Abstract
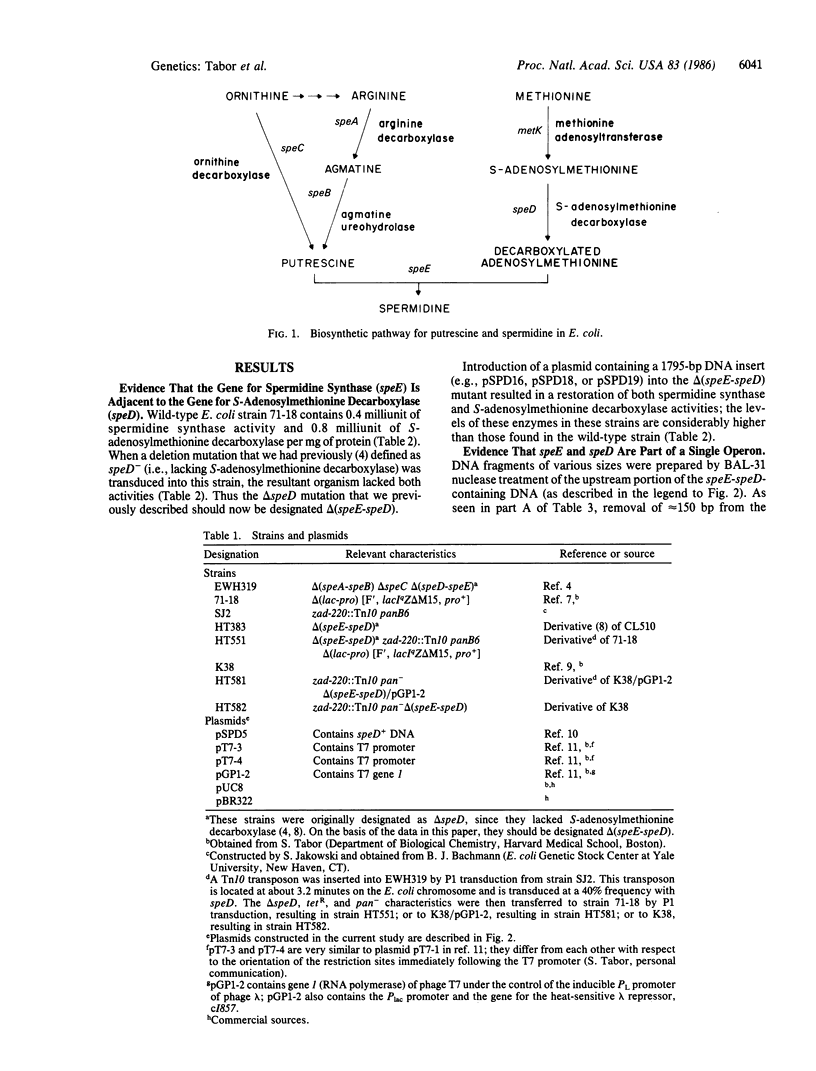
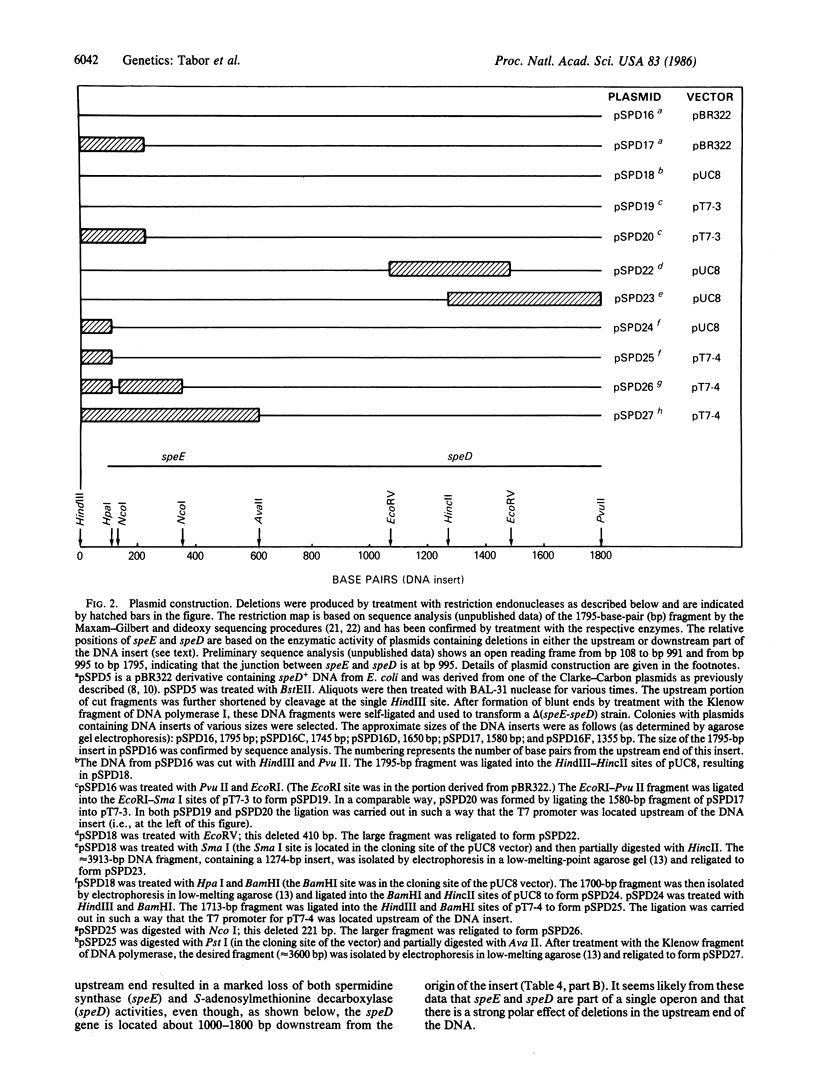
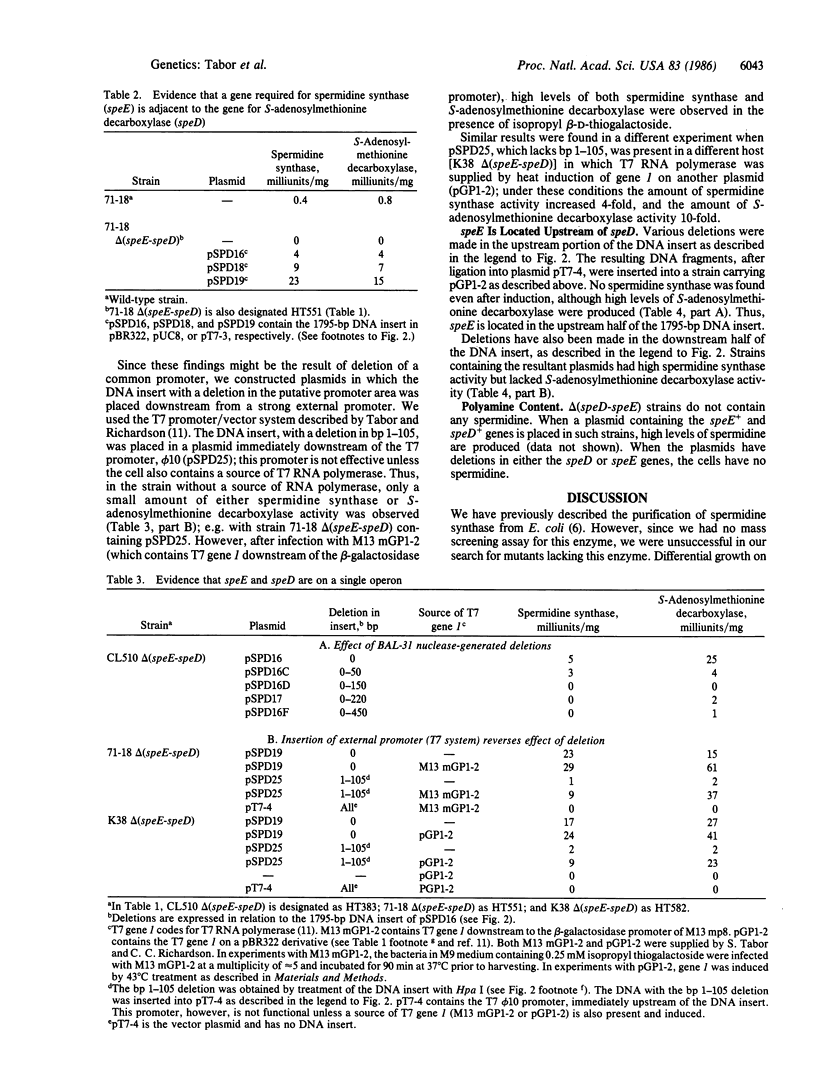
We have obtained Escherichia coli mutants lacking spermidine synthase (putrescine aminopropyltransferase) and have found that the mutated gene (speE) is located immediately upstream from the gene coding for S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase (speD); these genes are located at 2.7 minutes on the E. coli chromosome. Both genes are present in a 1795-base-pair fragment of E. coli DNA that was cloned into pBR322. Deletion of 105 bases upstream of speE caused a coordinate loss of both activities, indicating that speE and speD constitute a single operon. speE and speD have also been cloned separately in a high-expression vector; strains carrying these plasmids overproduce the respective enzymes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson J. R., Hare P. E. O-phthalaldehyde: fluorogenic detection of primary amines in the picomole range. Comparison with fluorescamine and ninhydrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):619–622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman W. H., Tabor C. W., Tabor H. Spermidine biosynthesis. Purification and properties of propylamine transferase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2480–2486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle S. M., Markham G. D., Hafner E. W., Wright J. M., Tabor H., Tabor C. W. Expression of the cloned genes encoding the putrescine biosynthetic enzymes and methionine adenosyltransferase of Escherichia coli (speA, speB, speC and metK). Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., Frischauf A., Lehrach H. An integrated and simplified approach to cloning into plasmids and single-stranded phages. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:78–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafner E. W., Tabor C. W., Tabor H. Mutants of Escherichia coli that do not contain 1,4-diaminobutane (putrescine) or spermidine. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12419–12426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maas W. K. Mapping of genes involved in the synthesis of spermidine in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00270439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham G. D., Tabor C. W., Tabor H. S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase of Escherichia coli. Studies on the covalently linked pyruvate required for activity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12063–12068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Gronenborn B., Müller-Hill B., Hans Hopschneider P. Filamentous coliphage M13 as a cloning vehicle: insertion of a HindII fragment of the lac regulatory region in M13 replicative form in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3642–3646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS M. A note on the use of cellulose phosphate cation-exchange paper for the separation of catecholamines, and some other biogenic amines. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1962 Nov;14:746–749. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1962.tb11170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel M., Model P. Replacement of the fip gene of Escherichia coli by an inactive gene cloned on a plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):1034–1039. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.1034-1039.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W., Tabor H., Hafner E. W. Escherichia coli mutants completely deficient in adenosylmethionine decarboxylase and in spermidine biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3671–3676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W., Tabor H., Hafner E. W., Markham G. D., Boyle S. M. Cloning of the Escherichia coli genes for the biosynthetic enzymes for polyamines. Methods Enzymol. 1983;94:117–121. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)94019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W., Tabor H. Polyamines in microorganisms. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):81–99. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.81-99.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W., Tabor H. Polyamines. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:749–790. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



