Abstract
Catalysis of ligand-receptor interactions is proposed as an important function of the lipid phase of the cell membrane. The catalytic mechanism is deduced from observed specific interactions of amphiphilic peptides with artificial lipid bilayers. In our model a direct ligand-receptor reaction is replaced by multiple sequential steps including surface accumulation of charged ligands, ligand-membrane interactions, and ultimately binding to the receptor itself. By dividing the total free energy of binding among several steps, the energy per step, including the intrinsic receptor interaction energy, is kept to moderate values. The model thereby yields simple explanations for the large apparent association constants, the high association and dissociation rates, and the heterogeneity of binding sites so frequently found with pharmacological and biochemical ligand-receptor interactions. Furthermore, the measured apparent association constant is a function of the whole system rather than just the receptor. The same, fully functional receptor may show different binding characteristics in different surroundings, such as in another tissue or in a reconstituted system.
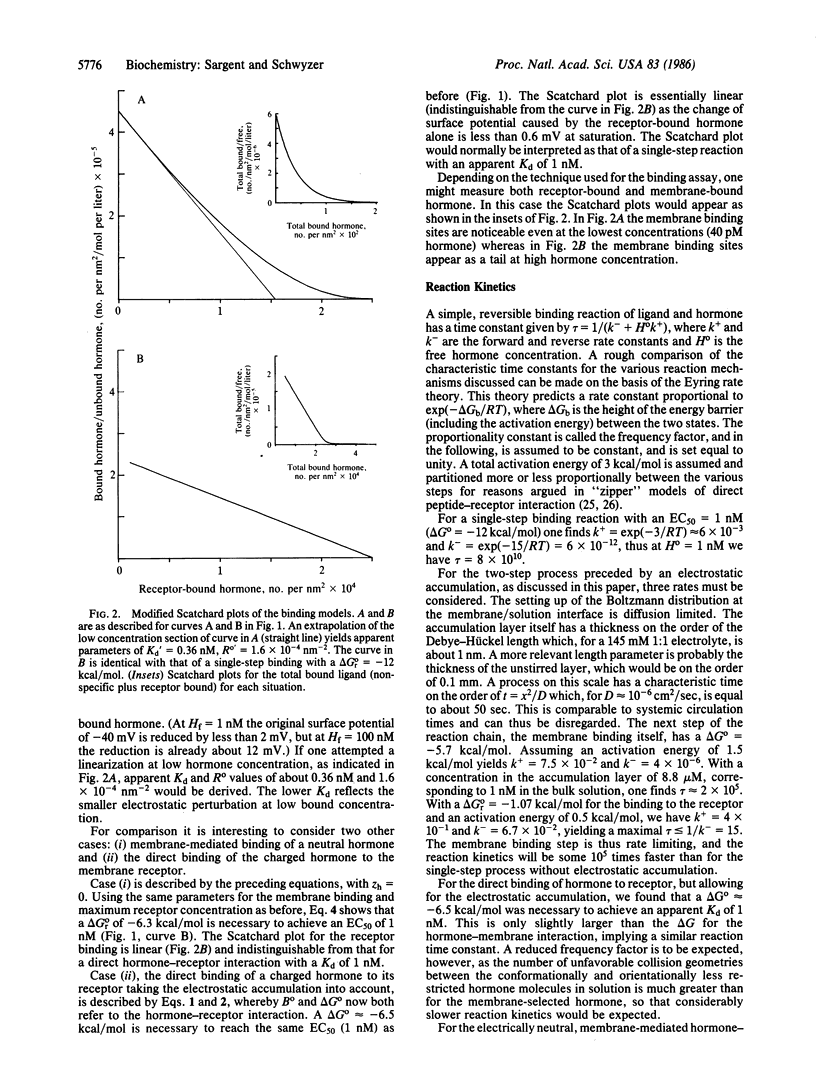
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg H. C., Purcell E. M. Physics of chemoreception. Biophys J. 1977 Nov;20(2):193–219. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85544-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgen A. S., Roberts G. C., Feeney J. Binding of flexible ligands to macromolecules. Nature. 1975 Feb 27;253(5494):753–755. doi: 10.1038/253753a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavkin C., Goldstein A. Specific receptor for the opioid peptide dynorphin: structure--activity relationships. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6543–6547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deber C. M., Behnam B. A. Role of membrane lipids in peptide hormone function: binding of enkephalins to micelles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):61–65. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erne D., Sargent D. F., Schwyzer R. Preferred conformation, orientation, and accumulation of dynorphin A-(1-13)-tridecapeptide on the surface of neutral lipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 30;24(16):4261–4263. doi: 10.1021/bi00337a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin T. J. Binding energy and the activation of hormone receptors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Mar 15;29(6):853–856. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gremlich H. U., Fringeli U. P., Schwyzer R. Conformational changes of adrenocorticotropin peptides upon interaction with lipid membranes revealed by infrared attenuated total reflection spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 30;22(18):4257–4264. doi: 10.1021/bi00287a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gremlich H. U., Fringeli U. P., Schwyzer R. Interaction of adrenocorticotropin-(11-24)-tetradecapeptide with neutral lipid membranes revealed by infrared attenuated total reflection spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1808–1810. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gysin B., Schwyzer R. Head group and structure specific interactions of enkephalins and dynorphin with liposomes: investigation by hydrophobic photolabeling. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Sep;225(2):467–474. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gysin B., Schwyzer R. Hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions between adrenocorticotropin-(1-24) -tetracosapeptide and lipid vesicles. Amphiphilic primary structures. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1811–1818. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gysin B., Schwyzer R. Liposome-mediated labeling of adrenocorticotropin fragments parallels their biological activity. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 11;158(1):12–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80666-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jencks W. P. Binding energy, specificity, and enzymic catalysis: the circe effect. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1975;43:219–410. doi: 10.1002/9780470122884.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser E. T., Kézdy F. J. Secondary structures of proteins and peptides in amphiphilic environments. (A review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1137–1143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Paterson S. J. Types of opioid receptors: relation to antinociception. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Feb 19;308(1136):291–297. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1985.0029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiken N., Némethy G. A new model for the binding of flexible ligands to proteins. Biochemistry. 1971 May 25;10(11):2101–2106. doi: 10.1021/bi00787a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang U., Karlaganis G., Vogel R., Schwyzer R. Hormone-receptor interactions. Adrenocorticotropic hormone binding site increase in isolated fat cells by phenoxazones. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2626–2633. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoch P., Sargent D. F., Schwyzer R. Hormone-receptor interactions: corticotropin-(1-24)-tetracosapeptide spans artificial lipid-bilayer membranes. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Oct;7(5):846–849. doi: 10.1042/bst0070846a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyzer R. ACTH: a short introductory review. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Oct 28;297:3–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb41843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seltzman T. P., Finn F. M., Widnell C. C., Hofmann K. Lipids of bovine adrenal plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1193–1196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. R. Membrane receptors for polypeptide hormones. Adv Clin Chem. 1977;19:91–124. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2423(08)60171-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theuvenet A. P., Borst-Pauwels G. W. The influence of surface charge on the kinetics of ion-translocation across biological membranes. J Theor Biol. 1976 Apr;57(2):313–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(76)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



