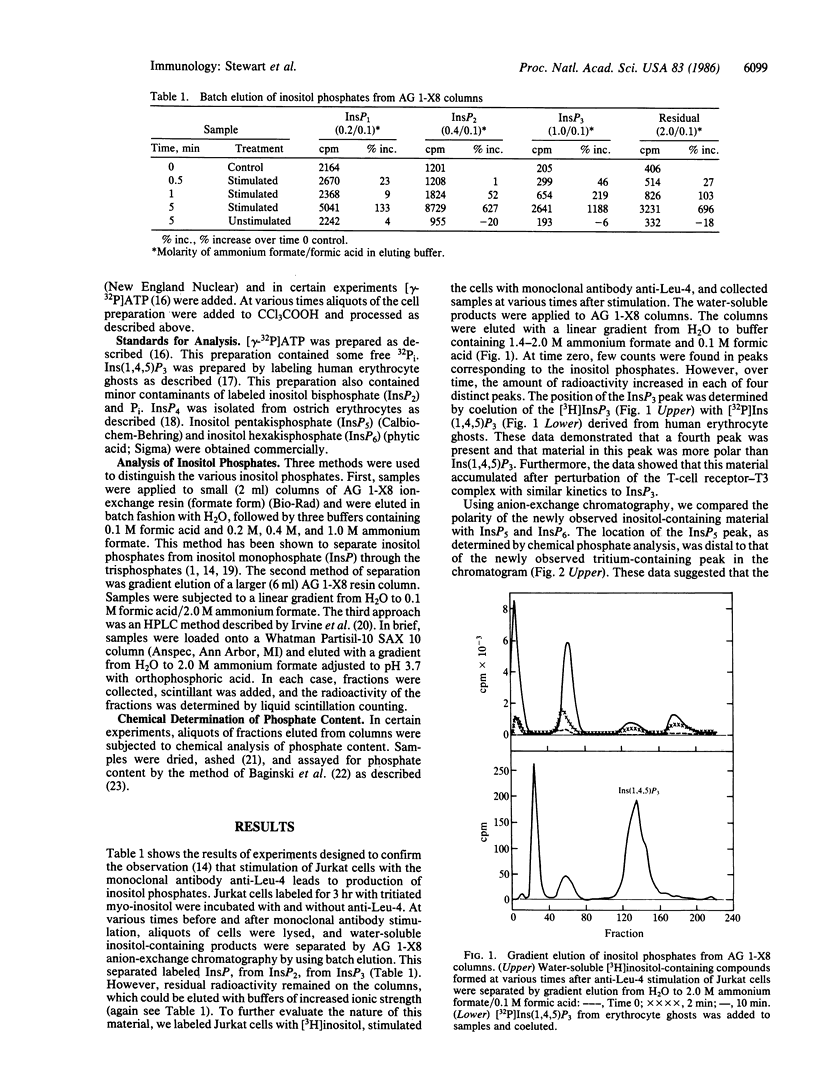
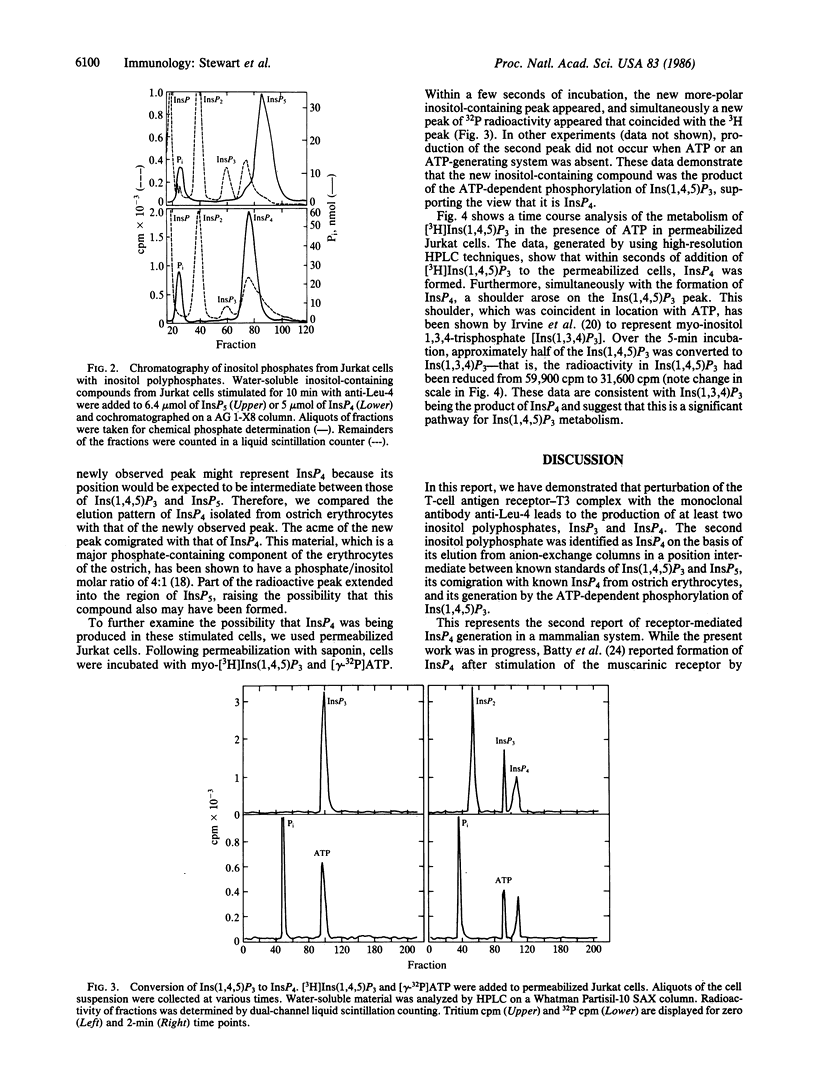
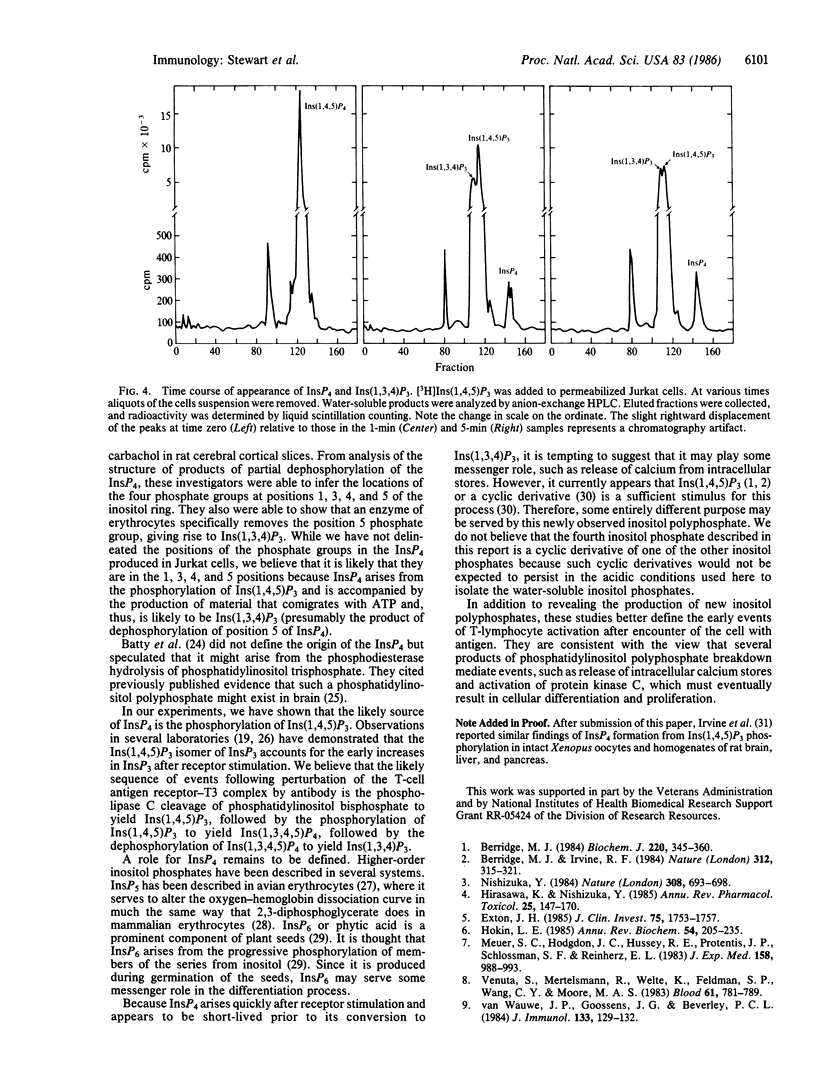
Abstract
Antibodies directed against the T-cell antigen receptor-T3 complex mimic antigen and lead to cellular changes consistent with activation. When cells of the human T-cell line Jurkat were stimulated with a monoclonal antibody directed against T3, inositol phosphates were produced. In addition to inositol trisphosphate, which is the product of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate cleavage, a second inositol polyphosphate was formed. This compound was more polar than inositol trisphosphate but less polar than inositol pentakisphosphate. It cochromatographed with inositol tetrakisphosphate from ostrich erythrocytes. In permeabilized Jurkat cells, this compound was shown to be formed from inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, but only in the presence of ATP, and 32P was incorporated into it from [gamma-32P]ATP. There also was coincident formation of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate. We conclude that the more polar compound is inositol tetrakisphosphate, which is formed by phosphorylation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and may be the precursor of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett G. R. Isolation and assay of red-cell inositol polyphosphates. Anal Biochem. 1982 Aug;124(2):425–431. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batty I. R., Nahorski S. R., Irvine R. F. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate following muscarinic receptor stimulation of rat cerebral cortical slices. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):211–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2320211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., McKinney J. S., Irvine R. F., Putney J. W., Jr Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate formation in Ca2+-mobilizing-hormone-activated cells. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):237–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2320237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest R., Prpić V., Exton J. H., Blackmore P. F. Stimulation of inositol trisphosphate formation in hepatocytes by vasopressin, adrenaline and angiotensin II and its relationship to changes in cytosolic free Ca2+. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 1;227(1):79–90. doi: 10.1042/bj2270079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Mussat M. C., Michell R. H. The inositol trisphosphate phosphomonoesterase of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):169–177. doi: 10.1042/bj2030169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Role of calcium and phosphoinositides in the actions of certain hormones and neurotransmitters. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jun;75(6):1753–1757. doi: 10.1172/JCI111886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Watson J. Biochemical and biological characterization of lymphocyte regulatory molecules. V. Identification of an interleukin 2-producing human leukemia T cell line. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1709–1719. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess H. H., Derr J. E. Assay of inorganic and organic phosphorus in the 0.1-5 nanomole range. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):607–613. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90388-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirasawa K., Nishizuka Y. Phosphatidylinositol turnover in receptor mechanism and signal transduction. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:147–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.001051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin L. E. Receptors and phosphoinositide-generated second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:205–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden J. B., Stobo J. D. Transmembrane signalling by the T cell antigen receptor. Perturbation of the T3-antigen receptor complex generates inositol phosphates and releases calcium ions from intracellular stores. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):446–456. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden J. B., Weiss A., Stobo J. D. The antigen receptor on a human T cell line initiates activation by increasing cytoplasmic free calcium. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):663–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Anggård E. E., Letcher A. J., Downes C. P. Metabolism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):505–511. doi: 10.1042/bj2290505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. The inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate pathway--demonstration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 3-kinase activity in animal tissues. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):631–634. doi: 10.1038/320631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacks R., Harkness D., Sampsell R., Adler J., Roth S., Kim C., Goldman P. Studies on avian erythrocyte metabolism. Inositol tetrakisphosphate: the major phosphate compound in the erythrocytes of the ostrich (Struthio camelus camelus). Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 1;77(3):567–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandal N. C., Biswas B. B. Metabolism of inositol phosphates. II. Biosynthesis of inositol polyphosphates in germinating seeds of Phaseolus aureus. Indian J Biochem. 1970 Mar;7(1):63–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hodgdon J. C., Hussey R. E., Protentis J. P., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Antigen-like effects of monoclonal antibodies directed at receptors on human T cell clones. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):988–993. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Pantaleo G., Lopez-Botet M., Mingari M. C., Moretta L. Anticlonotypic monoclonal antibodies induce proliferation of clonotype-positive T cells in peripheral blood human T lymphocytes. Evidence for a phenotypic (T4/T8) heterogeneity of the clonotype-positive proliferating cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Oct 1;162(4):1393–1398. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.4.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpić V., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. myo-Inositol uptake and metabolism in isolated rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11315–11322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANTIAGO-CALVO E., MULE S. J., HOKIN L. E. A new phosphoinositide containing four phosphates per inositol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 19;70:91–93. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90724-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wauwe J. P., De Mey J. R., Goossens J. G. OKT3: a monoclonal anti-human T lymphocyte antibody with potent mitogenic properties. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2708–2713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wauwe J. P., Goossens J. G., Beverley P. C. Human T lymphocyte activation by monoclonal antibodies; OKT3, but not UCHT1, triggers mitogenesis via an interleukin 2-dependent mechanism. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):129–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venuta S., Mertelsmann R., Welte K., Feldman S. P., Wang C. Y., Moore M. A. Production and regulation of interleukin-2 in human lymphoblastic leukemias studied with T-cell monoclonal antibodies. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):781–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walseth T. F., Johnson R. A. The enzymatic preparation of [alpha-(32)P]nucleoside triphosphates, cyclic [32P] AMP, and cyclic [32P] GMP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 28;562(1):11–31. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Shoback D., Stobo J. Role of T3 surface molecules in human T-cell activation: T3-dependent activation results in an increase in cytoplasmic free calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4169–4173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Connolly T. M., Bross T. E., Majerus P. W., Sherman W. R., Tyler A. N., Rubin L. J., Brown J. E. Isolation and characterization of the inositol cyclic phosphate products of polyphosphoinositide cleavage by phospholipase C. Physiological effects in permeabilized platelets and Limulus photoreceptor cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13496–13501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



