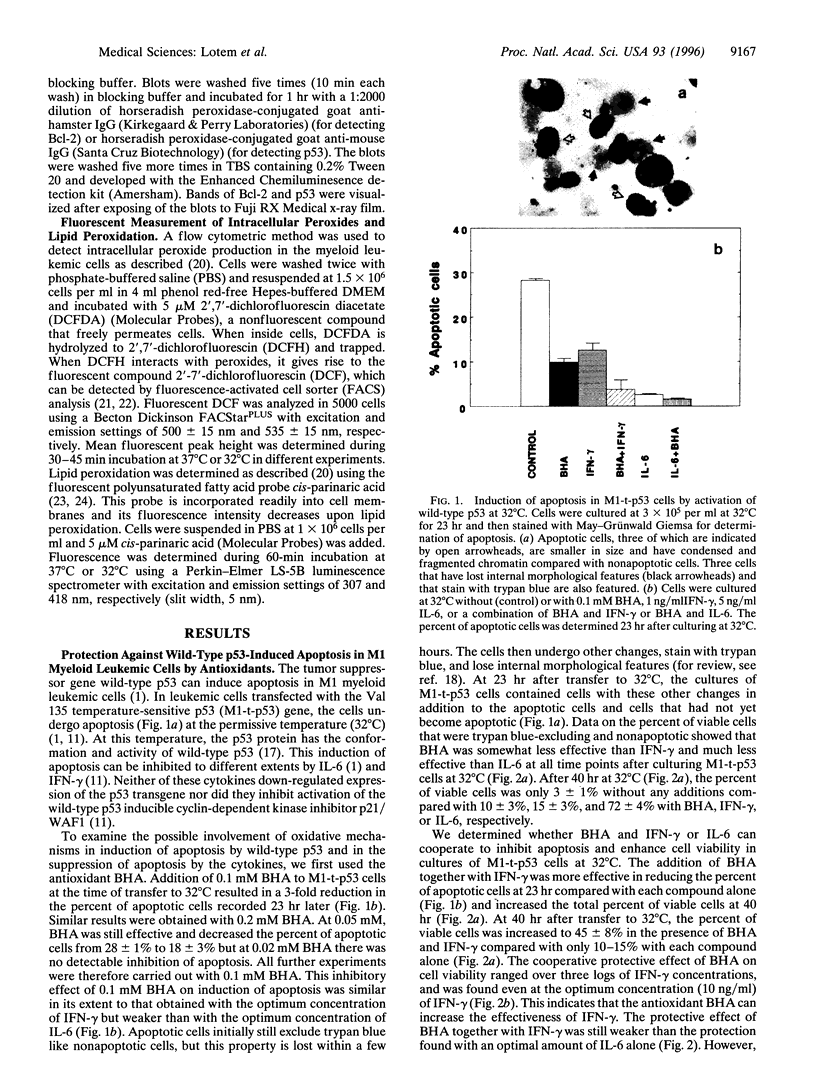
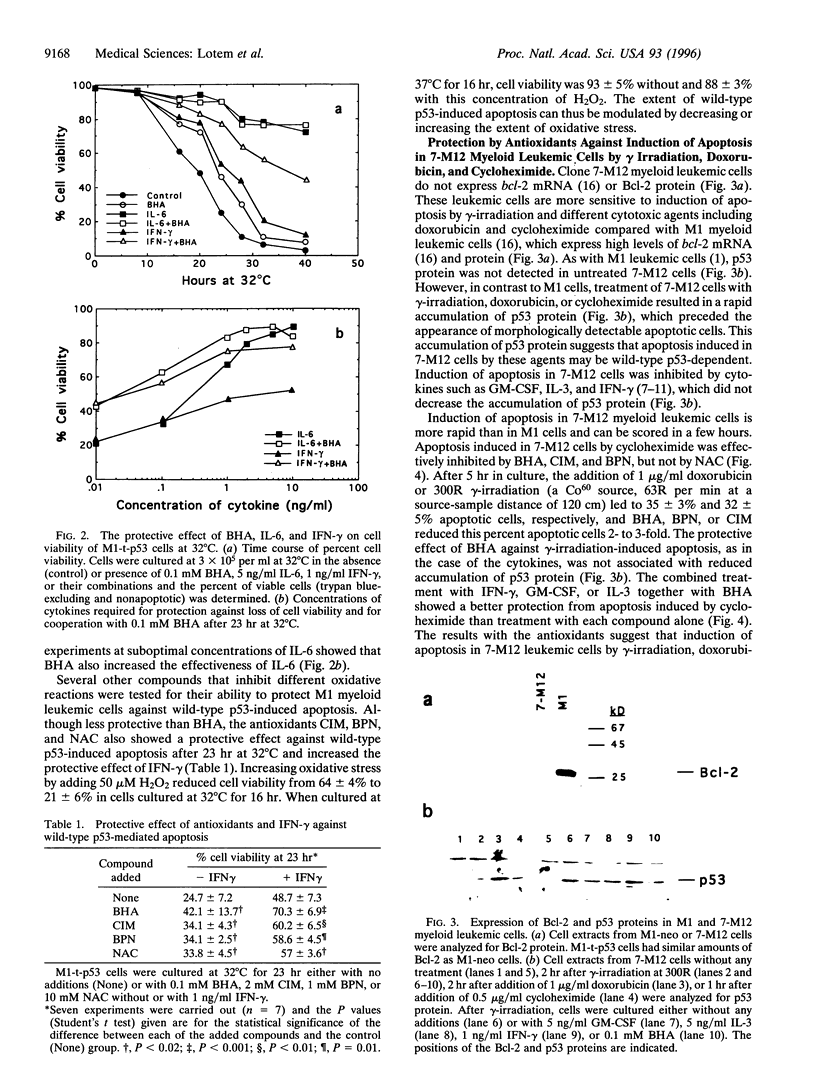
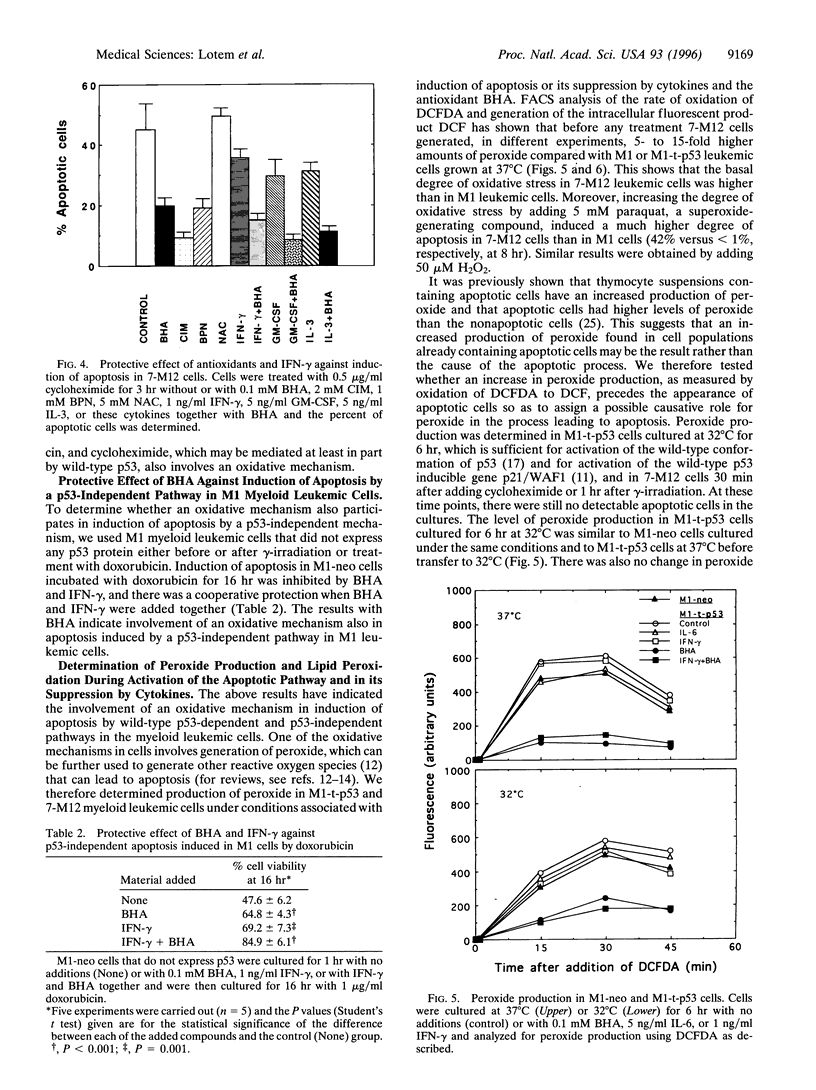
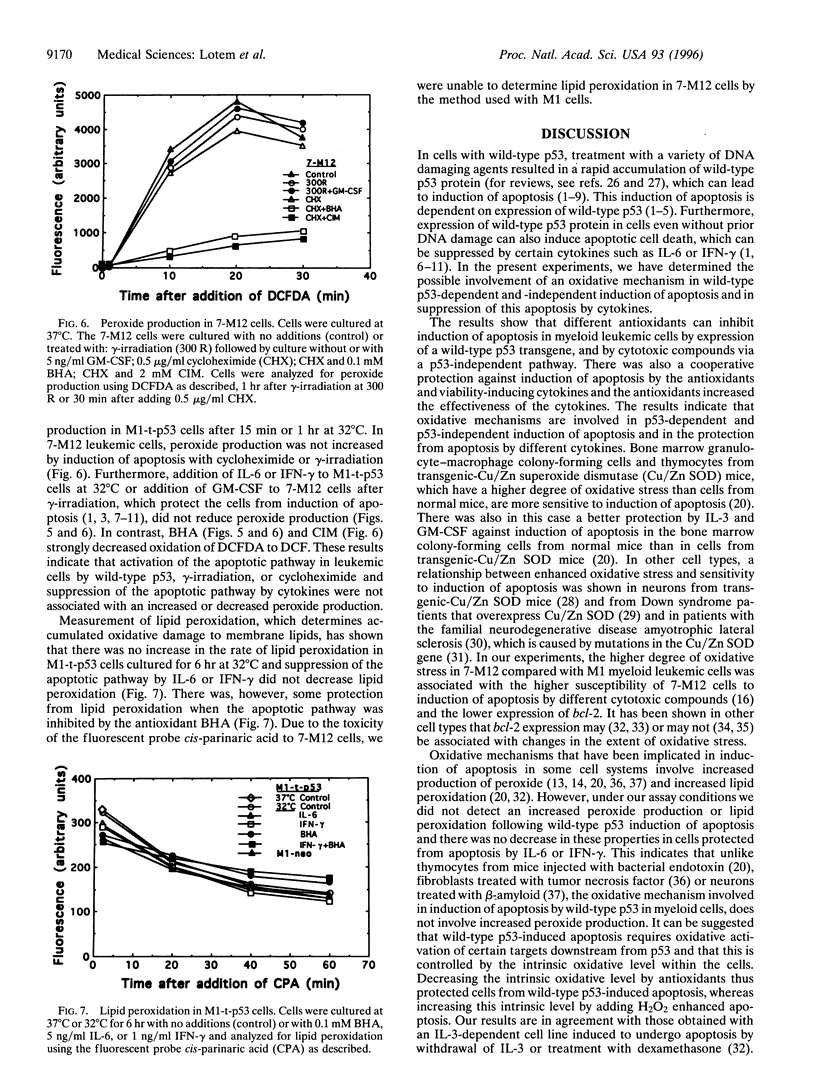
Apoptosis induced by wild-type p53 or cytotoxic compounds in myeloid leukemic cells can be inhibited by the cytokines interleukin 6, interleukin 3, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and interferon gamma and by antioxidants. The antioxidants and cytokines showed a cooperative protective effect against induction of apoptosis. Cells with a higher intrinsic level of peroxide production showed a higher sensitivity to induction of apoptosis and required a higher cytokine concentration to inhibit apoptosis. Decreasing the intrinsic oxidative stress in cells by antioxidants thus inhibited apoptosis, whereas increasing this intrinsic stress by adding H2O2 enhanced apoptosis. Induction of apoptosis by wild-type p53 was not preceded by increased peroxide production or lipid peroxidation and the protective effect of cytokines was not associated with a decrease in these properties. The results indicate that the intrinsic degree of oxidative stress can regulate cell susceptibility to wild-type p53-dependent and p53-independent induction of apoptosis and the ability of cytokines to protect cells against apoptosis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arends M. J., Wyllie A. H. Apoptosis: mechanisms and roles in pathology. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1991;32:223–254. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-364932-4.50010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Peled O., Korkotian E., Segal M., Groner Y. Constitutive overexpression of Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase exacerbates kainic acid-induced apoptosis of transgenic-Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Aug 6;93(16):8530–8535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.16.8530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behl C., Davis J. B., Lesley R., Schubert D. Hydrogen peroxide mediates amyloid beta protein toxicity. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):817–827. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. H., Jr Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: recent insights from genetics and transgenic mice. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):687–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busciglio J., Yankner B. A. Apoptosis and increased generation of reactive oxygen species in Down's syndrome neurons in vitro. Nature. 