Abstract
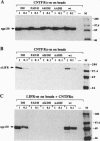
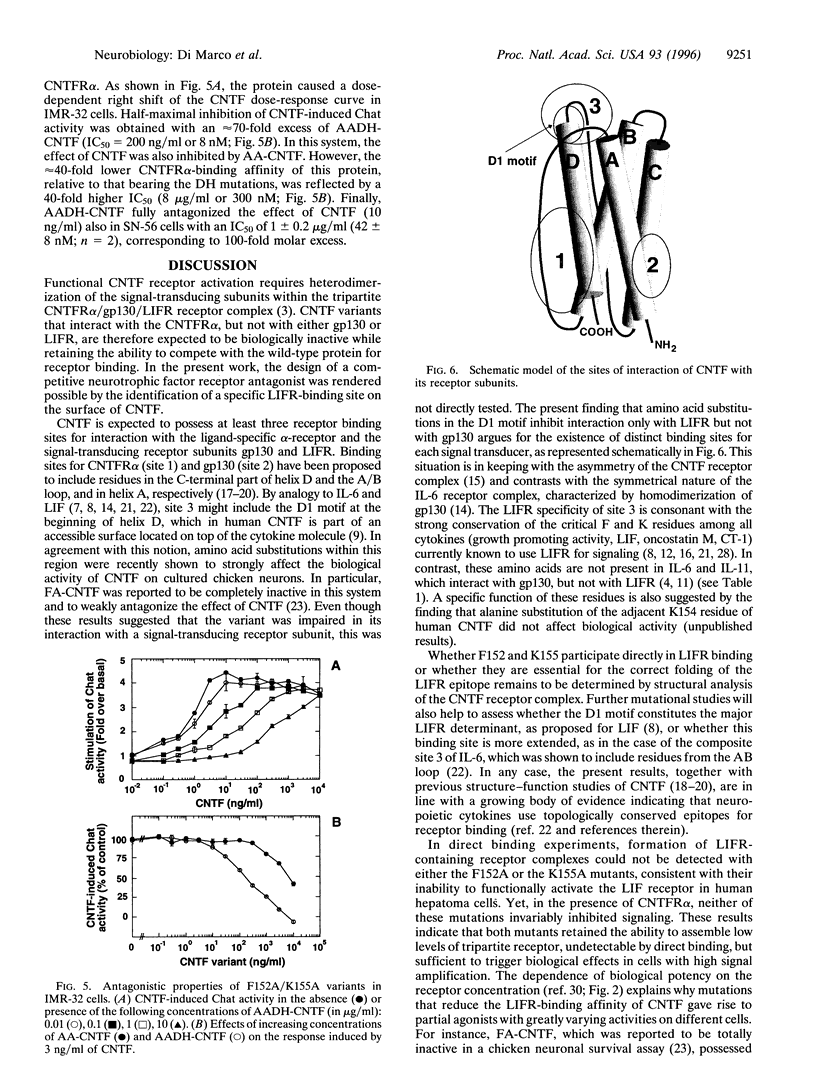
Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) drives the sequential assembly of a receptor complex containing the ligand-specific alpha-receptor subunit (CNTFR alpha) and the signal transducers gp130 and leukemia inhibitory factor receptor-beta (LIFR). The D1 structural motif, located at the beginning of the D-helix of human CNTF, contains two amino acid residues, F152 and K155, which are conserved among all cytokines that signal through LIFR. The functional importance of these residues was assessed by alanine mutagenesis. Substitution of either F152 or K155 with alanine was found to specifically inhibit cytokine interaction with LIFR without affecting binding to CNTFR alpha or gp130. The resulting variants behaved as partial agonists with varying degrees of residual bioactivity in different cell-based assays. Simultaneous alanine substitution of both F152 and K155 totally abolished biological activity. Combining these mutations with amino acid substitutions in the D-helix, which enhance binding affinity for the CNTFR alpha, gave rise to a potent competitive CNTF receptor antagonist. This protein constitutes a new tool for studies of CNTF function in normal physiology and disease.
