Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOCH H., SEGAL W. Viability and multiplication of vaccines in immunization against tuberculosis. Am Rev Tuberc. 1955 Feb;71(2):228–248. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1955.71.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOS R. J. Effect of metabolic factors on the susceptibility of albino mice to experimental tuberculosis. J Exp Med. 1955 Jan 1;101(1):59–84. doi: 10.1084/jem.101.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBLE R. H., HEDGECOCK L. W. Antagonism of chemotherapeutic activity of p-aminosalicylic acid in experimental tuberculosis by p-aminobenzoic acid. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Dec;84(3):526–528. doi: 10.3181/00379727-84-20700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
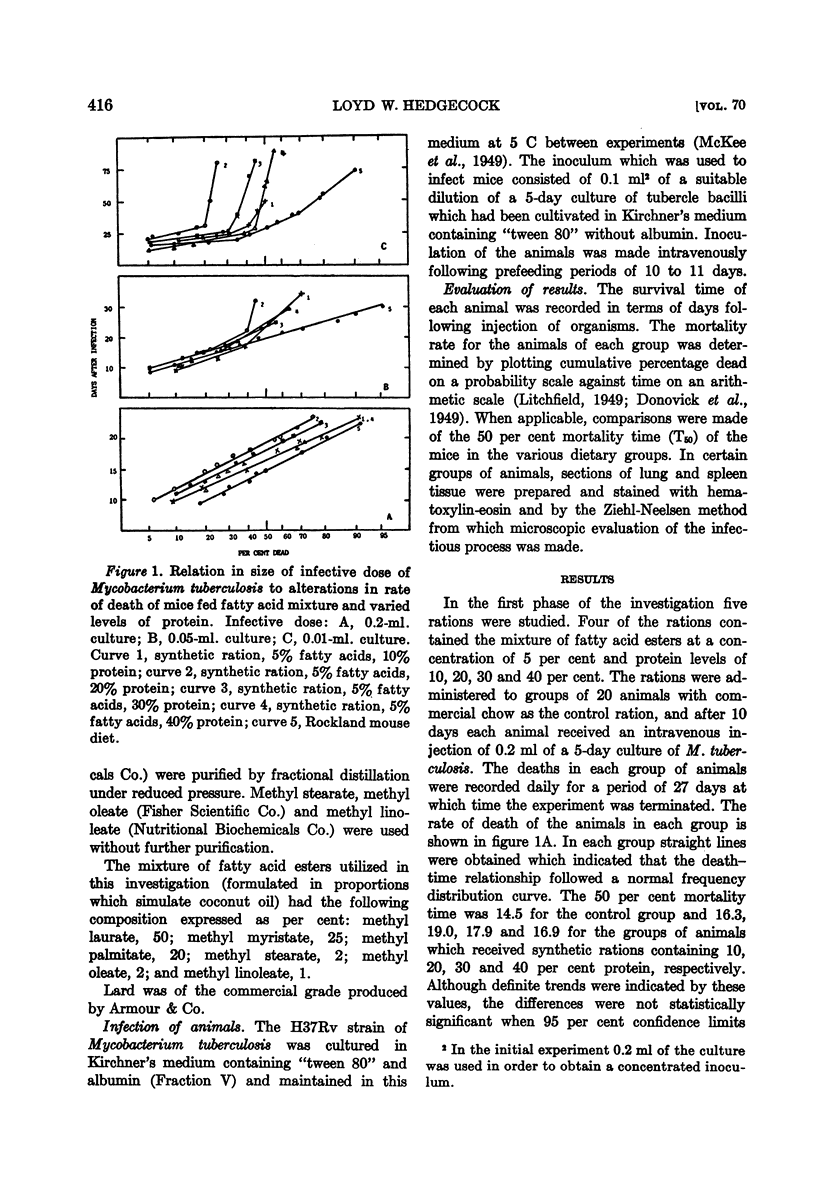
- LITCHFIELD J. T., Jr A method for rapid graphic solution of time-per cent effect curves. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1949 Dec;97(4):399-408, 3 tab. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesson L. G. A MODIFICATION OF THE OSBORNEMENDEL SALT MIXTURE CONTAINING ONLY INORGANIC CONSTITUENTS. Science. 1932 Mar 25;75(1943):339–340. doi: 10.1126/science.75.1943.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