1995 Dec 21;378(6559):776–779. doi: 10.1038/378776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttke T. M., Sandstrom P. A. Oxidative stress as a mediator of apoptosis. Immunol Today. 1994 Jan;15(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathcart R., Schwiers E., Ames B. N. Detection of picomole levels of hydroperoxides using a fluorescent dichlorofluorescein assay. Anal Biochem. 1983 Oct 1;134(1):111–116. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90270-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Purdie C. A., Harrison D. J., Morris R. G., Bird C. C., Hooper M. L., Wyllie A. H. Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):849–852. doi: 10.1038/362849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez A., Kiefer J., Fosdick L., McConkey D. J. Oxygen radical production and thiol depletion are required for Ca(2+)-mediated endogenous endonuclease activation in apoptotic thymocytes. J Immunol. 1995 Dec 1;155(11):5133–5139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goossens V., Grooten J., De Vos K., Fiers W. Direct evidence for tumor necrosis factor-induced mitochondrial reactive oxygen intermediates and their involvement in cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 29;92(18):8115–8119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.18.8115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B. Free radicals, antioxidants, and human disease: curiosity, cause, or consequence? Lancet. 1994 Sep 10;344(8924):721–724. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92211-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley D., Chow S. Flow cytometric measurement of lipid peroxidation in vital cells using parinaric acid. Cytometry. 1992;13(7):686–692. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990130704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D. M., Oltvai Z. N., Yin X. M., Milliman C. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 functions in an antioxidant pathway to prevent apoptosis. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80066-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. D., Raff M. C. Programmed cell death and Bcl-2 protection in very low oxygen. Nature. 1995 Apr 27;374(6525):814–816. doi: 10.1038/374814a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane D. J., Sarafian T. A., Anton R., Hahn H., Gralla E. B., Valentine J. S., Ord T., Bredesen D. E. Bcl-2 inhibition of neural death: decreased generation of reactive oxygen species. Science. 