Abstract
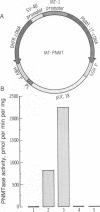
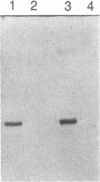
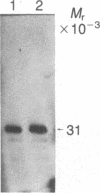
We report here the isolation of a cDNA clone containing the full coding region of bovine phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PNMTase, EC 2.1.1.28, S-adenosyl-L-methionine:phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase). The complete nucleotide sequence of the cDNA has been determined, and the amino acid sequence of PNMTase deduced. Cultured cells transfected with an expression vector containing this cDNA produced high levels of PNMTase enzymatic activity. Antibodies specific for tyrosine hydroxylase [EC 1.14.16.2, tyrosine 3-monooxygenase; L-tyrosine, tetrahydrobiopterine: oxygen oxidoreductase (3-hydroxylating)], the first enzyme in the catecholamine pathway, possess a striking affinity for the PNMTase protein synthesized in vitro. Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequence of bovine PNMTase to rat tyrosine hydroxylase reveals that PNMTase shares significant homology with tyrosine hydroxylase and supports previous protein and immunological data suggesting that the catecholamine biosynthetic enzymes are structurally related.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELROD J. Purification and properties of phenylethanolamine-N-methyl transferase. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1657–1660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohn M. C., Goldstein M., Black I. B. Expression of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase in rat sympathetic ganglia and extra-adrenal chromaffin tissue. Dev Biol. 1982 Feb;89(2):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90319-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Warren R., Sarthy A., Palmiter R. D. Regulation of metallothionein--thymidine kinase fusion plasmids injected into mouse eggs. Nature. 1982 Mar 4;296(5852):39–42. doi: 10.1038/296039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Sharp P. A. SV40 DNA transfection of cells in suspension: analysis of efficiency of transcription and translation of T-antigen. Gene. 1981 Mar;13(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobberstein B., Garoff H., Warren G., Robinson P. J. Cell-free synthesis and membrane insertion of mouse H-2Dd histocompatibility antigen and beta 2-microglobulin. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):759–769. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eränkö O., Pickel V. M., Härkönen M., Eränko L., Joh T. H., Reis D. J. Effect of hydrocortisone on catecholamines and the enzymes synthesizing them in the developing sympathetic ganglion. Histochem J. 1982 May;14(3):461–478. doi: 10.1007/BF01011857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara P., Duchange N., Zakin M. M., Cohen G. N. Internal homologies in the two aspartokinase-homoserine dehydrogenases of Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3019–3023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster G. A., Hökfelt T., Coyle J. T., Goldstein M. Immunohistochemical evidence for phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase-positive/tyrosine hydroxylase-negative neurones in the retina and the posterior hypothalamus of the rat. Brain Res. 1985 Mar 18;330(1):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein M., Fuxe K., Hökfelt T., Joh T. H. Immunohistochemical studies on phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase, dopa-decarboxylase and dopamine- -hydroxylase. Experientia. 1971 Aug;27(8):951–952. doi: 10.1007/BF02135767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grima B., Lamouroux A., Blanot F., Biguet N. F., Mallet J. Complete coding sequence of rat tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):617–621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjiconstantinou M., Mariani A. P., Panula P., Joh T. H., Neff N. H. Immunohistochemical evidence for epinephrine-containing retinal amacrine cells. Neuroscience. 1984 Oct;13(2):547–551. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90247-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook L., Brown I. R. Disaggregation of brain polysomes after administration of d-lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) in vivo. J Neurochem. 1976 Jul;27(1):77–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb01546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalia M., Fuxe K., Goldstein M. Rat medulla oblongata. III. Adrenergic (C1 and C2) neurons, nerve fibers and presumptive terminal processes. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Mar 15;233(3):333–349. doi: 10.1002/cne.902330304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalia M., Woodward D. J., Smith W. K., Fuxe K. Rat medulla oblongata. IV. Topographical distribution of catecholaminergic neurons with quantitative three-dimensional computer reconstruction. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Mar 15;233(3):350–364. doi: 10.1002/cne.902330305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D. H., Baetge E. E., Kaplan B. B., Albert V. R., Reis D. J., Joh T. H. Different forms of adrenal phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase: species-specific posttranslational modification. J Neurochem. 1982 Feb;38(2):410–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08644.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickel V. M., Joh T. H., Reis D. J. Monoamine-synthesizing enzymes in central dopaminergic, noradrenergic and serotonergic neurons. Immunocytochemical localization by light and electron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1976 Jul;24(7):792–306. doi: 10.1177/24.7.8567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero D. A., Ross C. A., Anwar M., Park D. H., Joh T. H., Reis D. J. Distribution of neurons containing phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase in medulla and hypothalamus of rat. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Sep 8;239(2):127–154. doi: 10.1002/cne.902390202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saavedra J. M., Palkovits M., Brownstein M. J., Axelrod J. Localisation of phenylethanolamine N-methyl transferase in the rat brain nuclei. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):695–696. doi: 10.1038/248695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabban E. L., Goldstein M. Subcellular site of biosynthesis of the catecholamine biosynthetic enzymes in bovine adrenal medulla. J Neurochem. 1984 Dec;43(6):1663–1668. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb06093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F., Davison B. L., Stuart G. W., Wilkie T. M., Norstedt G., Palmiter R. D. Regulation, linkage, and sequence of mouse metallothionein I and II genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1221–1230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F., Stuart G. W., Palmiter R. D. Building a metal-responsive promoter with synthetic regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1480–1489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Isolation and expression of an altered mouse dihydrofolate reductase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2495–2499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. A 12-base-pair DNA motif that is repeated several times in metallothionein gene promoters confers metal regulation to a heterologous gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7318–7322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Palmiter R. D. Identification of multiple metal regulatory elements in mouse metallothionein-I promoter by assaying synthetic sequences. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):828–831. doi: 10.1038/317828a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelman G., Joh T. H., Grayson L., Park D. H., Reis D. J., Iacovitti L. Cholinergic neurons of the chick ciliary ganglia express adrenergic traits in vivo and in vitro. J Neurosci. 1985 Jan;5(1):29–39. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-01-00029.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waechter D. E., Baserga R. Effect of methylation on expression of microinjected genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1106–1110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh W. K., Davis G., Fletcher P., Ornston L. N. Homologous amino acid sequences in enzymes mediating sequential metabolic reactions. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4920–4923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh W. K., Ornston L. N. Origins of metabolic diversity: substitution of homologous sequences into genes for enzymes with different catalytic activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5365–5369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh W. K., Ornston L. N. Similar structures in gamma-carboxymuconolactone decarboxylase and beta-ketoadipate succinyl coenzyme A transferase. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):374–377. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.374-377.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh W. K., Shih C., Ornston L. N. Overlapping evolutionary affinities revealed by comparison of amino acid compositions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3794–3797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]