Full text
PDF
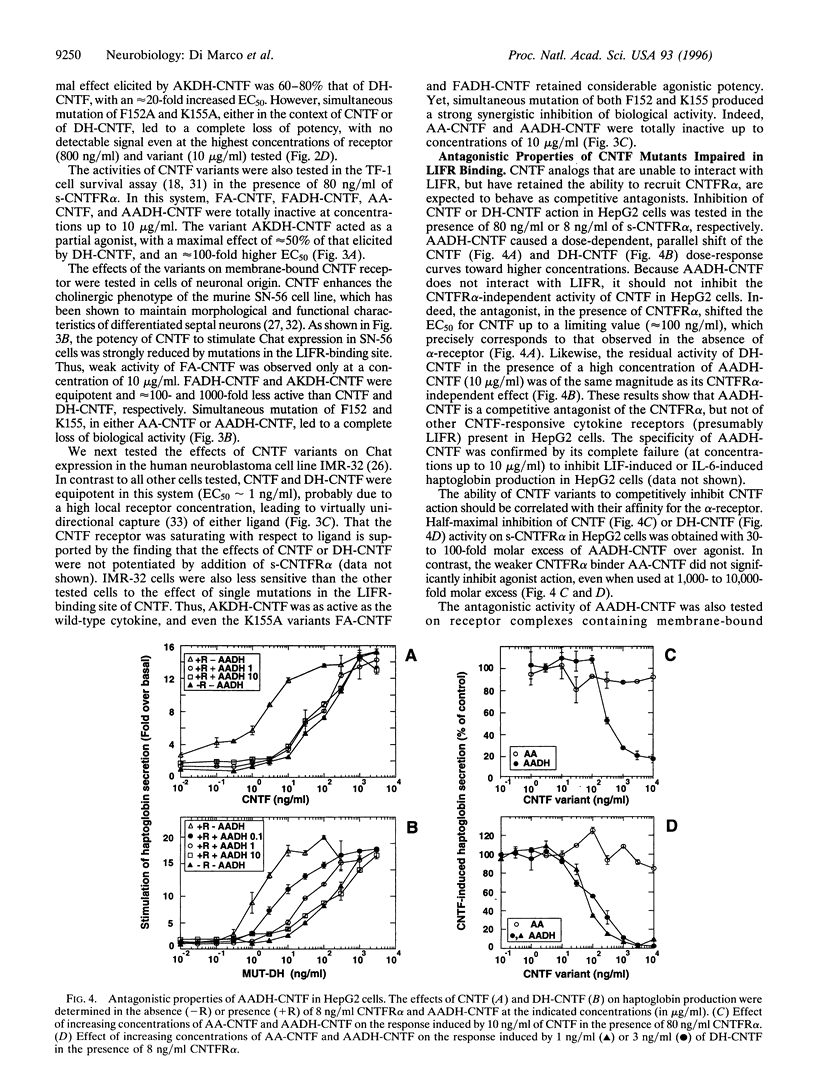

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann G., Lowman H. B., Mercado M., Wells J. A. The stoichiometry of growth hormone-binding protein complexes in human plasma: comparison with cell surface receptors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994 May;78(5):1113–1118. doi: 10.1210/jcem.78.5.8175967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Ziegler S. F., Mosley B., Morella K. K., Pajovic S., Gearing D. P. Reconstitution of the response to leukemia inhibitory factor, oncostatin M, and ciliary neurotrophic factor in hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8414–8417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Neuropoietic cytokines in the hematopoietic fold. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):197–208. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90258-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berse B., Blusztajn J. K. Coordinated up-regulation of choline acetyltransferase and vesicular acetylcholine transporter gene expression by the retinoic acid receptor alpha, cAMP, and leukemia inhibitory factor/ciliary neurotrophic factor signaling pathways in a murine septal cell line. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 22;270(38):22101–22104. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.38.22101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulay J. L., Paul W. E. Hematopoietin sub-family classification based on size, gene organization and sequence homology. Curr Biol. 1993 Sep 1;3(9):573–581. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brakenhoff J. P., de Hon F. D., Fontaine V., ten Boekel E., Schooltink H., Rose-John S., Heinrich P. C., Content J., Aarden L. A. Development of a human interleukin-6 receptor antagonist. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):86–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciapponi L., Graziani R., Paonessa G., Lahm A., Ciliberto G., Savino R. Definition of a composite binding site for gp130 in human interleukin-6. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 29;270(52):31249–31254. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.52.31249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Serio A., Graziani R., Laufer R., Ciliberto G., Paonessa G. In vitro binding of ciliary neurotrophic factor to its receptors: evidence for the formation of an IL-6-type hexameric complex. J Mol Biol. 1995 Dec 15;254(5):795–800. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChiara T. M., Vejsada R., Poueymirou W. T., Acheson A., Suri C., Conover J. C., Friedman B., McClain J., Pan L., Stahl N. Mice lacking the CNTF receptor, unlike mice lacking CNTF, exhibit profound motor neuron deficits at birth. Cell. 1995 Oct 20;83(2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuh G., Cunningham B. C., Fukunaga R., Nagata S., Goeddel D. V., Wells J. A. Rational design of potent antagonists to the human growth hormone receptor. Science. 1992 Jun 19;256(5064):1677–1680. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5064.1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., Ziegler S. F., Comeau M. R., Friend D., Thoma B., Cosman D., Park L., Mosley B. Proliferative responses and binding properties of hematopoietic cells transfected with low-affinity receptors for leukemia inhibitory factor, oncostatin M, and ciliary neurotrophic factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):1119–1123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemsley A., Arnheim N., Toney M. D., Cortopassi G., Galas D. J. A simple method for site-directed mutagenesis using the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6545–6551. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson K. R., Vernallis A. B., Heath J. K. Characterization of the receptor binding sites of human leukemia inhibitory factor and creation of antagonists. J Biol Chem. 1996 May 17;271(20):11971–11978. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.20.11971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Nakayama C., Kikuchi K., Kimura T., Ishige Y., Ito A., Kanaoka M., Noguchi H. D1 cap region involved in the receptor recognition and neural cell survival activity of human ciliary neurotrophic factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 12;92(19):8579–8583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., McClain J., Barrezueta N. X., Aldrich T. H., Pan L., Li Y., Wiegand S. J., Friedman B., Davis S., Yancopoulos G. D. The alpha component of the CNTF receptor is required for signaling and defines potential CNTF targets in the adult and during development. Neuron. 1993 Jan;10(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90245-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Akira S., Narazaki M., Taga T. Interleukin-6 family of cytokines and gp130. Blood. 1995 Aug 15;86(4):1243–1254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüttgen A., Grötzinger J., Kurapkat G., Weis J., Simon R., Thier M., Schröder M., Heinrich P., Wollmer A., Comeau M. Human ciliary neurotrophic factor: a structure-function analysis. Biochem J. 1995 Jul 1;309(Pt 1):215–220. doi: 10.1042/bj3090215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. J., Hammond D. N., Large T. H., Wainer B. H. Immortalized young adult neurons from the septal region: generation and characterization. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1990 Mar 1;52(1-2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(90)90238-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Parent A. S., Cachianes G., Esch F., Coulombe J. N., Nikolics K., Eckenstein F. P., Nishi R. Cloning, expression during development, and evidence for release of a trophic factor for ciliary ganglion neurons. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):1045–1053. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., Sendtner M., Smith A. Essential function of LIF receptor in motor neurons. Nature. 1995 Dec 14;378(6558):724–727. doi: 10.1038/378724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald N. Q., Panayotatos N., Hendrickson W. A. Crystal structure of dimeric human ciliary neurotrophic factor determined by MAD phasing. EMBO J. 1995 Jun 15;14(12):2689–2699. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Everdeen D., Liten A., Somogyi R., Acheson A. Recombinant human CNTF receptor alpha: production, binding stoichiometry, and characterization of its activity as a diffusible factor. Biochemistry. 1994 May 17;33(19):5813–5818. doi: 10.1021/bi00185a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Radziejewska E., Acheson A., Pearsall D., Thadani A., Wong V. Exchange of a single amino acid interconverts the specific activity and gel mobility of human and rat ciliary neurotrophic factors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):19000–19003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Radziejewska E., Acheson A., Somogyi R., Thadani A., Hendrickson W. A., McDonald N. Q. Localization of functional receptor epitopes on the structure of ciliary neurotrophic factor indicates a conserved, function-related epitope topography among helical cytokines. