Abstract
The versatility of copper-catalyzed alkyne-azide coupling (CuAAC) in functionalizing drug-loaded polymer nanoparticles is demonstrated via the modification of surfaces of acetylene-functionalized PNPs with folate, biotin, and gold nanoparticles.
Surface functionalization of nanoparticles with biomolecules has received considerable attention due to the multitude of applications that such modification makes possible.1–3 Indeed, when nanoparticles are surface-functionalized with constrast agents or ligands, they can become imaging platforms for the tissue of interest or highly specific targeted therapies to a disease site.4–6 Unfortunately, currently available surface attachment methods are limited, because few reactions are fully compatible with most of the bioactive species.7–9 Thus, there is a clear need for strategies that can efficiently modify nanoparticles with a wide range of sensitive biomolecules under mild conditions.
Previously, we have shown that monodisperse drug-containing amphiphilic block copolymers can undergo directed assembly into therapeutically active core-shell polymer nanoparticles (PNPs) with uniform, tunable diameter.10,11 To yield targeted delivery vehicles, these PNPs were modified with an antibody via nucleophilic displacement of surface tosyl groups.12 Although this chemistry successfully yielded antibody-functionalized PNPs that were internalized into breast cancer cells, the degree of functionalization was difficult to control. Herein, we report a modular “click-based” copper-catalyzed alkyne-azide coupling (CuAAC) strategy for the conjugation of a diverse group of bioactive ligands/nanoparticles to drug-loaded PNPs under mild reaction conditions with a high degree of control over surface functionalization.
For CuAAC, the PNP surfaces can be decorated with either alkyne or azide functionalities for conjugation to the complementarily functionalized bioactive molecules. Given the ready availability of azide-substituted biomolecules through commercial sources or via one-step modifications,13 we chose to modify the PNP surface with alkynes (Scheme 1), similar to the choice made by Evans and Lovell.14 In addition, localizing a single azido functional group on each bioactive molecule would minimize any potential safety concerns that may arise from having a large number of azides present on the surface of a nanoparticle.15
Scheme 1.
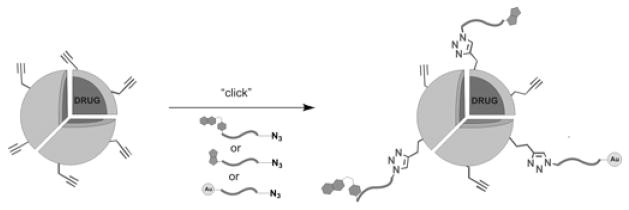
Schematic illustration of modification of alkyne-functionalized PNPs with azide-functionalized biomolecules via click chemistry.
To introduce alkyne moieties on the PNP surface, we synthesized monomer 3, an acetylene-terminated hydrophilic derivative of norbornene. In this design, retention of the poly(ethylene) glycol (PEG) segment was essential to maintain the amphiphilic nature of the final block copolymer to be used in PNP formation (see below).16 Monomer 3 was readily prepared from hexa(ethylene) glycol norbornene monomer (2)12 (Scheme 2). However, initial attempts at the polymerization of 3 using catalyst 5 ((PCy3)2Cl2Ru=CHPh) did not result in complete polymerization, as indicated by 1H NMR spectroscopy and gel permeation chromatography (GPC) (Electronic Supporting Information (ESI†), section VII).
Scheme 2.
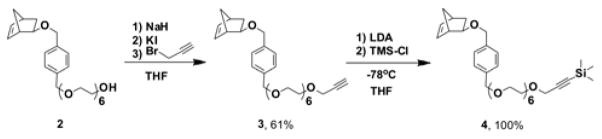
Synthesis of monomer 4.
