Abstract
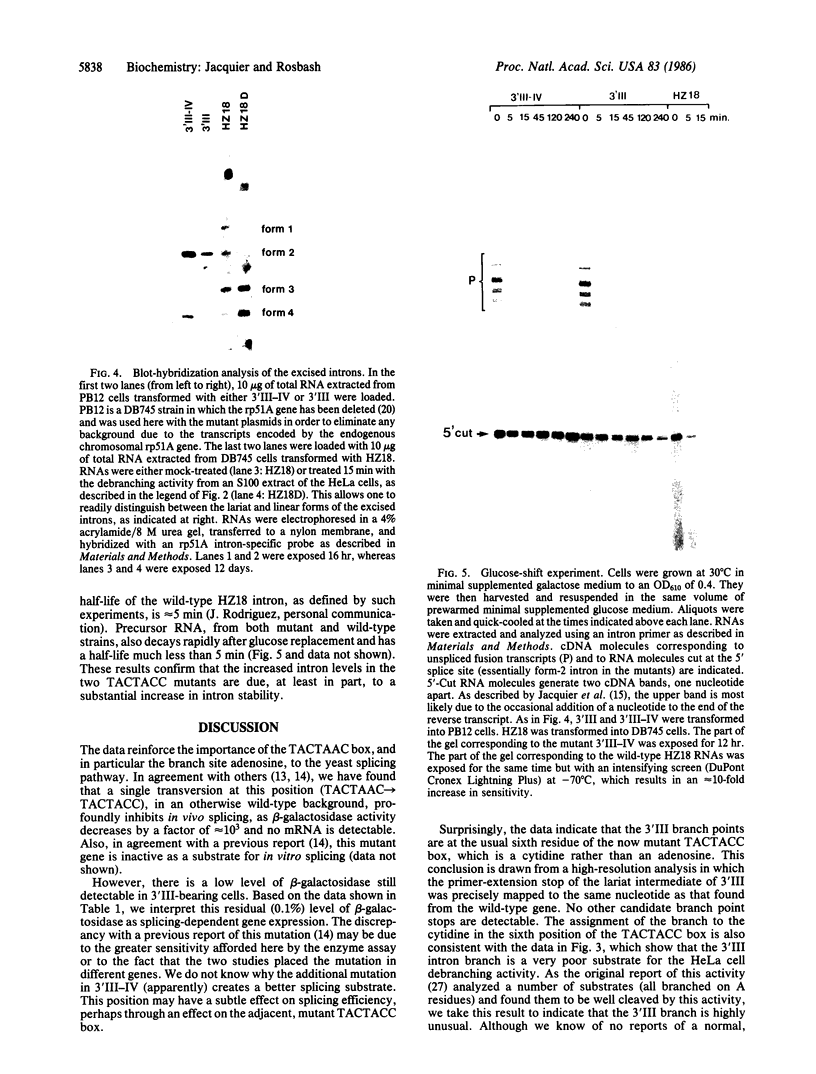
Two mutant genes, both of which contain an A----C transversion at the absolutely conserved branch point of the yeast "TACTAAC box" (TACTAAC----TACTACC), were constructed and introduced into yeast cells. Splicing and gene expression are almost completely eliminated by this mutation, but a low level (approximately equal to 0.1%) of proper splicing is detectable. Branch point mapping indicates that the mutant branch is formed at the normal location--i.e., to cytidine rather than adenosine. The mutant branch is also a very poor substrate for the HeLa cell debranching enzyme. Although splicing of the mutant transcripts is very poor, the cells contain a high level of mutant intron because these excised introns are remarkably stable. The results imply that the normal branch point is important not only for branch formation and splicing but also for intron turnover.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brody E., Abelson J. The "spliceosome": yeast pre-messenger RNA associates with a 40S complex in a splicing-dependent reaction. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):963–967. doi: 10.1126/science.3890181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colot H. V., Rosbash M. Behavior of individual maternal pA+ RNAs during embryogenesis of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1982 Nov;94(1):79–86. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domdey H., Apostol B., Lin R. J., Newman A., Brody E., Abelson J. Lariat structures are in vivo intermediates in yeast pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):611–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouser L. A., Friesen J. D. Mutations in a yeast intron demonstrate the importance of specific conserved nucleotides for the two stages of nuclear mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90540-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frendewey D., Keller W. Stepwise assembly of a pre-mRNA splicing complex requires U-snRNPs and specific intron sequences. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):355–367. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Messenger RNA splicing in vitro: an excised intervening sequence and a potential intermediate. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):415–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90372-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Seiler S. R., Sharp P. A. A multicomponent complex is involved in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):345–353. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Rodriguez J. R., Rosbash M. A quantitative analysis of the effects of 5' junction and TACTAAC box mutants and mutant combinations on yeast mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):423–430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Gallwitz D. Evidence for an intron-contained sequence required for the splicing of yeast RNA polymerase II transcripts. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):519–527. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90433-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Klinz F. J., Donath C., Gallwitz D. Point mutations identify the conserved, intron-contained TACTAAC box as an essential splicing signal sequence in yeast. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. J., Newman A. J., Cheng S. C., Abelson J. Yeast mRNA splicing in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14780–14792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Lin R. J., Cheng S. C., Abelson J. Molecular consequences of specific intron mutations on yeast mRNA splicing in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):335–344. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A., Hereford L. Identification of a sequence responsible for periodic synthesis of yeast histone 2A mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7689–7693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Konarska M. M., Grabowski P. J., Hardy S. F., Sharp P. A. Lariat RNA's as intermediates and products in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):898–903. doi: 10.1126/science.6206566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Guthrie C. A point mutation in the conserved hexanucleotide at a yeast 5' splice junction uncouples recognition, cleavage, and ligation. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):107–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Rosbash M. mRNA splicing efficiency in yeast and the contribution of nonconserved sequences. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Teem J. L., Rosbash M. Evidence for the biochemical role of an internal sequence in yeast nuclear mRNA introns: implications for U1 RNA and metazoan mRNA splicing. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90373-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. R., Pikielny C. W., Rosbash M. In vivo characterization of yeast mRNA processing intermediates. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90467-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. Preparation of RNA and ribosomes from yeast. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:45–64. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60951-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. An RNA processing activity that debranches RNA lariats. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):135–140. doi: 10.1126/science.2990042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Greene J. M., Green M. R. Cryptic branch point activation allows accurate in vitro splicing of human beta-globin intron mutants. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):833–844. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Green M. R. Excision of an intact intron as a novel lariat structure during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Pikielny C. W., Rosbash M., Green M. R. Alternative branch points are selected during splicing of a yeast pre-mRNA in mammalian and yeast extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2022–2026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teem J. L., Rosbash M. Expression of a beta-galactosidase gene containing the ribosomal protein 51 intron is sensitive to the rna2 mutation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4403–4407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace J. C., Edmonds M. Polyadenylylated nuclear RNA contains branches. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):950–954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Meyer F., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Unusual splice sites revealed by mutagenic inactivation of an authentic splice site of the rabbit beta-globin gene. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):38–43. doi: 10.1038/301038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Efstratiadis A. In vivo splicing products of the rabbit beta-globin pre-mRNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):589–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90466-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]