Abstract
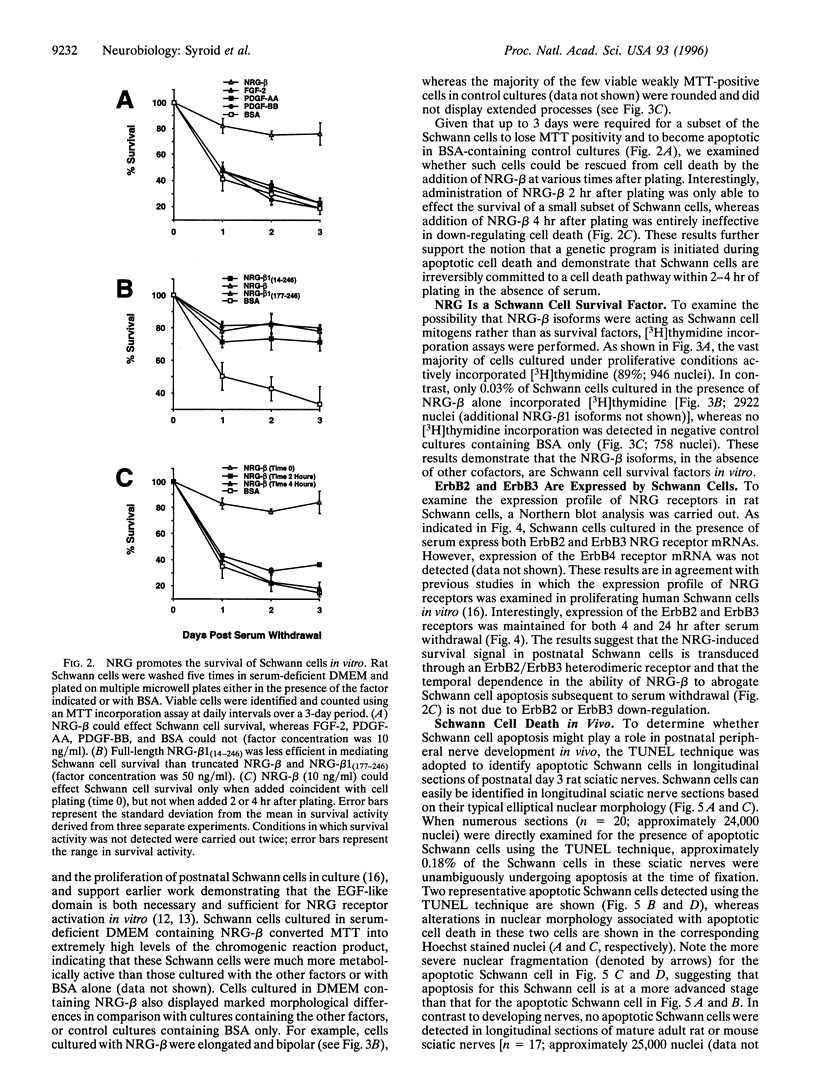
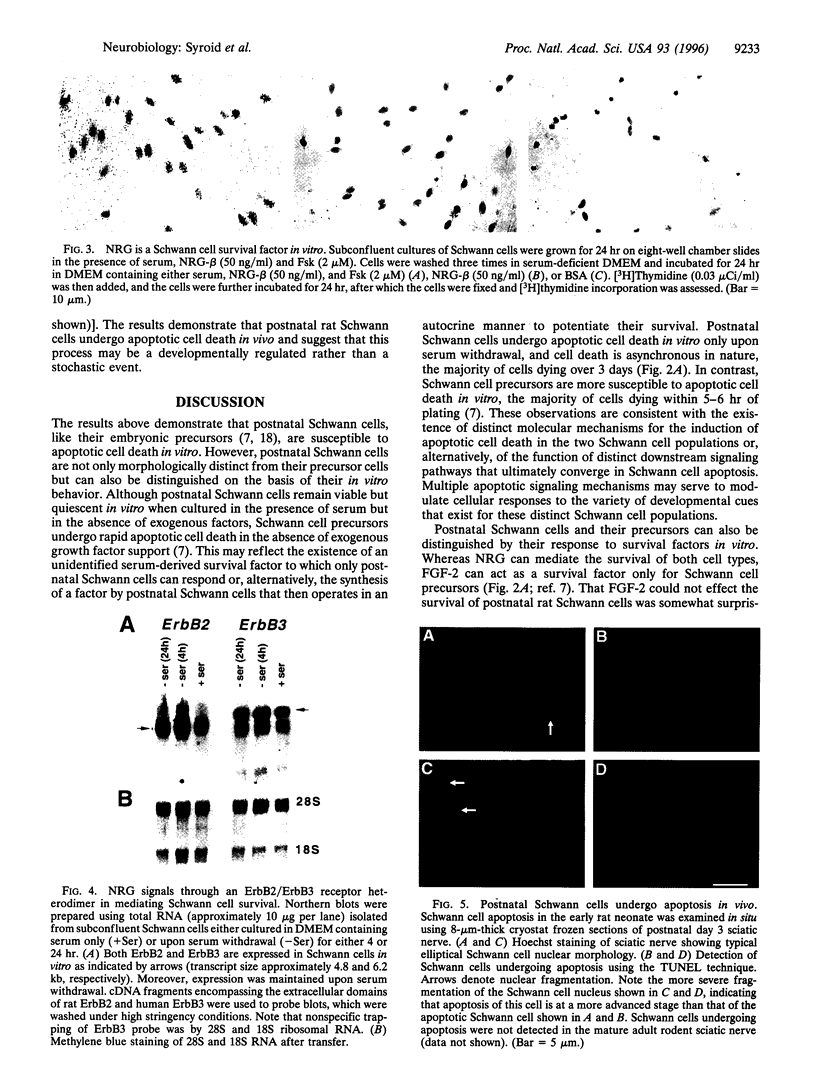
The development of Schwann cells, the myelin-forming glial cells of the vertebrate peripheral nervous system, involves a neonatal phase of proliferation in which cells migrate along and segregate newly formed axons. Withdrawal from the cell cycle, around postnatal days 2-4 in rodents, initiates terminal differentiation to the myelinating state. During this time, Schwann cell number is subject to stringent regulation such that within the first postnatal week, axons and myelinating Schwann cells attain the one-to-one relationship characteristic of the mature nerve. The mechanisms that underly this developmental control remain largely undefined. In this report, we examine the role of apoptosis in the determination of postnatal Schwann cell number. We find that Schwann cells isolated from postnatal day 3 rat sciatic nerve undergo apoptosis in vitro upon serum withdrawal and that Schwann cell death can be prevented by beta forms of neuregulin (NRG-beta) but not by fibroblast growth factor 2 or platelet-derived growth factors AA and BB. This NRG-beta-mediated Schwann cell survival is apparently transduced through an ErbB2/ErbB3 receptor heterodimer. We also provide evidence that postnatal Schwann cells undergo developmentally regulated apoptosis in vivo. Together with other recent findings, these results suggest that Schwann cell apoptosis may play an important role in peripheral nerve development and that Schwann cell survival may be regulated by access to axonally derived NRG.
Full text
PDF

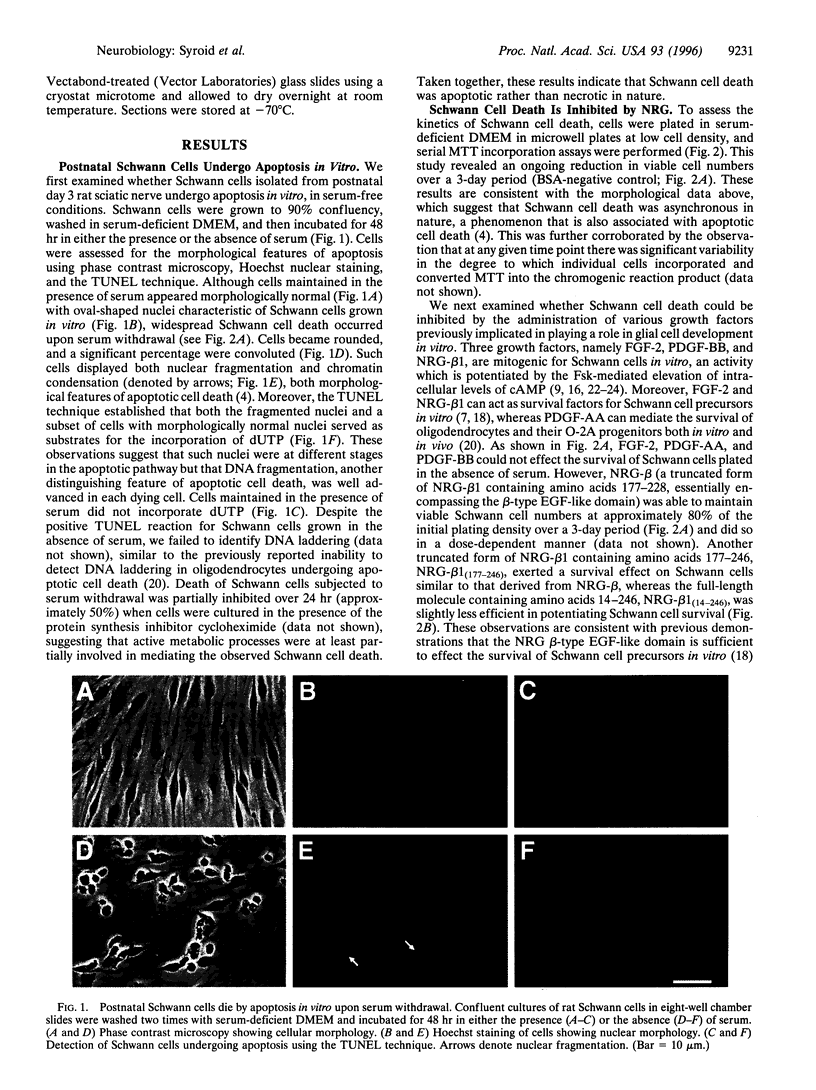

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barde Y. A. Trophic factors and neuronal survival. Neuron. 1989 Jun;2(6):1525–1534. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barres B. A., Hart I. K., Coles H. S., Burne J. F., Voyvodic J. T., Richardson W. D., Raff M. C. Cell death and control of cell survival in the oligodendrocyte lineage. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):31–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90531-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barres B. A., Raff M. C. Control of oligodendrocyte number in the developing rat optic nerve. Neuron. 1994 May;12(5):935–942. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P., Fields K. L., Raff M. C. Studies on cultured rat Schwann cells. I. Establishment of purified populations from cultures of peripheral nerve. Brain Res. 1979 Apr 6;165(1):105–118. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. J., Asbury A. K. Schwann cell proliferation in the postnatal mouse: timing and topography. Exp Neurol. 1981 Oct;74(1):170–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(81)90157-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway K. L., 3rd, Burden S. J. Neuregulins and their receptors. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995 Oct;5(5):606–612. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(95)80065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. B., Stroobant P. Platelet-derived growth factors and fibroblast growth factors are mitogens for rat Schwann cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1353–1360. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong Z., Brennan A., Liu N., Yarden Y., Lefkowitz G., Mirsky R., Jessen K. R. Neu differentiation factor is a neuron-glia signal and regulates survival, proliferation, and maturation of rat Schwann cell precursors. Neuron. 1995 Sep;15(3):585–596. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccleston P. A. Regulation of Schwann cell proliferation: mechanisms involved in peripheral nerve development. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Mar;199(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90455-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavrieli Y., Sherman Y., Ben-Sasson S. A. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):493–501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerschenson L. E., Rotello R. J. Apoptosis: a different type of cell death. FASEB J. 1992 Apr;6(7):2450–2455. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.7.1563596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy M., Reddy U. R., Pleasure D. Platelet-derived growth factor and regulation of Schwann cell proliferation in vivo. J Neurosci Res. 1992 Feb;31(2):254–262. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490310206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessen K. R., Brennan A., Morgan L., Mirsky R., Kent A., Hashimoto Y., Gavrilovic J. The Schwann cell precursor and its fate: a study of cell death and differentiation during gliogenesis in rat embryonic nerves. Neuron. 1994 Mar;12(3):509–527. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessen K. R., Mirsky R. Schwann cells: early lineage, regulation of proliferation and control of myelin formation. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1992 Oct;2(5):575–581. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(92)90021-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke G. E., Brockes J. P. Identification and purification of glial growth factor. J Neurosci. 1984 Jan;4(1):75–83. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-01-00075.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke G. Neuregulins in development. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1996 Apr;7(4):247–262. doi: 10.1006/mcne.1996.