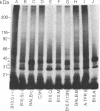
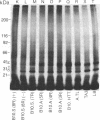
Abstract
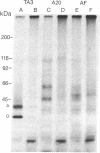
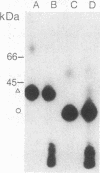
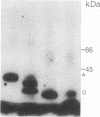
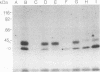
We have used radioiodinated photoreactive bovine insulin as antigen to examine the molecular nature of immunogenic complexes that form on antigen-presenting cells. The probe was allowed to bind to either insulin-presenting B-hybridoma cells, lipopolysaccharide-stimulated blasts, or bovine insulin-specific helper-T-hybridoma cells in the dark. Samples were then exposed to light to induce crosslinkage, solubilized, and analyzed by gel electrophoresis. Two protein bands at about 36 kDa and 27 kDa were specifically labeled on antigen-presenting cells but not on helper T cells. Treatment of these bands with dithiothreitol or endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F showed that each is composed of a single glycoprotein. These proteins are immunoprecipitable with haplotype-specific but not control anti-Ia antibodies. This identifies the labeled bands as the alpha and beta subunits of class II major histocompatibility antigens. We conclude that a molecular complex may form between Ia and antigen on antigen-presenting cells and that formation of this complex does not require the presence of a helper-T-cell antigen receptor.
Full text
PDF


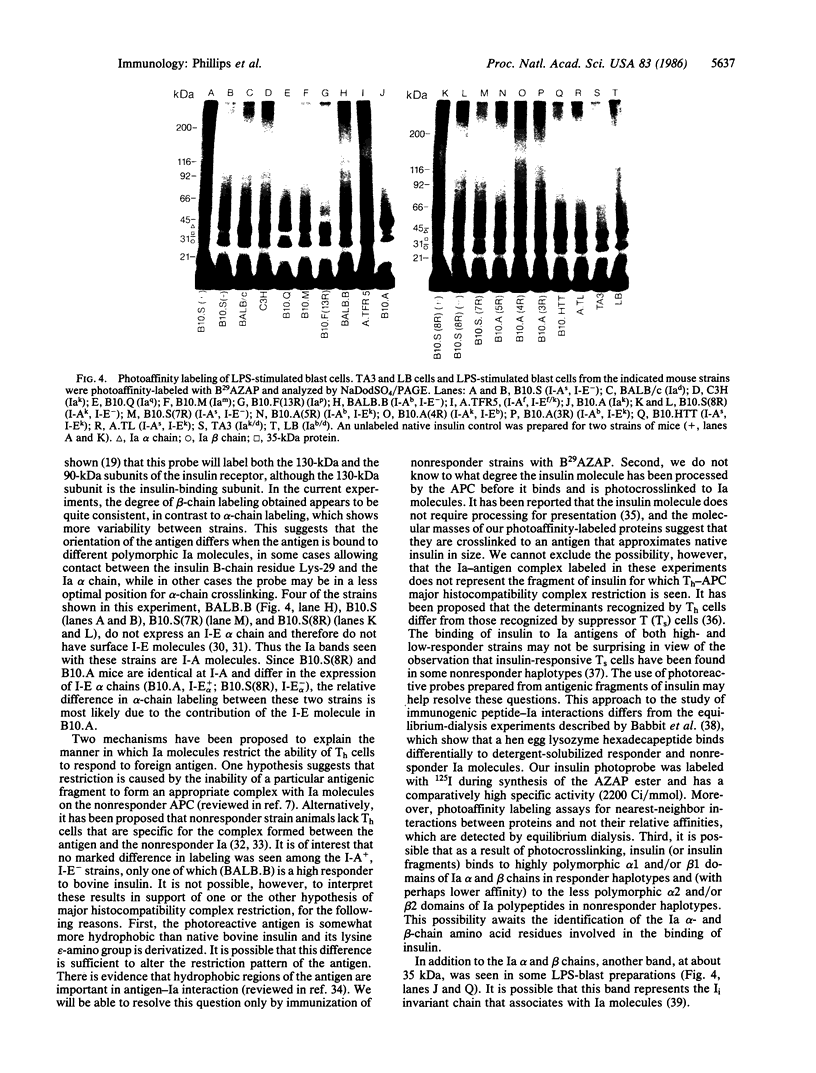

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen P. M., Beller D. I., Braun J., Unanue E. R. The handling of Listeria monocytogenes by macrophages: the search for an immunogenic molecule in antigen presentation. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):323–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babbitt B. P., Allen P. M., Matsueda G., Haber E., Unanue E. R. Binding of immunogenic peptides to Ia histocompatibility molecules. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):359–361. doi: 10.1038/317359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benacerraf B. A hypothesis to relate the specificity of T lymphocytes and the activity of I region-specific Ir genes in macrophages and B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):1809–1812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C., Berzofsky J. A. T-cell antigenic sites tend to be amphipathic structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7048–7052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delovitch T. L., Biggin J., Fung F. Y. In vitro analysis of allogeneic lymphocyte interaction. II. I-region control of the activity of a B-cell-derived H-2-restricted allogeneic effect factor and its receptor during B-cell activation. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1198–1212. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny J. B., Blobel G. 125I-labeled crosslinking reagent that is hydrophilic, photoactivatable, and cleavable through an azo linkage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5286–5290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erb P., Feldmann M., Hogg N. Role of macrophages in the generation of T helper cells. IV. Nature of genetically related factor derived from macrophages incubated with soluble antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1976 May;6(5):365–372. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glimcher L. H., Schroer J. A., Chan C., Shevach E. M. Fine specificity of cloned insulin-specific T cell hybridomas: evidence supporting a role for tertiary conformation. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2868–2874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heber-Katz E., Hansburg D., Schwartz R. H. The Ia molecule of the antigen-presenting cell plays a critical role in immune response gene regulation of T cell activation. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1983;1(1):3–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. E., Pierce C. W., Kapp J. A. Regulatory mechanisms in immune responses to heterologous insulins. II. Suppressor T cell activation associated with nonresponsiveness in H-2b mice. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1012–1026. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. P., Murphy D. B., Hewgill D., McDevitt H. O. Detection of a common polypeptide chain in I--A and I--E sub-region immunoprecipitates. Mol Immunol. 1979 Jan;16(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. P., Murphy D. B., McDevitt H. O. Two-gene control of the expression of a murine Ia antigen. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):925–939. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J., White J., Wegmann D., Mustain E., Marrack P. Antigen presentation by Ia+ B cell hybridomas to H-2-restricted T cell hybridomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3604–3607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. What causes immunological nonresponsiveness? Immunol Rev. 1984 Oct;81:177–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb01110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno Y., Berzofsky J. A. Genetic control of the immune response to myoglobin. V. Antibody production in vitro is macrophage and T cell-dependent and is under control of two determinant-specific Ir genes. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2458–2464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupinski J. M., Plunkett M. L., Freed J. H. Assignment of antigenic determinants to separated I-A kappa chains. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2277–2281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letarte M., Teh H. S., Meghji G. Increased expression of Ia and Thy-1 antigens on mitogen-activated murine spleen lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):370–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengle-Gaw L., McDevitt H. O. Genetics and expression of mouse Ia antigens. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:367–396. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy Z. A., Baxevanis C. N., Ishii N., Klein J. Ia antigens as restriction molecules in Ir-gene controlled T-cell proliferation. Immunol Rev. 1981;60:59–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn R., Spengler M. L., Hoffman M. D., Solvay M. J., Thomas D. W. Macrophage processing of peptide antigens: identification of an antigenic complex. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3225–3234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng D. S., Yip C. C. Peptide mapping of the insulin-binding site of the 130-kDa subunit of the insulin receptor by means of a novel cleavable radioactive photoprobe. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 27;133(1):154–160. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91854-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norcross M. A. A synaptic basis for T-lymphocyte activation. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1984 Sep-Oct;135D(2):113–134. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(84)81105-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patten P., Yokota T., Rothbard J., Chien Y., Arai K., Davis M. M. Structure, expression and divergence of T-cell receptor beta-chain variable regions. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):40–46. doi: 10.1038/312040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Benacerraf B. Functional specificity of thymus- dependent lymphocytes. Science. 1977 Mar 25;195(4284):1293–1300. doi: 10.1126/science.320663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Shevach E. M., Thomas D. W., Pickeral S. F., Rosenthal A. S. Genetic restriction in T-lymphocyte activation by antigen-pulse peritoneal exudate cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):571–578. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierres M., Devaux C., Dosseto M., Marchetto S. Clonal analysis of B- and T-cell responses to Ia antigens. I. Topology of epitope regions on I-Ak and I-Ek molecules analyzed with 35 monoclonal alloantibodies. Immunogenetics. 1981 Dec;14(6):481–495. doi: 10.1007/BF00350120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri J., Lonai P. Mechanism of antigen binding by T cells. H-2(I-A)-restricted binding of antigen plus Ia by helper cells. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Apr;10(4):273–281. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock K. L., Benacerraf B. Selective modification of a private I-A allo-stimulating determinant(s) upon association of antigen with an antigen-presenting cell. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1238–1252. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A. S. Determinant selection and macrophage function in genetic control of the immune response. Immunol Rev. 1978;40:136–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A. S., Shevach E. M. Function of macrophages in antigen recognition by guinea pig T lymphocytes. I. Requirement for histocompatible macrophages and lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1194–1212. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenwasser L. J., Barcinski M. A., Schwartz R. H., Rosenthal A. S. Immune response gene control of determinant selection. II. Genetic control of the murine T lymphocyte proliferative response to insulin. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):471–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig S. A., Madison L. D., Jamieson J. D. Analysis of cholecystokinin-binding proteins using endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):1110–1116. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroer J., Rosenthal A. S. Function of macrophages as antigen presenting cells. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1980 Aug;3(2):247–264. doi: 10.1007/BF02053977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H. T-lymphocyte recognition of antigen in association with gene products of the major histocompatibility complex. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:237–261. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastri N., Miller A., Sercarz E. E. The expressed T cell repertoire is hierarchical: the precise focus of lysozyme-specific T cell clones is dependent upon the structure of the immunogen. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1984;1(6):369–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. W., Danho W., Bullesbach E., Föhles J., Rosenthal A. S. Immune response gene control of determinant selection. III. Polypeptide fragments of insulin are differentially recognized by T but not by B cells in insulin immune guinea pigs. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):1095–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walden P., Nagy Z. A., Klein J. Induction of regulatory T-lymphocyte responses by liposomes carrying major histocompatibility complex molecules and foreign antigen. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):327–329. doi: 10.1038/315327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassmer P., Chan C., Lögdberg L., Shevach E. M. Role of the L3T4-antigen in T cell activation. II. Inhibition of T cell activation by monoclonal anti-L3T4 antibodies in the absence of accessory cells. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2237–2242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]