Abstract
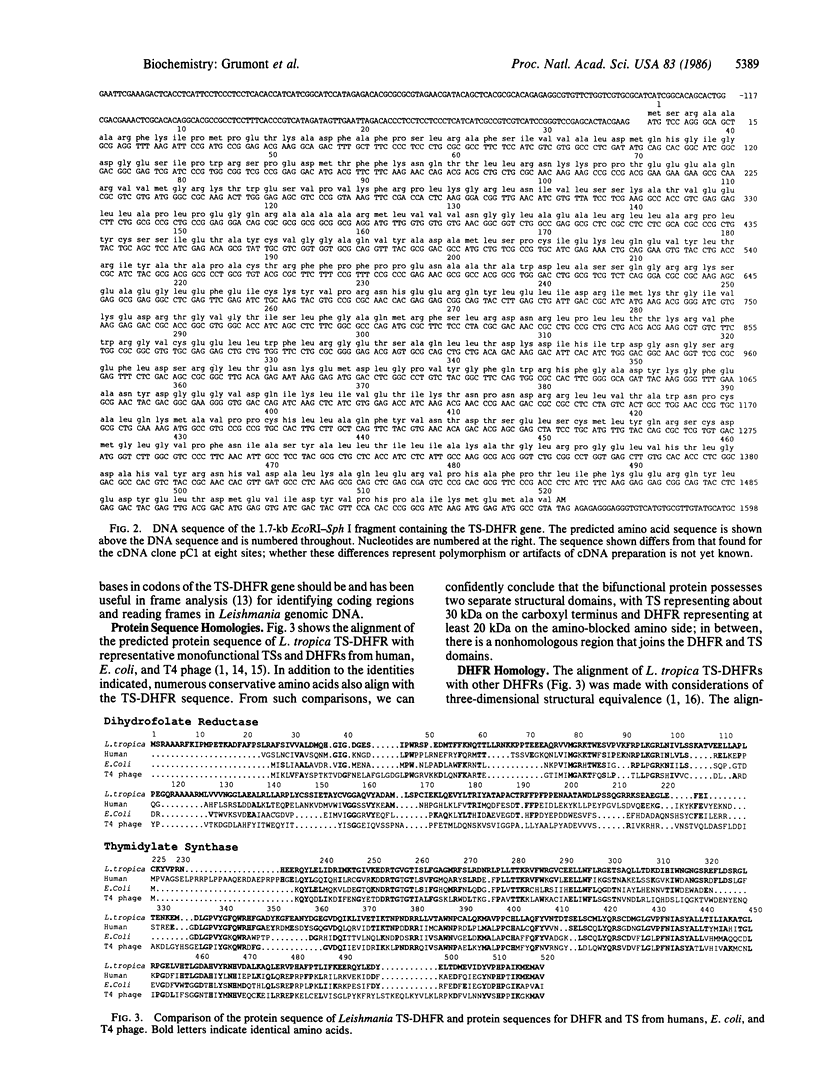
In protozoa, thymidylate synthase (TS; EC 2.1.1.45) and dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR; EC 1.5.1.3) exist as a bifunctional protein. Full-length cDNA and genomic DNA clones encoding the bifunctional TS-DHFR from Leishmania tropica have been isolated, characterized, and sequenced. There are no intervening sequences within the coding region for TS-DHFR, and the G+C content is high, with a strong bias for codons possessing guanine or cytosine in the third base. From the predicted protein sequence for TS-DHFR, we conclude that the enzymes exist as separate structural domains with DHFR located at the amino terminus and TS at the carboxyl terminus; in between, there is a junctional peptide predicted to consist of a random coil flanked by two alpha-helices that corresponds to the site of a putative gene fusion. Comparison of the predicted amino acid sequence of L. tropica TS-DHFR with sequences of the monofunctional enzymes from other sources shows that the TS domain is much more conserved than is the DHFR domain and that both enzymes are more related to their monofunctional counterparts in vertebrates than in prokaryotes. Most of the recognized elements of secondary structure of other DHFRs, as ascertained by x-ray crystallography, are found in the predicted structure of the DHFR domain of the bifunctional protein.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aull J. L., Loeble R. B., Dunlap R. B. The carboxypeptidase-dependent inactivation of thymidylate synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1167–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Findlay P. R., Johnson M. W. The relationship between base composition and codon usage in bacterial genes and its use for the simple and reliable identification of protein-coding sequences. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferone R., Roland S. Dihydrofolate reductase: thymidylate synthase, a bifunctional polypeptide from Crithidia fasciculata. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5802–5806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett C. E., Coderre J. A., Meek T. D., Garvey E. P., Claman D. M., Beverley S. M., Santi D. V. A bifunctional thymidylate synthetase-dihydrofolate reductase in protozoa. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Apr;11:257–265. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey E. P., Santi D. V. Limited proteolysis of the bifunctional thymidylate synthase-dihydrofolate reductase from Leishmania tropica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7188–7192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Hillcoat B. L. Interaction of thymidylate synthetase and dihydrofolate reductase enzymes in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 1974 Jul;34(7):1619–1626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maley G. F., Maley F., Baugh C. M. Studies on identifying the folylpolyglutamate binding sites of Lactobacillus casei thymidylate synthetase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Jul;216(2):551–558. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90244-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon F. D., Kirschner M. W., Caput D. Homologies in both primary and secondary structure between nuclear envelope and intermediate filament proteins. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):463–468. doi: 10.1038/319463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek T. D., Garvey E. P., Santi D. V. Purification and characterization of the bifunctional thymidylate synthetase-dihydrofolate reductase from methotrexate-resistant Leishmania tropica. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):678–686. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myoda T. T., Funanage V. L. Coregulation of dihydrofolate reductase and thymidylate synthase B in bacillus subtilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 20;824(2):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purohit S., Mathews C. K. Nucleotide sequence reveals overlap between T4 phage genes encoding dihydrofolate reductase and thymidylate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6261–6266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sather S., Agabian N. A 5' spliced leader is added in trans to both alpha- and beta-tubulin transcripts in Trypanosoma brucei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5695–5699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeishi K., Kaneda S., Ayusawa D., Shimizu K., Gotoh O., Seno T. Nucleotide sequence of a functional cDNA for human thymidylate synthase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2035–2043. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volz K. W., Matthews D. A., Alden R. A., Freer S. T., Hansch C., Kaufman B. T., Kraut J. Crystal structure of avian dihydrofolate reductase containing phenyltriazine and NADPH. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2528–2536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washtien W. L., Grumont R., Santi D. V. DNA amplification in antifolate-resistant Leishmania. The thymidylate synthase-dihydrofolate reductase gene and abundant mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):7809–7812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