The inability of monomer 3 to undergo facile polymerization is attributed to the strong coordination of the acetylene moiety to the ruthenium catalyst,17 which competes against the binding of the norbornenyl olefin, a necessary step prior to ring-opening metathesis. Supporting this conjecture is the observation that the polymerization of indomethacin-containing norbornene monomer 110 by catalyst 5 was inhibited in the presence of excess phenylacetylene (ESI†, section VII). Hence, we masked the terminal acetylene in 3 with trimethylsilane (TMS) to prevent coordination to the Ru center and lead to polymerization.15 Indeed, monomer 4, the TMS-protected analog of 3, was successfully polymerized using catalyst 5 as shown by 1H NMR and GPC analyses (Mn = 10000 (theoretical Mn = 9000), PDI = 1.25).
Monodisperse amphiphilic block copolymer 135-b-415 was prepared by sequential polymerization of 1 and 4 (Scheme 3). A molar ratio of 35:15 was chosen to keep the molecular weight of the polymer ≤ 45 kDa, which restricts the diameter of PNPs to ≤ 400 nm10 and ensures bioclearance via the reticuloendothelial system.18 The polymerization proceeded smoothly, affording well-defined blocks 1 (theoretical Mn = 20000 for block 1; Mn = 21000 and PDI = 1.13) and 4 (theoretical Mn = 29000 for the whole copolymer, Mn = 30000, PDI = 1.15). Co-polymerization reactions initiated first with monomer 4 also afforded similar results, suggesting that polymerization can be initiated with either the hydrophilic or hydrophobic monomer (ESI†, section IV).
Scheme 3.
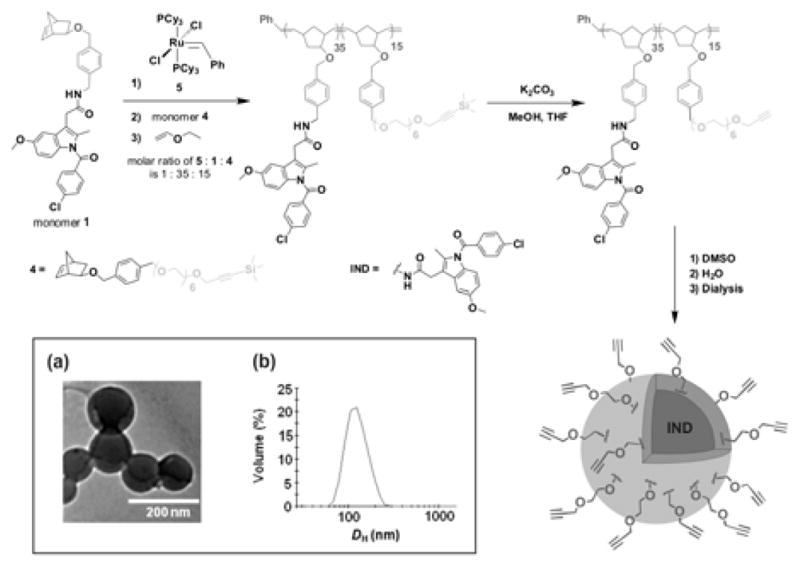
Synthesis of block copolymer 135-b-315 and subsequent formation of PNPs from this copolymer. Inset shows: (a) A representative TEM image of the resulting PNPs. (b) DH distribution of the PNPs as measured by DLS.
To form clickable alkynyl-functionalized PNPs from 135-b-415, the terminal TMS groups in the hydrophilic block 4 were deprotected in a mixture of THF and MeOH using K2CO3 (Scheme 3).19 Complete conversion to copolymer 135-b-315 was verified by 1H NMR and FT-IR spectroscopies (ESI†, section IV). GPC analysis of the deprotected copolymer also revealed a slight decrease in Mn (28000), attributable to the loss of the TMS groups, while retaining the narrow molecular weight distribution (PDI = 1.10) of the parent copolymer.
An aqueous suspension of alkyne-functionalized PNPs was obtained by dropwise addition of water to a DMSO solution of copolymer 135-b-315 followed by exhaustive dialysis against ultrapure deionized water (Scheme 3).10 Dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements indicated a narrow size distribution of particles centered at DH = 128 nm (Scheme 3b) with a PDI of 0.060. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM, Scheme 3a) also confirmed the homogeneous spherical morphology of these PNPs with diameters of ~130 nm.