1993 Nov 19;262(5137):1274–1277. doi: 10.1126/science.8235659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuypers F. A., van den Berg J. J., Schalkwijk C., Roelofsen B., Op den Kamp J. A. Parinaric acid as a sensitive fluorescent probe for the determination of lipid peroxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 25;921(2):266–274. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Control of apoptosis in hematopoiesis and leukemia by cytokines, tumor suppressor and oncogenes. Leukemia. 1996 Jun;10(6):925–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Genetic dissection of the control of normal differentiation in myeloid leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5554–5558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Hematopoietic cells from mice deficient in wild-type p53 are more resistant to induction of apoptosis by some agents. Blood. 1993 Aug 15;82(4):1092–1096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Hematopoietic cytokines inhibit apoptosis induced by transforming growth factor beta 1 and cancer chemotherapy compounds in myeloid leukemic cells. Blood. 1992 Oct 1;80(7):1750–1757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Interferon-gamma inhibits apoptosis induced by wild-type p53, cytotoxic anti-cancer agents and viability factor deprivation in myeloid cells. Leukemia. 1995 Apr;9(4):685–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Regulation by bcl-2, c-myc, and p53 of susceptibility to induction of apoptosis by heat shock and cancer chemotherapy compounds in differentiation-competent and -defective myeloid leukemic cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Jan;4(1):41–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Schmitt E. M., Smith S. W., Osborne B. A., Jacks T. p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):847–849. doi: 10.1038/362847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalovitz D., Halevy O., Oren M. Conditional inhibition of transformation and of cell proliferation by a temperature-sensitive mutant of p53. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90113-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M. p53: the ultimate tumor suppressor gene? FASEB J. 1992 Oct;6(13):3169–3176. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.13.1397838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peled-Kamar M., Lotem J., Okon E., Sachs L., Groner Y. Thymic abnormalities and enhanced apoptosis of thymocytes and bone marrow cells in transgenic mice overexpressing Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase: implications for Down syndrome. EMBO J. 1995 Oct 16;14(20):4985–4993. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00181.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royall J. A., Ischiropoulos H. Evaluation of 2',7'-dichlorofluorescin and dihydrorhodamine 123 as fluorescent probes for intracellular H2O2 in cultured endothelial cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 May;302(2):348–355. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs L., Lotem J. Control of programmed cell death in normal and leukemic cells: new implications for therapy. Blood. 1993 Jul 1;82(1):15–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs L. The control of hematopoiesis and leukemia: from basic biology to the clinic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 May 14;93(10):4742–4749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.10.4742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P., Bovey R., Tardy S., Sahli R., Sordat B., Costa J. Induction of apoptosis by wild-type p53 in a human colon tumor-derived cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4495–4499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu S., Eguchi Y., Kosaka H., Kamiike W., Matsuda H., Tsujimoto Y. Prevention of hypoxia-induced cell death by Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. Nature. 1995 Apr 27;374(6525):811–813. doi: 10.1038/374811a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater A. F., Nobel C. S., Orrenius S. The role of intracellular oxidants in apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 May 24;1271(1):59–62. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(95)00010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedau-Pazos M., Goto J. J., Rabizadeh S., Gralla E. B., Roe J. A., Lee M. K., Valentine J. S., Bredesen D. E. Altered reactivity of superoxide dismutase in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science. 1996 Jan 26;271(5248):515–518. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5248.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Resnitzky D., Lotem J., Sachs L., Kimchi A., Oren M. Wild-type p53 induces apoptosis of myeloid leukaemic cells that is inhibited by interleukin-6. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):345–347. doi: 10.1038/352345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]