Abstract
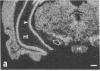
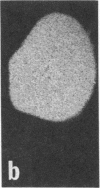
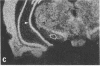
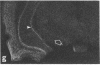
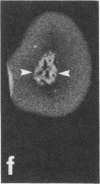
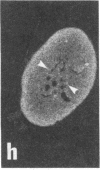
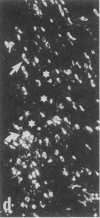
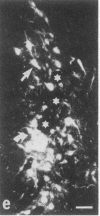
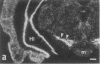
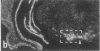
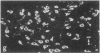
Rat brain and adrenal gland were analyzed by hybridization histochemistry using an RNA probe complementary to mRNA for tyrosine 3-hydroxylase (TyrOHase; tyrosine 3-monooxygenase, EC 1.14.16.2), by immunohistochemistry using TyrOHase antiserum, and by retrograde tracing using the fluorescent compound Fast blue. Cell bodies in the ventral mesencephalon contained mRNA for TyrOHase, and these cells were also TyrOHase immunoreactive. After injection of Fast blue into the striatum, such double-labeled cells in addition contained the retrograde tracer, showing that these cells send axonal projections to the injection site. These results show that hybridization histochemistry can be used to identify transmitter-specific neuron populations and that their projections can be established.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bentivoglio M., Kuypers H. G., Catsman-Berrevoets C. E., Loewe H., Dann O. Two new fluorescent retrograde neuronal tracers which are transported over long distances. Neurosci Lett. 1980 May 15;18(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch B., Le Guellec D., de Keyzer Y. Detection of the messenger RNAs coding for the opioid peptide precursors in pituitary and adrenal by "in situ' hybridization: study in several mammal species. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Jan 21;53(2):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahic M., Haase A. T. Detection of viral sequences of low reiteration frequency by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6125–6129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERANKO O. Histochemistry of noradrenaline in the adrenal medulla of rats and mice. Endocrinology. 1955 Sep;57(3):363–368. doi: 10.1210/endo-57-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee C. E., Chen C. L., Roberts J. L., Thompson R., Watson S. J. Identification of proopiomelanocortin neurones in rat hypothalamus by in situ cDNA-mRNA hybridization. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):374–376. doi: 10.1038/306374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee C. E., Roberts J. L. In situ hybridization histochemistry: a technique for the study of gene expression in single cells. DNA. 1983;2(2):157–163. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geffen L. B., Livett B. G., Rush R. A. Immunohistochemical localizatio of protein components of catecholamine storage vesicles. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(3):593–605. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILLARP N. A., HOKFELT B. Evidence of adrenaline and noradrenaline in separate adrenal medullary cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1953 Dec 31;30(1):55–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1954.tb01074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafen E., Levine M., Garber R. L., Gehring W. J. An improved in situ hybridization method for the detection of cellular RNAs in Drosophila tissue sections and its application for localizing transcripts of the homeotic Antennapedia gene complex. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):617–623. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01472.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson P., Penschow J., Shine J., Ryan G., Niall H., Coghlan J. Hybridization histochemistry: use of recombinant DNA as a "homing probe" for tissue localization of specific mRNA populations. Endocrinology. 1981 Jan;108(1):353–356. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-1-353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Nogueira Araujo G. M. A simple method of reducing the fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy. J Immunol Methods. 1981;43(3):349–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamouroux A., Faucon Biguet N., Samolyk D., Privat A., Salomon J. C., Pujol J. F., Mallet J. Identification of cDNA clones coding for rat tyrosine hydroxylase antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3881–3885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. J., Tank A. W., Weiner N., Chikaraishi D. M. Regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA by glucocorticoid and cyclic AMP in a rat pheochromocytoma cell line. Isolation of a cDNA clone for tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14632–14637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER O. L., Jr, STONE G. E., PRESCOTT D. M. AUTORADIOGRAPHY OF SOLUBLE MATERIALS. J Cell Biol. 1964 Dec;23:654–658. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.3.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markey K. A., Kondo H., Shenkman L., Goldstein M. Purification and characterization of tyrosine hydroxylase from a clonal pheochromocytoma cell line. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;17(1):79–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe J. T., Morrell J. I., Ivell R., Schmale H., Richter D., Pfaff D. W. In situ hybridization technique to localize rRNA and mRNA in mammalian neurons. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Jan;34(1):45–50. doi: 10.1177/34.1.3941265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moench T. R., Gendelman H. E., Clements J. E., Narayan O., Griffin D. E. Efficiency of in situ hybridization as a function of probe size and fixation technique. J Virol Methods. 1985 Jun;11(2):119–130. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(85)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata T., Nawa T. A modification of dry-mounting technique for radioautography of water-soluble compounds. Histochemie. 1966;7(4):370–371. doi: 10.1007/BF00306625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nojiri H., Sato M., Urano A. In situ hybridization of the vasopressin mRNA in the rat hypothalamus by use of a synthetic oligonucleotide probe. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Jul 4;58(1):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt J. L., Michael A. F. Retardation of fading and enhancement of intensity of immunofluorescence by p-phenylenediamine. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Jun;31(6):840–842. doi: 10.1177/31.6.6341464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivers B. D., Harlan R. E., Pfaff D. W., Schachter B. S. Combination of immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization in the same tissue section of rat pituitary. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Jan;34(1):39–43. doi: 10.1177/34.1.3510246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel R. E., Young W. S., 3rd Detection of preprocholecystokinin and preproenkephalin A mRNAs in rat brain by hybridization histochemistry using complementary RNA probes. Neuropeptides. 1985 Dec;6(6):573–580. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(85)90121-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirboll L., Hökfelt T., Norell G., Phillipson O., Kuypers H. G., Bentivoglio M., Catsman-Berrevoets C. E., Visser T. J., Steinbusch H., Verhofstad A. A method for specific transmitter identification of retrogradely labeled neurons: immunofluorescence combined with fluorescence tracing. Brain Res. 1984 Dec;320(2-3):99–127. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(84)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl G. R., Zingg H. H., Habener J. F. Vasopressin mRNA in situ hybridization: localization and regulation studied with oligonucleotide cDNA probes in normal and Brattleboro rat hypothalamus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5555–5559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson B., Manning R. W., Davis L. G., Arentzen R., Baldino F., Jr Co-localization of corticotropin releasing factor and vasopressin mRNA in neurones after adrenalectomy. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):59–61. doi: 10.1038/315059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]