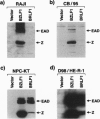
Abstract
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), the causative agent of infectious mononucleosis, is a human herpesvirus associated with epithelial cell malignancies (nasopharyngeal carcinoma) as well as B-cell malignancies. Understanding how viral latency is disrupted is a central issue in herpesvirus biology. Epithelial cells are the major site of lytic EBV replication within the human host, and viral reactivation occurs in EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinomas. It is known that expression of a single viral immediate-early protein, BZLF1, is sufficient to initiate the switch from latent to lytic infection in B cells. Cellular regulation of BZLF1 transcription is therefore thought to play a key role in regulating the stringency of viral latency. Here we show that, unexpectedly, expression of another viral immediate-early protein, BRLF1, can disrupt viral latency in an epithelial cell-specific fashion. Therefore, the mechanisms leading to disruption of EBV latency appear to be cell-type specific.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogedain C., Alliger P., Schwarzmann F., Marschall M., Wolf H., Jilg W. Different activation of Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early and early genes in Burkitt lymphoma cells and lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):1200–1203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.1200-1203.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. N., Dong D. L., Hayward G. S., Hayward S. D. The Epstein-Barr virus Zta transactivator: a member of the bZIP family with unique DNA-binding specificity and a dimerization domain that lacks the characteristic heptad leucine zipper motif. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3358–3369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3358-3369.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier-Greco A., Gruffat H., Manet E., Calender A., Sergeant A. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DR enhancer contains two functionally different domains: domain A is constitutive and cell specific, domain B is transactivated by the EBV early protein R. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):615–623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.615-623.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier-Greco A., Manet E., Chavrier P., Mosnier C., Daillie J., Sergeant A. Both Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded trans-acting factors, EB1 and EB2, are required to activate transcription from an EBV early promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3243–3249. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countryman J., Miller G. Activation of expression of latent Epstein-Barr herpesvirus after gene transfer with a small cloned subfragment of heterogeneous viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4085–4089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. A., Leahy J., Hardwick J. M. An enhancer within the divergent promoter of Epstein-Barr virus responds synergistically to the R and Z transactivators. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):313–321. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.313-321.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Rowe D. T., Rooney C. M., Kouzarides T. Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 trans-activator specifically binds to a consensus AP-1 site and is related to c-fos. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):127–132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03356.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E. K., Goldfeld A. E., Speck S. H. Efficient transcription of the Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early BZLF1 and BRLF1 genes requires protein synthesis. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):7073–7077. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.7073-7077.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Speck S. H. Autoregulation of Epstein-Barr virus putative lytic switch gene BZLF1. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1227–1232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1227-1232.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Speck S. H. Evidence for coiled-coil dimer formation by an Epstein-Barr virus transactivator that lacks a heptad repeat of leucine residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9459–9463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Speck S. H. Identification of phorbol ester response elements in the promoter of Epstein-Barr virus putative lytic switch gene BZLF1. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1217–1226. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1217-1226.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Blanco M. A., Cullen B. R. Molecular basis of latency in pathogenic human viruses. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):815–820. doi: 10.1126/science.1658933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser R., O'Neill F. J. Hybridization of Burkitt lymphoblastoid cells. Science. 1972 Jun 16;176(4040):1245–1247. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4040.1245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruffat H., Duran N., Buisson M., Wild F., Buckland R., Sergeant A. Characterization of an R-binding site mediating the R-induced activation of the Epstein-Barr virus BMLF1 promoter. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):46–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.46-52.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruffat H., Sergeant A. Characterization of the DNA-binding site repertoire for the Epstein-Barr virus transcription factor R. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Apr 11;22(7):1172–1178. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.7.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. M., Lieberman P. M., Hayward S. D. A new Epstein-Barr virus transactivator, R, induces expression of a cytoplasmic early antigen. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2274–2284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2274-2284.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. M., Tse L., Applegren N., Nicholas J., Veliuona M. A. The Epstein-Barr virus R transactivator (Rta) contains a complex, potent activation domain with properties different from those of VP16. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5500–5508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5500-5508.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Holley-Guthrie E., Mar E. C., Smith M. The Epstein-Barr virus BMLF1 promoter contains an enhancer element that is responsive to the BZLF1 and BRLF1 transactivators. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3878–3883. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3878-3883.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolman J. L., Taylor N., Gradoville L., Countryman J., Miller G. Comparing transcriptional activation and autostimulation by ZEBRA and ZEBRA/c-Fos chimeras. J Virol. 1996 Mar;70(3):1493–1504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.3.1493-1504.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Freese U. K., Fischer R., Polack A., Kofler E., Bornkamm G. W. TPA-inducible Epstein-Barr virus genes in Raji cells and their regulation. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):503–507. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90496-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q. X., Young L. S., Niedobitek G., Dawson C. W., Birkenbach M., Wang F., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus infection and replication in a human epithelial cell system. Nature. 1992 Mar 26;356(6367):347–350. doi: 10.1038/356347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manet E., Gruffat H., Trescol-Biemont M. C., Moreno N., Chambard P., Giot J. F., Sergeant A. Epstein-Barr virus bicistronic mRNAs generated by facultative splicing code for two transcriptional trans-activators. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1819–1826. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03576.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martel-Renoir D., Grunewald V., Touitou R., Schwaab G., Joab I. Qualitative analysis of the expression of Epstein-Barr virus lytic genes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma biopsies. J Gen Virol. 1995 Jun;76(Pt 6):1401–1408. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-76-6-1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlivan E. B., Holley-Guthrie E. A., Norris M., Gutsch D., Bachenheimer S. L., Kenney S. C. Direct BRLF1 binding is required for cooperative BZLF1/BRLF1 activation of the Epstein-Barr virus early promoter, BMRF1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):1999–2007. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruf I. K., Rawlins D. R. Identification and characterization of ZIIBC, a complex formed by cellular factors and the ZII site of the Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 promoter. J Virol. 1995 Dec;69(12):7648–7657. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.12.7648-7657.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Takimoto T., Tanaka S., Tanaka J., Raab-Traub N. Concatameric replication of Epstein-Barr virus: structure of the termini in virus-producer and newly transformed cell lines. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5295–5300. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5295-5300.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair A. J., Brimmell M., Shanahan F., Farrell P. J. Pathways of activation of the Epstein-Barr virus productive cycle. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2237–2244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2237-2244.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Nedrud J. G., Raab-Traub N., Hanes R. A., Pagano J. S. Epstein-Barr virus replication in oropharyngeal epithelial cells. N Engl J Med. 1984 May 10;310(19):1225–1230. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198405103101905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Ono Y. Synchronous and sequential activation of latently infected Epstein-Barr virus genomes. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):445–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.445-449.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Shimizu N., Sakuma S., Ono Y. trans activation of the latent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome after transfection of the EBV DNA fragment. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1016–1022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1016-1022.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto T., Kamide M., Umeda R. Establishment of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated nuclear antigen (EBNA)-positive nasopharyngeal carcinoma hybrid cell line (NPC-KT). Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1984;239(1):87–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00454266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalani S., Holley-Guthrie E. A., Gutsch D. E., Kenney S. C. The Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early promoter BRLF1 can be activated by the cellular Sp1 transcription factor. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7282–7292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7282-7292.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalani S., Holley-Guthrie E., Kenney S. The Zif268 cellular transcription factor activates expression of the Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early BRLF1 promoter. J Virol. 1995 Jun;69(6):3816–3823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.6.3816-3823.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., Bornkamm G. W., Schmidt R., Hecker E. Tumor initiators and promoters in the induction of Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):782–785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]