Abstract
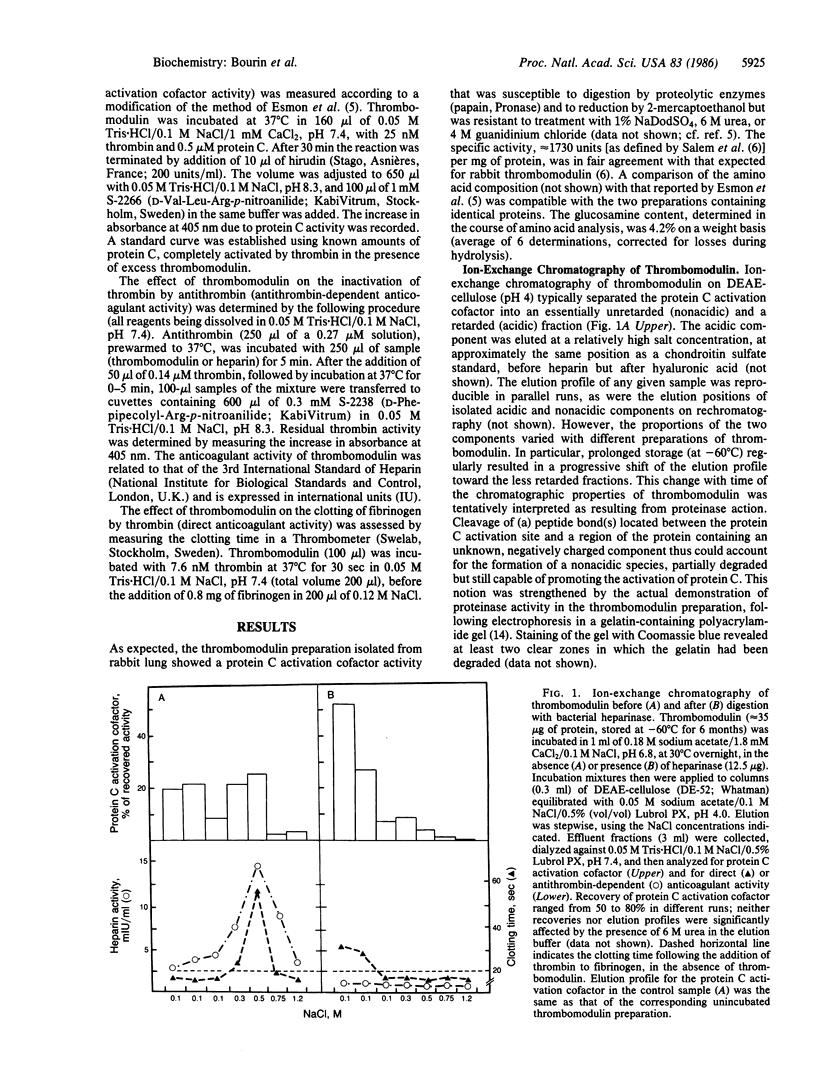
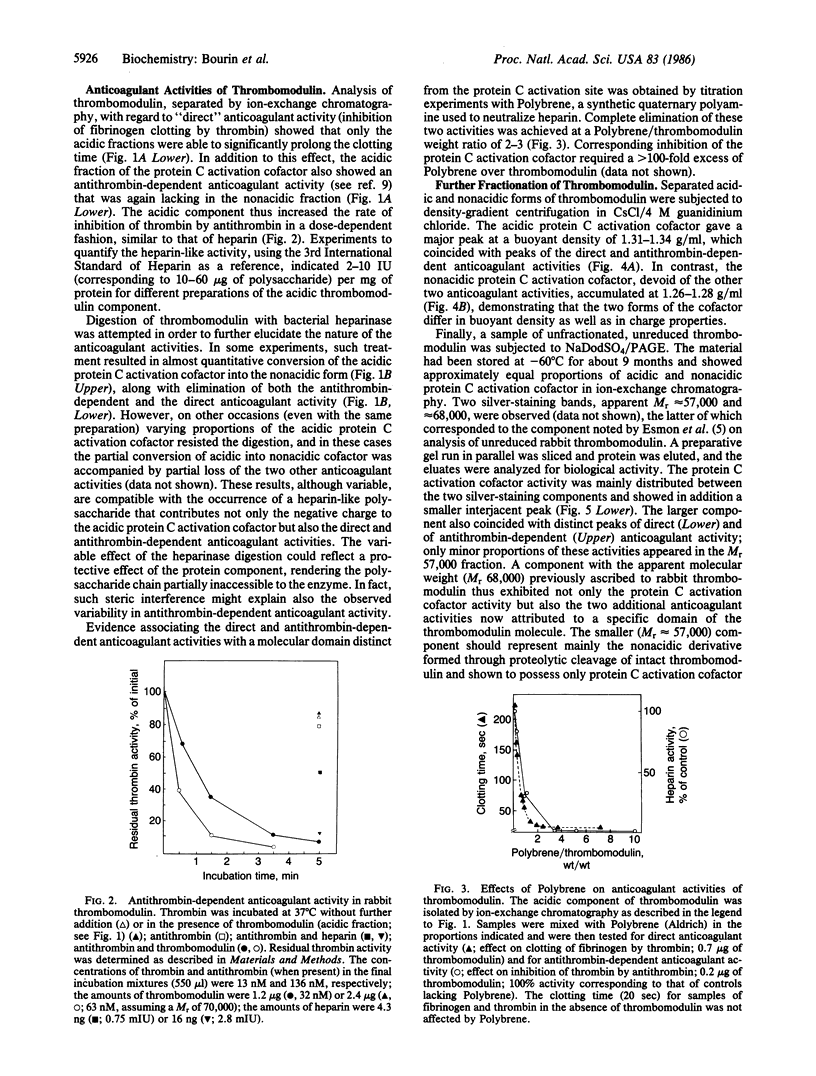
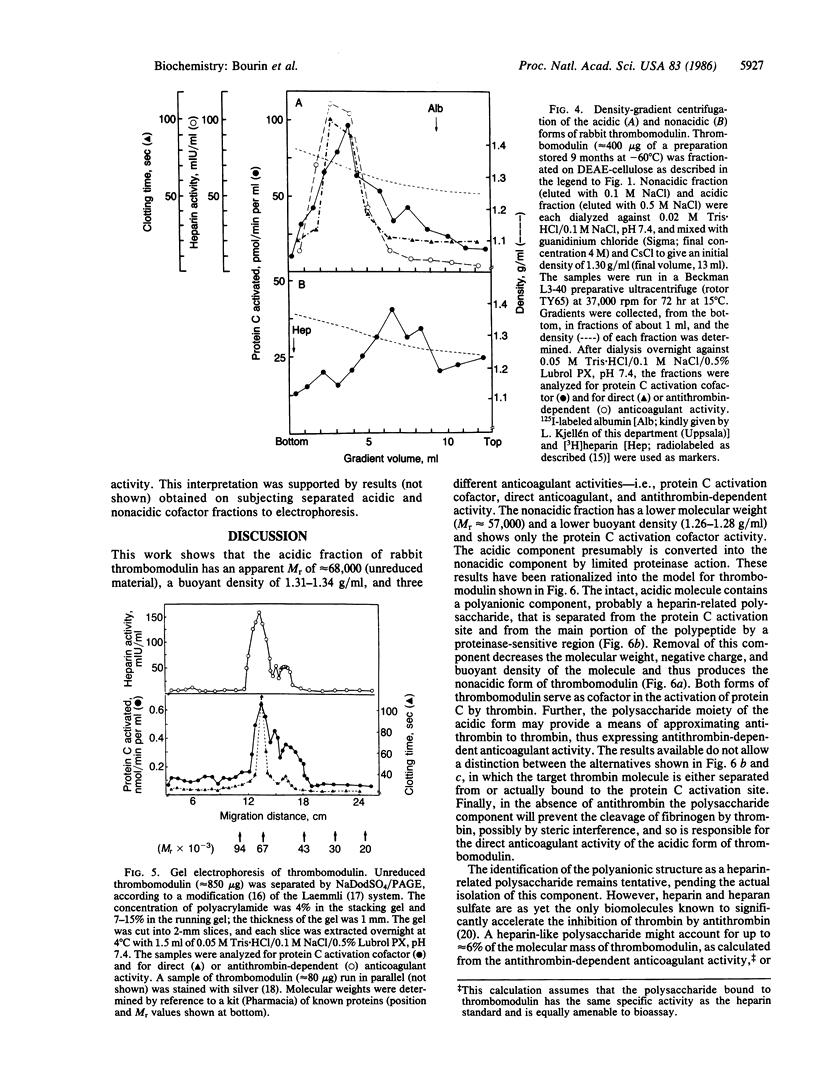
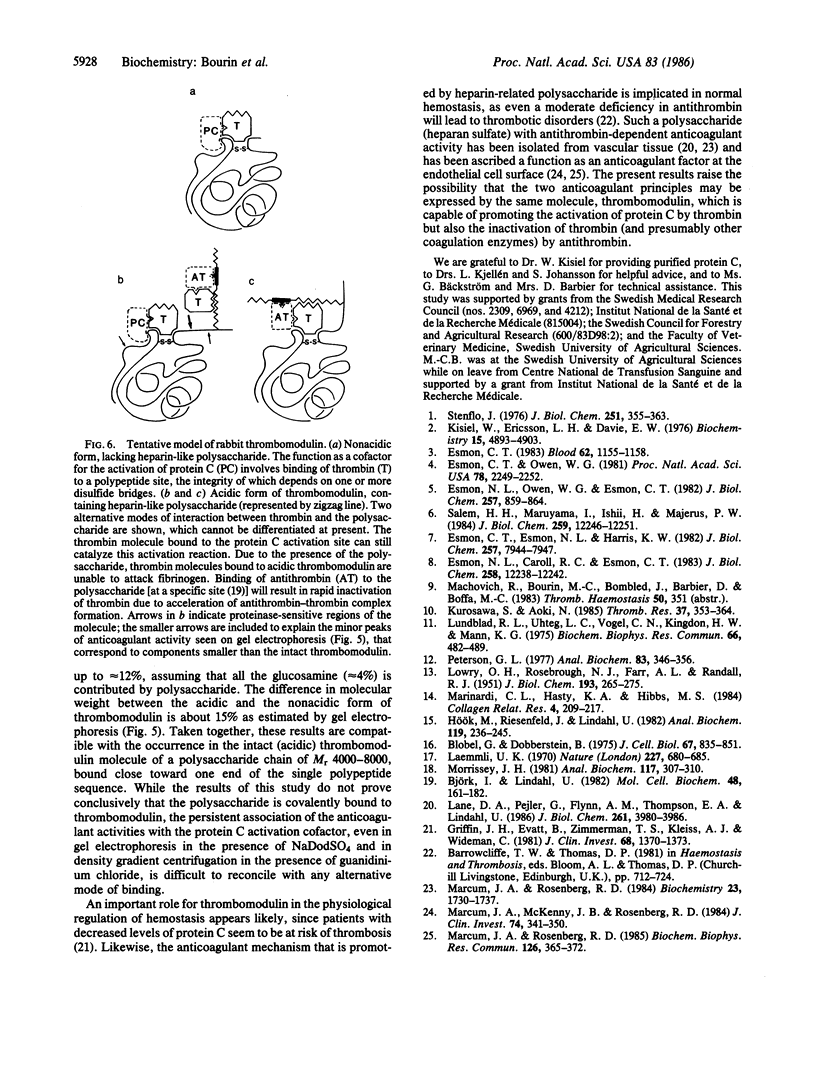
Thrombomodulin isolated from rabbit lung was separated by ion-exchange chromatography on DEAE-cellulose into a retarded (acidic) and a nonretarded (nonacidic) fraction. Both fractions contained the cofactor required for the activation of protein C. In addition, the acidic fraction (but not the nonacidic fraction) prevented the clotting of fibrinogen by thrombin ("direct" anticoagulant activity) and accelerated the inhibition of thrombin by antithrombin (effect corresponding to 2-10 international units of heparin per mg of protein). Both of these activities were readily neutralized by the synthetic polycation Polybrene, which did not appreciably affect protein C activation. They were also eliminated by digestion of thrombomodulin with bacterial heparinase, which, in addition, converted the acidic form of the protein C activation cofactor to a nonacidic form. Similar conversion observed during storage of thrombomodulin was attributed to endogenous proteinase activity. Density-gradient centrifugation of the acidic form of thrombomodulin in CsCl/4M guanidinium chloride failed to separate either of the direct or antithrombin-dependent anticoagulant activities from the protein C activation cofactor, which showed a buoyant density of 1.31-1.34 g/ml. The nonacidic cofactor had a lower density, 1.26-1.28 g/ml. Unreduced thrombomodulin yielded two major fractions of protein C activation