Abstract
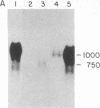
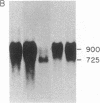
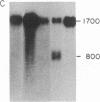
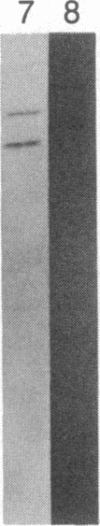
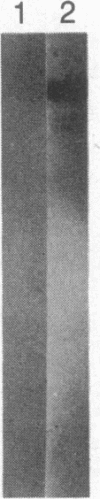
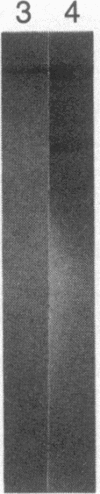
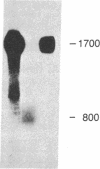
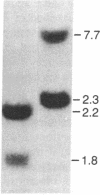
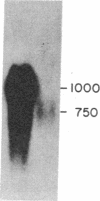
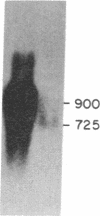
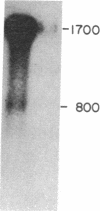
Little is known about the mechanisms that control transformations during the life cycle of Schistosoma mansoni. To enable isolation of DNA sequences encoding developmentally regulated antigens a cDNA expression library in the vector lambda gt11 amp3 was constructed from adult mRNA and immunologically screened with sera from infected individuals. We report here on the properties of three recombinant clones that derive from developmentally regulated genes. Clone 10-3 encoded a beta-galactosidase fusion protein present in high abundance in infected Escherichia coli. Clones 7-2 and 8-2 also produced immunologically recognized proteins; however, the peptides did not appear to be beta-galactosidase fusion proteins. The expression of mRNAs hybridizing to these cDNAs was examined in the different stages of the parasite life cycle. Messenger RNA corresponding to clone 10-3, approximately equal to 1000 bases in length, was present in higher abundance in male worms than in females but was not detected in schistosome eggs. A 900-base mRNA hybridizing to clone 7-2 was observed in adult worms and eggs. Both clone 10-3 and clone 7-2 hybridized to smaller mRNAs in cercariae and freshly transformed schistosomula than in adult worms. Clone 8-2 contained tandem cDNA inserts. One cDNA hybridized to a 1700-base mRNA present in all stages, while the second hybridized to an 800-base mRNA specific to adult female worms.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronstein W. S., Strand M. Gender-specific and pair-dependent glycoprotein antigens of Schistosoma mansoni. J Parasitol. 1984 Aug;70(4):545–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson B. G., Atkinson K. H. Schistosoma mansoni: one- and two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins synthesized in vitro by males, females, and juveniles. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Feb;53(1):26–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90089-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Warren K. S. Specific granulomatous hypersensitivity elicited by bentonite particles coated with soluble antigens from schistosome eggs and turcle bacilli. Nature. 1971 Jan 15;229(5281):200–201. doi: 10.1038/229200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein K., Lew K. K., Jarvik V., Swanson C. A. Role of antirepressor in the bipartite control of repression and immunity by bacteriophage P22. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 5;91(4):439–462. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90271-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowtell D. D., Saint R. B., Rickard M. D., Mitchell G. F. Expression of Taenia taeniaeformis antigens in Escherichia coli. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Oct;13(2):173–185. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugra K., Tanaka R. D., Boyle W. J., MacInnis A. J. Isolation of poly A(+) RNA from Schistosoma mansoni and immunoprecipitation of its in vitro translation products. J Parasitol. 1983 Jun;69(3):486–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles G. C. Recent advances in schistosome biochemistry. Parasitology. 1984 Dec;89(Pt 3):603–637. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000056808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley J. S., Taylor D. W., Dunne D. W., Butterworth A. E. Clone banks of cDNA from the parasite Schistosoma mansoni: isolation of clones containing a potentially immunodiagnostic antigen gene. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):25–39. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox E. C., Yanofsky C. Mutator gene studies in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):390–397. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.390-397.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. N., Hirsh D. Stage-specific patterns of collagen gene expression during development of Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):363–372. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dame J. B., Williams J. L., McCutchan T. F., Weber J. L., Wirtz R. A., Hockmeyer W. T., Maloy W. L., Haynes J. D., Schneider I., Roberts D. Structure of the gene encoding the immunodominant surface antigen on the sporozoite of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):593–599. doi: 10.1126/science.6204383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. H., Blanton R., Klich P. Stage and sex specific differences in actin gene expression in Schistosoma mansoni. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Dec;17(3):289–298. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dissous C., Capron A. Schistosoma mansoni: antigenic community between schistosomula surface and adult worm incubation products as a support for concomitant immunity. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 17;162(2):355–359. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80787-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvall R. H., DeWitt W. B. An improved perfusion technique for recovering adult schistosomes from laboratory animals. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1967 Jul;16(4):483–486. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1967.16.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner J. J., Mahmoud A. A. Phagocytes and worms: David and Goliath revisited. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 May-Jun;4(3):698–714. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.3.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto T., Wang J. C. Yeast DNA topoisomerase II is encoded by a single-copy, essential gene. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1073–1080. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grausz D., Dissous C., Capron A., Roskam W. Messenger RNA extracted from Schistosoma mansoni larval forms codes for parasite antigens when translated in vitro. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Apr;7(4):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harn D. A., Mitsuyama M., David J. R. Schistosoma mansoni. Anti-egg monoclonal antibodies protect against cercarial challenge in vivo. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1371–1387. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Coppel R. L., Cowman A. F., Saint R. B., Brown G. V., Anders R. F. Expression of Plasmodium falciparum blood-stage antigens in Escherichia coli: detection with antibodies from immune humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3787–3791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight M., Simpson A. J., Payares G., Chaudri M., Smithers S. R. Cell-free synthesis of Schistosoma mansoni surface antigens: stage specificity of their expression. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):213–219. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanar D. E., Pearce E. J., Sher A. Expression in Escherichia coli of two Schistosoma mansoni genes that encode major antigens recognized by immune mice. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Oct;17(1):45–60. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdins J. K., Stein M. J., David J. R., Sher A. Schistosoma mansoni: rapid isolation and purification of schistosomula of different developmental stages by centrifugation on discontinuous density gradients of Percoll. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Feb;53(1):39–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90090-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Brammar W. J., Murray K. Lambdoid phages that simplify the recovery of in vitro recombinants. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):53–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02425325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden A. P., Aronstein W. S., Strand M. Schistosoma mansoni: identification, characterization, and purification of the spine glycoprotein by monoclonal antibody. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Dec;54(3):432–442. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson A. J., Sher A., McCutchan T. F. The genome of Schistosoma mansoni: isolation of DNA, its size, bases and repetitive sequences. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1982 Aug;6(2):125–137. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(82)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand M., McMillan A., Pan X. Schistosoma mansoni: reactivity with infected human sera and monoclonal antibody characterization of a glycoprotein in different developmental stages. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Oct;54(2):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. W., Cordingley J. S., Butterworth A. E. Immunoprecipitation of surface antigen precursors from Schistosoma mansoni messenger RNA in vitro translation products. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Mar;10(3):305–318. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenniswood M. P., Simpson A. J. The extraction, characterization and in vitro translation of RNA from adult Schistosoma mansoni. Parasitology. 1982 Apr;84(Pt 2):253–261. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000044814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. S., Mahmoud A. A., Cummings P., Murphy D. J., Houser H. B. Schistosomiasis mansoni in Yemeni in California: duration of infection, presence of disease, therapeutic management. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1974 Sep;23(5):902–909. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1974.23.902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Bloom B. R., Grosskinsky C. M., Ivanyi J., Thomas D., Davis R. W. Dissection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens using recombinant DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2583–2587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]