To demonstrate the versatility of the alkyne-functionalized PNPs derived from 135-b-315, they were separately treated with azido-modified folate,20 biotin, and gold nanoparticles (AuNP-N3)21 in the presence of standard water-soluble CuSO4/sodium ascorbate catalyst.22 Biotin-23 and folate-24 conjugated drug delivery vehicles have been shown to significantly enhance cellular uptake into tumor cells, and thus improve efficacy, in comparison to non-functionalized systems. Additionally, AuNPs have been proposed as a photothermal therapy in cancer treatment25 as well as non- viral vectors for the delivery of siRNA and antisense DNA drugs.26 Hence, the modification of our drug-loaded PNPs with biotin, folate, and AuNPs could lead to combinational targeted platforms and new multimodal chemotherapies.
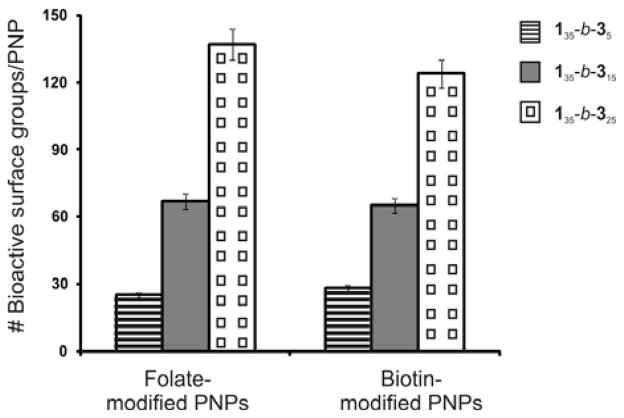
We were pleased to observe successful modifcations of our PNP by all three of the aforementioned ligands/AuNPs, especially within much shorter reaction times than previously reported.14 For folate-PEG-azide, ~67 folate groups were conjugated to each PNP surface after 6 h as determined by UV-vis spectroscopy. Biotin functionalization, determined using an avidin-based assay (ESI†, section V), proceeded in a similar fashion, resulting in ~65 biotin molecules bound per PNP after 24 h (Fig. 1a). Finally, TEM analysis of the alkyne-PNPs that have been click-conjugated to 13-nm AuNP-N3 clearly showed attachment of the AuNPs to the surface of PNPs after 12 h (Fig. 2a). These short reaction times at high dilution and neutral pH affirm that click chemistry can be used to effortlessly introduce sensitive biological functionalities to the PNP surface. Combining the alkyne-PNPs and the azide partners in the absence of the Cu catalyst showed minimal to no coupling (ESI†, section V). Additional control experiments suggested that oxidative coupling between the surface alkyne groups in a particle did not occur under our conditions (ESI†, section V).
Fig. 1.
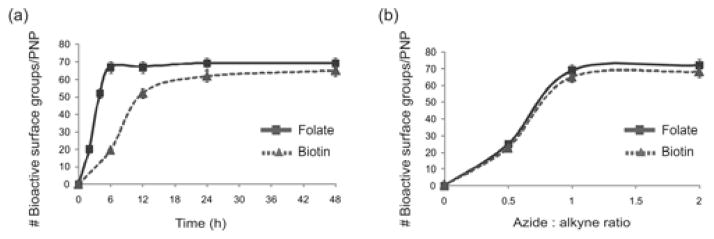
(a) Reaction profiles of the click reactions between alkyne PNPs and one equivalent of folate- or biotin-PEG-azide. (b) Plots of the degree of alkyne modifications achieved for different azide:alkyne ratios, showing that maximum modification is achieved with an equimolar ratio.
Fig. 2.
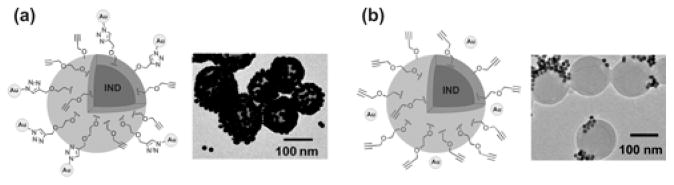
Schematic illustrations and TEM images of the products resulting from: (a) the click reaction between alkyne-functionalized PNPs and azide-modified AuNPs in the presence of a Cu/NaAsc catalyst and (b) the analogous reaction in the absence of the catalyst. The former TEM image clearly shows attachment of AuNPs to PNPs, while the latter displays non-specific interactions between AuNPs and PNPs.