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 9;270(23):14007–14014. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.23.14007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paonessa G., Graziani R., De Serio A., Savino R., Ciapponi L., Lahm A., Salvati A. L., Toniatti C., Ciliberto G. Two distinct and independent sites on IL-6 trigger gp 130 dimer formation and signalling. EMBO J. 1995 May 1;14(9):1942–1951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., King K. L., Shaw K. J., Luis E., Rullamas J., Luoh S. M., Darbonne W. C., Knutzon D. S., Yen R., Chien K. R. Expression cloning of cardiotrophin 1, a cytokine that induces cardiac myocyte hypertrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):1142–1146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.1142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Shaw K. J., Swanson T. A., Moore M. W., Shelton D. L., Zioncheck K. A., Rosenthal A., Taga T., Paoni N. F., Wood W. I. Cardiotrophin-1. Biological activities and binding to the leukemia inhibitory factor receptor/gp130 signaling complex. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 5;270(18):10915–10922. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.18.10915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson R. C., Grey L. M., Staunton D., Vankelecom H., Vernallis A. B., Moreau J. F., Stuart D. I., Heath J. K., Jones E. Y. The crystal structure and biological function of leukemia inhibitory factor: implications for receptor binding. Cell. 1994 Jul 1;77(7):1101–1116. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90449-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggio I., Gloaguen I., Laufer R. Functional phage display of ciliary neurotrophic factor. Gene. 1995 Jan 11;152(1):35–39. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)00733-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggio I., Gloaguen I., Poiana G., Laufer R. CNTF variants with increased biological potency and receptor selectivity define a functional site of receptor interaction. EMBO J. 1995 Jul 3;14(13):3045–3054. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07307.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggio I., Paonessa G., Gloaguen I., Graziani R., De Serio A., Laufer R. Nonradioactive receptor binding assay for ciliary neurotrophic factor. Anal Biochem. 1994 Sep;221(2):387–391. doi: 10.1006/abio.1994.1430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savino R., Ciapponi L., Lahm A., Demartis A., Cabibbo A., Toniatti C., Delmastro P., Altamura S., Ciliberto G. Rational design of a receptor super-antagonist of human interleukin-6. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 15;13(24):5863–5870. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06931.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sendtner M., Carroll P., Holtmann B., Hughes R. A., Thoenen H. Ciliary neurotrophic factor. J Neurobiol. 1994 Nov;25(11):1436–1453. doi: 10.1002/neu.480251110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporeno E., Savino R., Ciapponi L., Paonessa G., Cabibbo A., Lahm A., Pulkki K., Sun R. X., Toniatti C., Klein B. Human interleukin-6 receptor super-antagonists with high potency and wide spectrum on multiple myeloma cells. Blood. 1996 Jun 1;87(11):4510–4519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Yancopoulos G. D. The tripartite CNTF receptor complex: activation and signaling involves components shared with other cytokines. J Neurobiol. 1994 Nov;25(11):1454–1466. doi: 10.1002/neu.480251111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]