Abstract
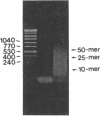
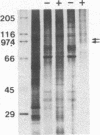
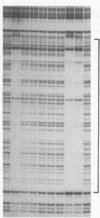
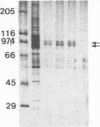
We describe a method for affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins that is fast and effective. Complementary chemically synthesized oligodeoxynucleotides that contain a recognition site for a sequence-specific DNA binding protein are annealed and ligated to give oligomers. This DNA is then covalently coupled to Sepharose CL-2B with cyanogen bromide to yield the affinity resin. A partially purified protein fraction is combined with competitor DNA and subsequently passed through the DNA-Sepharose resin. The desired sequence-specific DNA binding protein is purified because it preferentially binds to the recognition sites in the affinity resin rather than to the nonspecific competitor DNA in solution. For example, a protein fraction that is enriched for transcription factor Sp1 can be further purified 500- to 1000-fold by two sequential affinity chromatography steps to give Sp1 of an estimated 90% homogeneity with 30% yield. In addition, the use of tandem affinity columns containing different protein binding sites allows the simultaneous purification of multiple DNA binding proteins from the same extract. This method provides a means for the purification of rare sequence-specific DNA binding proteins, such as Sp1 and CAAT-binding transcription factor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B. M., Amodio F. J., Jenkins M., Gutmann E. D., Ferris F. L. Studies with DNA-cellulose chromatography. I. DNA-binding proteins from Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:289–305. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberts B. M. The DNA enzymology of protein machines. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:1–12. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt-Jovin D. J., Jovin T. M., Bähr W., Frischauf A. M., Marquardt M. Covalent attachment of DNA to agarose. Improved synthesis and use in affinity chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):411–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudray P., Tyndall C., Kamen R., Cuzin F. The high affinity binding site on polyoma virus DNA for the viral large-T protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5697–5710. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Kadonaga J. T., Barrera-Saldaña H., Takahashi K., Chambon P., Tjian R. Bidirectional SV40 transcription mediated by tandem Sp1 binding interactions. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):511–517. doi: 10.1126/science.2996137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrick G. Site-specific DNA-affinity chromatography of the lac repressor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3721–3728. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Winocour E., Prives C. Differential affinities of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen for DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):220–224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J. Purification of nuclear factor I by DNA recognition site affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1398–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Dervan P. B. Methidiumpropyl-EDTA.Fe(II) and DNase I footprinting report different small molecule binding site sizes on DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5555–5567. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]