To delineate the conjugation profiles of the CuAAC between alkyne-PNPs and biotin- or folate-PEG-azide, we varied the azide:alkyne ratio in the couplings while monitoring the number of modified alkyne groups over a 48 h period (Fig. 1b). Maximum conjugation was reached when an equimolar ratio of azide and alkyne was used. Interestingly, the conjugation with biotin initially appeared to be much slower compared to the coupling with folate. This apparent discrepancy in conjugation could be attributed to the fact that some surface biotin groups might be inaccessible to the avidin-binding assay, resulting in imprecise biotin quantification.27 Application of a correction factor (ESI†, section V) revealed that, indeed, the conjugations of folate and biotin to alkyne PNPs proceeded with similar efficiencies.
Because our PNPs are constructed from monodisperse 5 block copolymers, the level of surface conjugation can be easily tuned by varying the hydrophobic/hydrophilic block ratio in copolymers 1m-b-3n. To this end, two sets of copolymers were synthesized—one with varied hydrophobic block length and a constant hydrophilic block, and the second with the opposite block size variation—and assembled into alkyne-functionalized PNPs. Copolymers with higher hydrophobic:hydrophilic ratios afforded PNPs with larger diameters due to the increased proportion of hydrophobic core material per polymer chain (ESI†, section VI, Fig. S18). In contrast, PNPs fabricated from copolymers with lower hydrophobic:hydrophilic ratios tend to be smaller in sizes due to better packing of the PEGylated segments in the shell (ESI†, section VI, Fig. S18). Exposing both sets of PNPs to folate- and biotin-PEG-azide under our click conditions all resulted in successful conjugations. As expected, copolymers with the same alkyne-functionalized block length exhibited similar degrees of conjugation (ESI†, section VI, Fig. S20). Increasing the length of this hydrophilic block resulted in a proportional rise in conjugation levels, consistent with the increased density of surface functional groups (Fig. 3). These results indicate that the per-particle conjugation level can be tuned through the manipulation of the hydrophilic block length.
Fig. 3.
Proportional increase in alkyne modification achieved for PNPs derived from copolymers with increasing hydrophilic block length.
In summary, surface modification via CuAAC affords a facile and modular means to incorporate a diverse group of functionalities onto drug-loaded PNPs. This strategy can be expanded to combine targeting with imaging groups,28 paving the way for the development of multimodal nanocarriers.29,30
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this work was provided by the National Institute of Health (NCI 1U54 CA119341-01 through the CCNE program), the Rosenberg Foundation, the Malkin Foundation, and the National Science Foundation (EEC-0647560 through the NSEC program, and DMR-0520523 through the MRSEC program). Instruments in the Northwestern IMSERC facilities were purchased with grants from NSF-NSEC, NSF-MRSEC, Keck Foundation, the state of Illinois, and Northwestern University. We acknowledge the use of instruments at the Electron Probe Instrumentation Center and Keck II facility at Northwestern University.
