Abstract
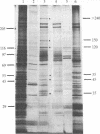
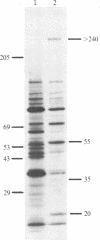
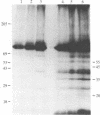
Plasmodium falciparum proteins associated with plasma membranes of infected erythrocytes were identified by using three techniques: isolated plasma membranes from infected and uninfected erythrocytes were compared by gel electrophoresis and silver staining; isolated plasma membranes from cells metabolically labeled with [35S]methionine were assayed by gel electrophoresis; and uninfected and infected intact erythrocytes were surface-labeled by lactoperoxidase iodination, and the labeled polypeptides were compared by gel electrophoresis. The results from these experiments indicate that at least six parasite-derived polypeptides (Mr = greater than 240,000, 150,000, 55,000, 45,000, 35,000, and 20,000) are associated with the infected erythrocyte plasma membrane. At least four of these peptides (Mr = 55,000, 45,000, 35,000, and 20,000) may be exposed on the surface of the infected erythrocytes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aley S. B., Sherwood J. A., Howard R. J. Knob-positive and knob-negative Plasmodium falciparum differ in expression of a strain-specific malarial antigen on the surface of infected erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1585–1590. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. V., Culvenor J. G., Crewther P. E., Bianco A. E., Coppel R. L., Saint R. B., Stahl H. D., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Localization of the ring-infected erythrocyte surface antigen (RESA) of Plasmodium falciparum in merozoites and ring-infected erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):774–779. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel R. L., Cowman A. F., Anders R. F., Bianco A. E., Saint R. B., Lingelbach K. R., Kemp D. J., Brown G. V. Immune sera recognize on erythrocytes Plasmodium falciparum antigen composed of repeated amino acid sequences. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):789–792. doi: 10.1038/310789a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenberg J., Sherman I. W. Isolation and characterization of the plasma membrane of human erythrocytes infected with the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1087–1091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A. Characterization of a protein correlated with the production of knob-like protrusions on membranes of erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4650–4653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambros C., Vanderberg J. P. Synchronization of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic stages in culture. J Parasitol. 1979 Jun;65(3):418–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langreth S. G., Reese R. T. Antigenicity of the infected-erythrocyte and merozoite surfaces in Falciparum malaria. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1241–1254. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leech J. H., Barnwell J. W., Miller L. H., Howard R. J. Identification of a strain-specific malarial antigen exposed on the surface of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1567–1575. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann H., Berzins K., Wahlgren M., Carlsson J., Björkman A., Patarroyo M. E., Perlmann P. Antibodies in malarial sera to parasite antigens in the membrane of erythrocytes infected with early asexual stages of Plasmodium falciparum. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1686–1704. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Morrison M. Exposed protein on the intact human erythrocyte. Biochemistry. 1971 May 11;10(10):1766–1771. doi: 10.1021/bi00786a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese R. T., Langreth S. G., Trager W. Isolation of stages of the human parasite Plasmodium falciparum from culture and from animal blood. Bull World Health Organ. 1979;57 (Suppl 1):53–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley H. A., Mayes J. T., Cooper N. R., Reese R. T. Complement activation by the surface of Plasmodium falciparum infected erythrocytes. Mol Immunol. 1984 Feb;21(2):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90129-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley H. A., Reese R. T. In vitro inhibition of intracellular growth of Plasmodium falciparum by immune sera. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Jan;33(1):12–16. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Jensen J. B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.781840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Rudzinska M. A., Bradbury P. C. The fine structure of Plasmodium falciparum and its host erythrocytes in natural malarial infections in man. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;35(6):883–885. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udeinya I. J., Miller L. H., McGregor I. A., Jensen J. B. Plasmodium falciparum strain-specific antibody blocks binding of infected erythrocytes to amelanotic melanoma cells. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):429–431. doi: 10.1038/303429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]