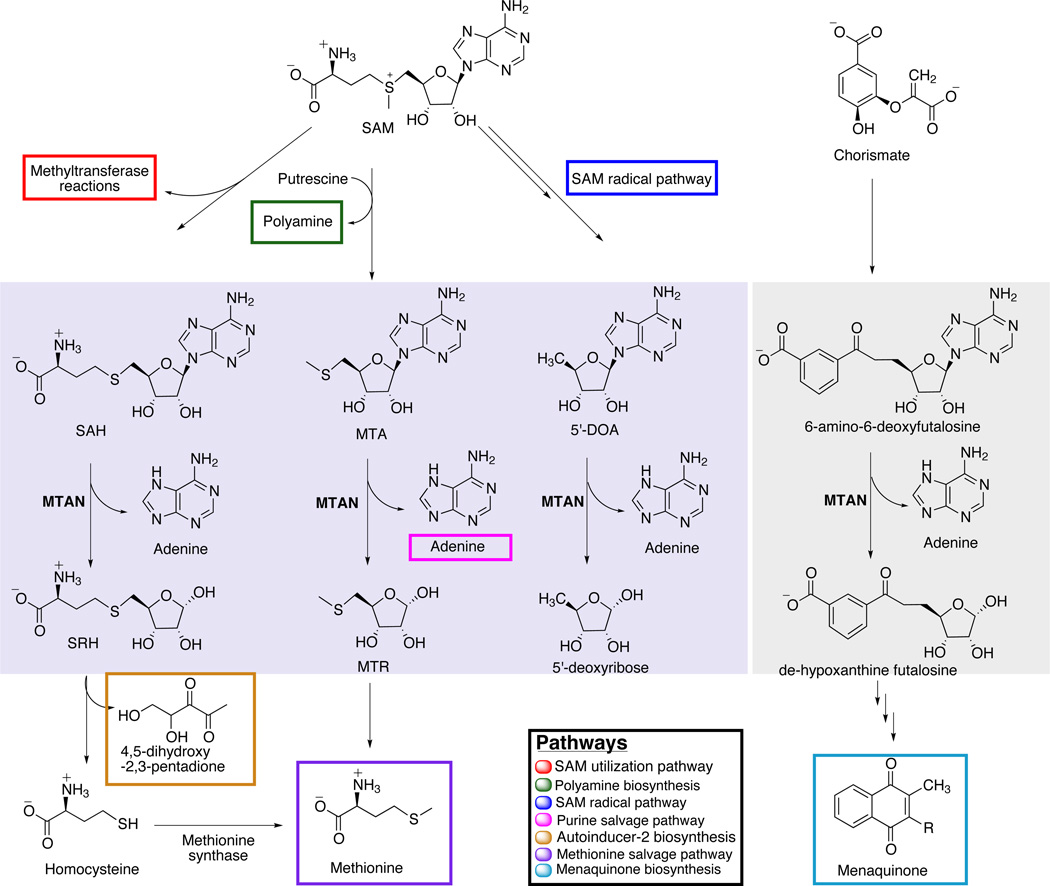
FIGURE 1.
MTAN is a multifunctional enzyme. MTAN has been shown to use three different adenosine-based substrates in diverse bacterial systems: SAH, MTA and 5’-DOA (light violet solid box). In Campylobacter, it also hydrolyzes the N-ribosidic bond of 6-amino-6-deoxyfutalosine (grey solid box). Colored boxes encompass the compounds relevant to the pathways directly affected by MTAN activity. Only one adenine is boxed, but all four MTAN catalyzed reactions allow adenine salvage.