Footnotes
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) available: Detailed experimental procedures, materials, instrumentation, and characterization. See DOI: 10.1039/b000000x/
Notes and references
- 1.Reddy GR, Bhojani MS, McConville P, Moody J, Moffat BA, Hall DE, Kim G, Koo YEL, Woolliscroft MJ, Sugai JV, Johnson TD, Philbert MA, Kopelman R, Rehemtulla A, Ross BD. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:6677–6686. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gu FX, Karnik R, Wang AZ, Alexis F, Levy-Nissenbaum E, Hong S, Langer RS, Farokhzad OC. Nano Today. 2007;2:14–21. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gullotti E, Yeo Y. Mol Pharmaceutics. 2009;6:1041–1051. doi: 10.1021/mp900090z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sahoo SK, Ma W, Labhasetwar V. Int J Cancer. 2004;112:335–340. doi: 10.1002/ijc.20405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Popielarski SR, Pun SH, Davis ME. Bioconjugate Chem. 2005;16:1063–1070. doi: 10.1021/bc050113d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gref R, Couvreur P, Barratt G, Mysiakine E. Biomaterials. 2003;24:4529–4537. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(03)00348-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yang SK, Weck M. Macromolecules. 2008;41:346–351. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shukla R, Thomas TP, Peters JL, Desai AM, Kukowska-Latallo J, Patri AK, Kotlyar A, Baker JR., Jr Bioconjugate Chem. 2006;17:1109–1115. doi: 10.1021/bc050348p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Diehl C, Fluegel S, Fischer K, Maskos M. Prog Colloid Polym Sci. 2008;134:128–133. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bertin PA, Watson KJ, Nguyen ST. Macromolecules. 2004;37:8364–8372. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bertin PA, Smith D, Nguyen ST. Chem Commun. 2005:3793–3795. doi: 10.1039/b504643b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bertin PA, Gibbs JM, Shen CKF, Thaxton CS, Russin WA, Mirkin CA, Nguyen ST. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:4168–4169. doi: 10.1021/ja056378k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Srinivasan R, Tan LP, Wu H, Yang PY, Kalesh KA, Yao SQ. Org Biomol Chem. 2009;7:1821–1828. doi: 10.1039/b902338k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Evans CE, Lovell PA. Chem Commun. 2009:2305–2307. doi: 10.1039/b821758k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ladmiral V, Mantovani G, Clarkson GJ, Cauet S, Irwin JL, Haddleton DM. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:4823–4830. doi: 10.1021/ja058364k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Maeda H, Wu J, Sawa T, Matsumura Y, Hori K. J Controlled Release. 2000;65:271–284. doi: 10.1016/s0168-3659(99)00248-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Binder WH, Kluger C. Macromolecules. 2004;37:9321–9330. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nori A, Kopecek J. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2005;57:609–636. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2004.10.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fletcher JT, Bumgarner BJ, Engels ND, Skoglund DA. Organometallics. 2008;27:5430–5433. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lee SM, Chen H, O’Halloran TV, Nguyen ST. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:9311–9320. doi: 10.1021/ja9017336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zhang T, Wu Y, Pan X, Zheng Z, Ding X, Peng Y. Eur Polym J. 2009;45:1625–1633. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Copolymer 135-b-415 easily formed monodisperse PNPs. Thus, they can, in theory, be subjected to a one-pot in situ TMS deprotection/CuAAC (see Aucagne V, Leigh DA. Org Lett. 2006;8:4505–4507. doi: 10.1021/ol061657d..). Unfortunately, these TMS-protected PNPs readily disintegrated during our attempt to carry out this one-pot procedure (ESI†, section VII).
- 23.Patil YB, Toti US, Khdair A, Ma L, Panyam J. Biomaterials. 2009;30:859–866. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.09.056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hong S, Leroueil PR, Majoros IJ, Orr BG, Baker JR, Banaszak-Holl MM. Chem Biol. 2007;14:107–115. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.11.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cai W, Gao T, Hong H, Sun J. Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2008;1:17–32. doi: 10.2147/NSA.S3788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rosi NL, Giljohann DA, Thaxton CS, Lytton-Jean AKR, Han MS, Mirkin CA. Science. 2006;312:1027–1030. doi: 10.1126/science.1125559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhang J, Wang X, Wu D, Liu L, Zhao H. Chem Mater. 2009;21:4012–4018. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Doiron AL, Homan KA, Emelianov S, Brannon-Peppas L. Pharm Res. 2009;26:674–682. doi: 10.1007/s11095-008-9786-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kim J, Piao Y, Hyeon T. Chem Soc Rev. 2009;38:372–390. doi: 10.1039/b709883a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Smith D, Pentzer EB, Nguyen ST. Polym Rev. 2007;47:419–459. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.