Abstract
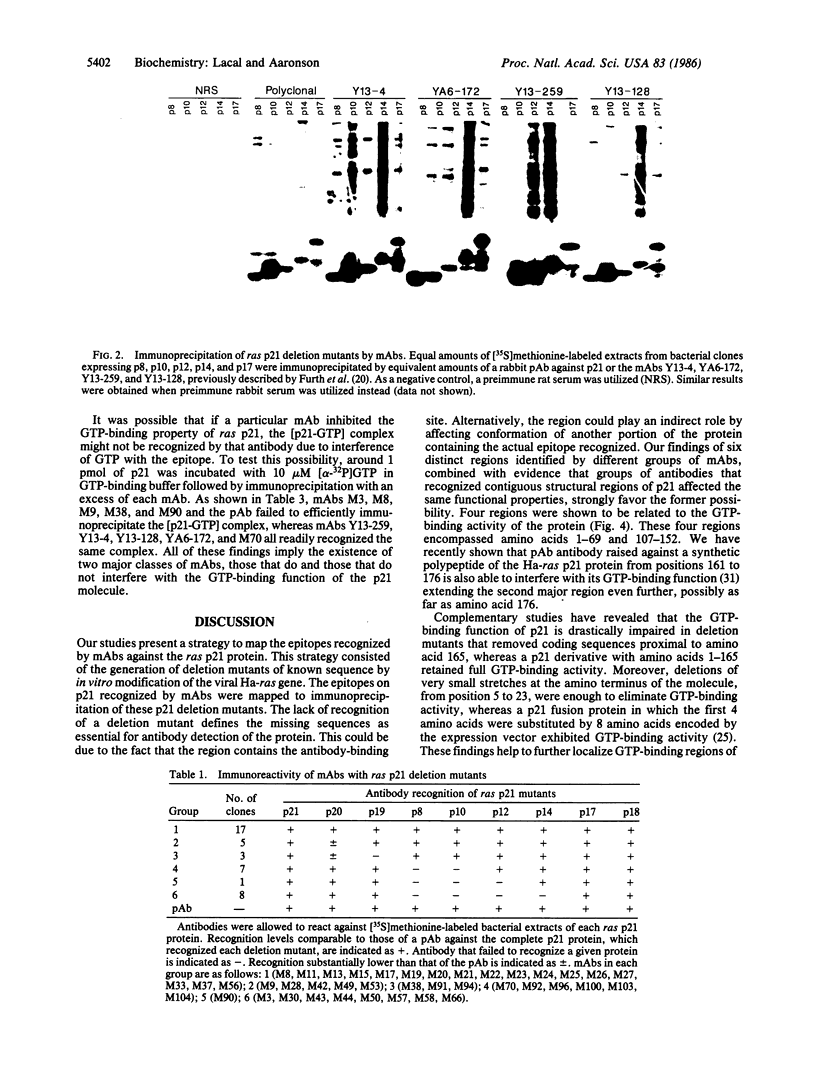
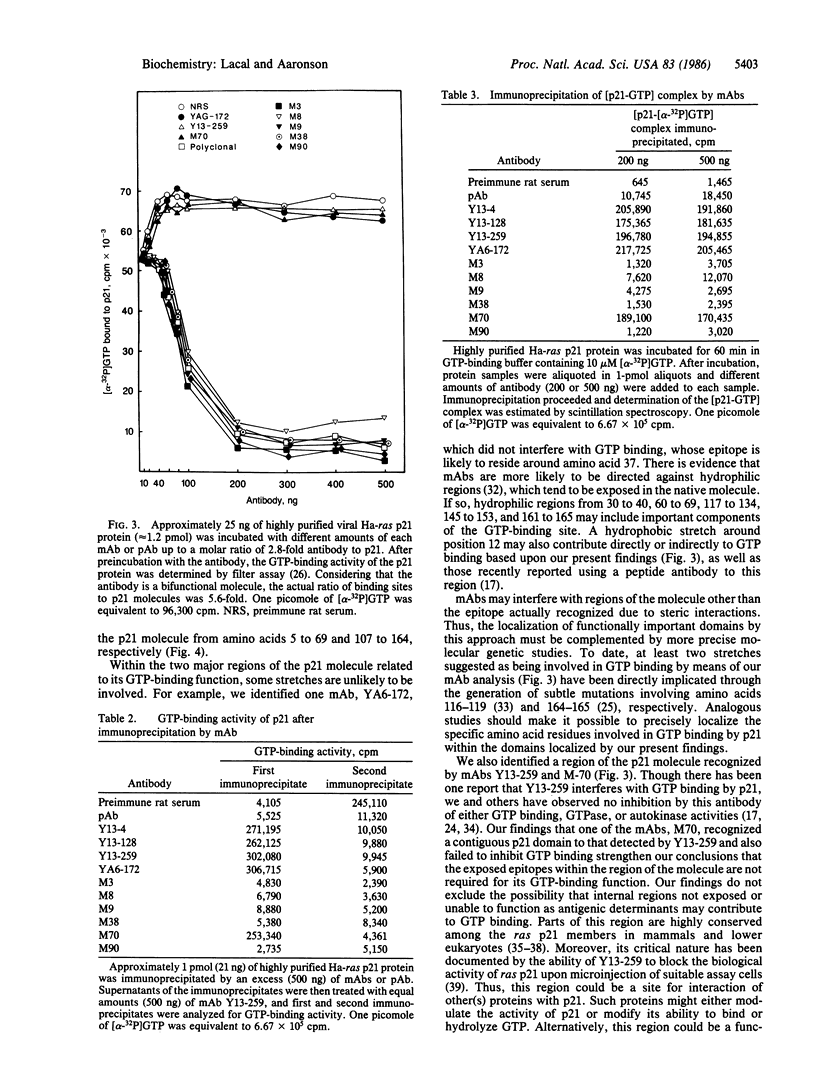
Deletion mutants of the viral Harvey ras oncogene were generated by removing different lengths of the gene from either the amino or the carboxyl terminus. The deletion mutants, ras p21 expressed in Escherichia coli, yielded proteins of approximately 8, 10, 12, 14, 17, 18, 19, and 20 kDa. These proteins were utilized to identify epitopes recognized by a series of recently generated monoclonal antibodies as well as some previously reported monoclonal antibodies. Monoclonal antibodies that inhibited GTP binding, a major biochemical activity of the p21 protein, recognized two major regions of the protein. These regions were localized from amino acids 5 to 69 and 107 to 164, respectively, and were separated by another stretch from residues 70 to 106, whose antigenic determinants were not directly involved in GTP binding. Thus, the mapping of epitopes within the p21 molecule recognized by monoclonal antibodies has made it possible to localize important functional regions within the ras p21 molecule.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark R., Wong G., Arnheim N., Nitecki D., McCormick F. Antibodies specific for amino acid 12 of the ras oncogene product inhibit GTP binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5280–5284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowl R., Seamans C., Lomedico P., McAndrew S. Versatile expression vectors for high-level synthesis of cloned gene products in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90200-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeo-Jones D., Scolnick E. M., Koller R., Dhar R. ras-Related gene sequences identified and isolated from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):707–709. doi: 10.1038/306707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel T., Der C. J., Cooper G. M. Activation of ras genes in human tumors does not affect localization, modification, or nucleotide binding properties of p21. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Davis L. J., Fleurdelys B., Scolnick E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the p21 products of the transforming gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and of the cellular ras gene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.294-304.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Sigal I. S., Poe M., Scolnick E. M. Intrinsic GTPase activity distinguishes normal and oncogenic ras p21 molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5704–5708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliday K. R. Regional homology in GTP-binding proto-oncogene products and elongation factors. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1983;9(6):435–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori S., Ulsh L. S., Halliday K., Shih T. Y. Biochemical properties of a highly purified v-rasH p21 protein overproduced in Escherichia coli and inhibition of its activities by a monoclonal antibody. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1449–1455. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Simon M. I., Teplow D. B., Robishaw J. D., Gilman A. G. Homologies between signal transducing G proteins and ras gene products. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):860–862. doi: 10.1126/science.6436980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacal J. C., Aaronson S. A. Monoclonal antibody Y13-259 recognizes an epitope of the p21 ras molecule not directly involved in the GTP-binding activity of the protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1002–1009. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacal J. C., Anderson P. S., Aaronson S. A. Deletion mutants of Harvey ras p21 protein reveal the absolute requirement of at least two distant regions for GTP-binding and transforming activities. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):679–687. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04267.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacal J. C., Santos E., Notario V., Barbacid M., Yamazaki S., Kung H., Seamans C., McAndrew S., Crowl R. Expression of normal and transforming H-ras genes in Escherichia coli and purification of their encoded p21 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5305–5309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacal J. C., Srivastava S. K., Anderson P. S., Aaronson S. A. Ras p21 proteins with high or low GTPase activity can efficiently transform NIH/3T3 cells. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):609–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90270-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leberman R., Egner U. Homologies in the primary structure of GTP-binding proteins: the nucleotide-binding site of EF-Tu and p21. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):339–341. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01808.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochrie M. A., Hurley J. B., Simon M. I. Sequence of the alpha subunit of photoreceptor G protein: homologies between transducin, ras, and elongation factors. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):96–99. doi: 10.1126/science.3856323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manne V., Bekesi E., Kung H. F. Ha-ras proteins exhibit GTPase activity: point mutations that activate Ha-ras gene products result in decreased GTPase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):376–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F., Clark B. F., la Cour T. F., Kjeldgaard M., Norskov-Lauritsen L., Nyborg J. A model for the tertiary structure of p21, the product of the ras oncogene. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):78–82. doi: 10.1126/science.3898366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Capon D. J., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Comparative biochemical properties of normal and activated human ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):644–649. doi: 10.1038/310644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy L. S., Smith M. R., Stacey D. W. Requirement for ras proto-oncogene function during serum-stimulated growth of NIH 3T3 cells. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):241–243. doi: 10.1038/313241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuman-Silberberg F. S., Schejter E., Hoffmann F. M., Shilo B. Z. The Drosophila ras oncogenes: structure and nucleotide sequence. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1027–1033. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90437-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowinski R. C., Lostrom M. E., Tam M. R., Stone M. R., Burnette W. N. The isolation of hybrid cell lines producing monoclonal antibodies against the p15(E) protein of ecotropic murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poe M., Scolnick E. M., Stein R. B. Viral Harvey ras p21 expressed in Escherichia coli purifies as a binary one-to-one complex with GDP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):3906–3909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., Kataoka T., Fasano O., Goldfarb M., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genes in S. cerevisiae encoding proteins with domains homologous to the mammalian ras proteins. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):607–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Reynolds R. K., Santos E., Barbacid M. A point mutation is responsible for the acquisition of transforming properties by the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):149–152. doi: 10.1038/300149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reymond C. D., Gomer R. H., Mehdy M. C., Firtel R. A. Developmental regulation of a Dictyostelium gene encoding a protein homologous to mammalian ras protein. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Papageorge A. G., Shih T. Y. Guanine nucleotide-binding activity as an assay for src protein of rat-derived murine sarcoma viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5355–5359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Papageorge A. G., Stokes P. E., Weeks M. O., Scolnick E. M. Guanine nucleotide-binding and autophosphorylating activities associated with the p21src protein of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):686–691. doi: 10.1038/287686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Stokes P. E., Smythers G. W., Dhar R., Oroszlan S. Characterization of the phosphorylation sites and the surrounding amino acid sequences of the p21 transforming proteins coded for by the Harvey and Kirsten strains of murine sarcoma viruses. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11767–11773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K., Birnbaum D., Ruley M. A., Fasano O., Suard Y., Edlund L., Taparowsky E., Goldfarb M., Wigler M. Structure of the Ki-ras gene of the human lung carcinoma cell line Calu-1. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):497–500. doi: 10.1038/304497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava S. K., Lacal J. C., Reynolds S. H., Aaronson S. A. Antibody of predetermined specificity to a carboxy-terminal region of H-ras gene products inhibits their guanine nucleotide-binding function. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3316–3319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava S. K., Yuasa Y., Reynolds S. H., Aaronson S. A. Effects of two major activating lesions on the structure and conformation of human ras oncogene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):38–42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet R. W., Yokoyama S., Kamata T., Feramisco J. R., Rosenberg M., Gross M. The product of ras is a GTPase and the T24 oncogenic mutant is deficient in this activity. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):273–275. doi: 10.1038/311273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabin C. J., Bradley S. M., Bargmann C. I., Weinberg R. A., Papageorge A. G., Scolnick E. M., Dhar R., Lowy D. R., Chang E. H. Mechanism of activation of a human oncogene. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):143–149. doi: 10.1038/300143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Nukada T., Nishikawa Y., Sugimoto K., Suzuki H., Takahashi H., Noda M., Haga T., Ichiyama A., Kangawa K. Primary structure of the alpha-subunit of transducin and its relationship to ras proteins. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):242–245. doi: 10.1038/315242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temeles G. L., Gibbs J. B., D'Alonzo J. S., Sigal I. S., Scolnick E. M. Yeast and mammalian ras proteins have conserved biochemical properties. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):700–703. doi: 10.1038/313700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulsh L. S., Shih T. Y. Metabolic turnover of human c-rasH p21 protein of EJ bladder carcinoma and its normal cellular and viral homologs. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1647–1652. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatsunami K., Khorana H. G. GTPase of bovine rod outer segments: the amino acid sequence of the alpha subunit as derived from the cDNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4316–4320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuasa Y., Srivastava S. K., Dunn C. Y., Rhim J. S., Reddy E. P., Aaronson S. A. Acquisition of transforming properties by alternative point mutations within c-bas/has human proto-oncogene. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):775–779. doi: 10.1038/303775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