cofactor on NaDodSO4/PAGE, with apparent Mr of approximately 68,000 and 57,000, respectively. The larger component contained essentially all of the direct and antithrombin-dependent anticoagulant activities. We propose that these activities as well as the negative charge and the higher buoyant density of the acidic, Mr 68,000 form of thrombomodulin are due to a heparin-like polysaccharide and, further, that this component can be separated from the major portion of the molecule, which contains the protein C activation site, through the action of a proteinase.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Björk I., Lindahl U. Mechanism of the anticoagulant action of heparin. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Oct 29;48(3):161–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00421226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Esmon N. L., Harris K. W. Complex formation between thrombin and thrombomodulin inhibits both thrombin-catalyzed fibrin formation and factor V activation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7944–7947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Owen W. G. Identification of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2249–2252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. Protein-C: biochemistry, physiology, and clinical implications. Blood. 1983 Dec;62(6):1155–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Carroll R. C., Esmon C. T. Thrombomodulin blocks the ability of thrombin to activate platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12238–12242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Isolation of a membrane-bound cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):859–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Evatt B., Zimmerman T. S., Kleiss A. J., Wideman C. Deficiency of protein C in congenital thrombotic disease. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1370–1373. doi: 10.1172/JCI110385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hök M., Riesenfeld J., Lindahl U. N-[3H]Acetyl-labeling, a convenient method for radiolabeling of glycosaminoglycans. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 15;119(2):236–245. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90580-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Ericsson L. H., Davie E. W. Proteolytic activation of protein C from bovine plasma. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4893–4900. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa S., Aoki N. Preparation of thrombomodulin from human placenta. Thromb Res. 1985 Feb 1;37(3):353–364. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. A., Pejler G., Flynn A. M., Thompson E. A., Lindahl U. Neutralization of heparin-related saccharides by histidine-rich glycoprotein and platelet factor 4. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):3980–3986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad R. L., Uhteg L. C., Vogel C. N., Kingdon H. S., Mann K. G. Preparation and partial characterization of two forms of bovine thrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 16;66(2):482–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90536-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainardi C. L., Hasty K. A., Hibbs M. S. Antibody to rabbit macrophage type V collagenase/gelatinase and its use to further characterize the enzyme. Coll Relat Res. 1984 May;4(3):209–217. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(84)80043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcum J. A., McKenney J. B., Rosenberg R. D. Acceleration of thrombin-antithrombin complex formation in rat hindquarters via heparinlike molecules bound to the endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):341–350. doi: 10.1172/JCI111429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcum J. A., Rosenberg R. D. Anticoagulantly active heparin-like molecules from vascular tissue. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1730–1737. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcum J. A., Rosenberg R. D. Heparinlike molecules with anticoagulant activity are synthesized by cultured endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90615-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salem H. H., Maruyama I., Ishii H., Majerus P. W. Isolation and characterization of thrombomodulin from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12246–12251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J. A new vitamin K-dependent protein. Purification from bovine plasma and preliminary characterization. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):355–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