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi A. D., Bunge R. P., Lofgren J. A., Meima L., Hefti F., Nikolics K., Sliwkowski M. X. The influence of heregulins on human Schwann cell proliferation. J Neurosci. 1995 Feb;15(2):1329–1340. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-02-01329.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing A., Behringer R. R., Hammang J. P., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Lemke G. P0 promoter directs expression of reporter and toxin genes to Schwann cells of transgenic mice. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):507–520. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90279-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim R. W. Cell death during development of the nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:453–501. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkas-Kramarski R., Eilam R., Spiegler O., Lavi S., Liu N., Chang D., Wen D., Schwartz M., Yarden Y. Brain neurons and glial cells express Neu differentiation factor/heregulin: a survival factor for astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 27;91(20):9387–9391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.20.9387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Abney E., Brockes J. P., Hornby-Smith A. Schwann cell growth factors. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):813–822. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah N. M., Marchionni M. A., Isaacs I., Stroobant P., Anderson D. J. Glial growth factor restricts mammalian neural crest stem cells to a glial fate. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):349–360. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart H. J., Eccleston P. A., Jessen K. R., Mirsky R. Interaction between cAMP elevation, identified growth factors, and serum components in regulating Schwann cell growth. J Neurosci Res. 1991 Oct;30(2):346–352. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490300210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachtenberg J. T., Thompson W. J. Schwann cell apoptosis at developing neuromuscular junctions is regulated by glial growth factor. Nature. 1996 Jan 11;379(6561):174–177. doi: 10.1038/379174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartanian T., Corfas G., Li Y., Fischbach G. D., Stefansson K. A role for the acetylcholine receptor-inducing protein ARIA in oligodendrocyte development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 22;91(24):11626–11630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.24.11626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmaster G., Lemke G. Cell-specific cyclic AMP-mediated induction of the PDGF receptor. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):915–920. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08189.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]